Fig. 3
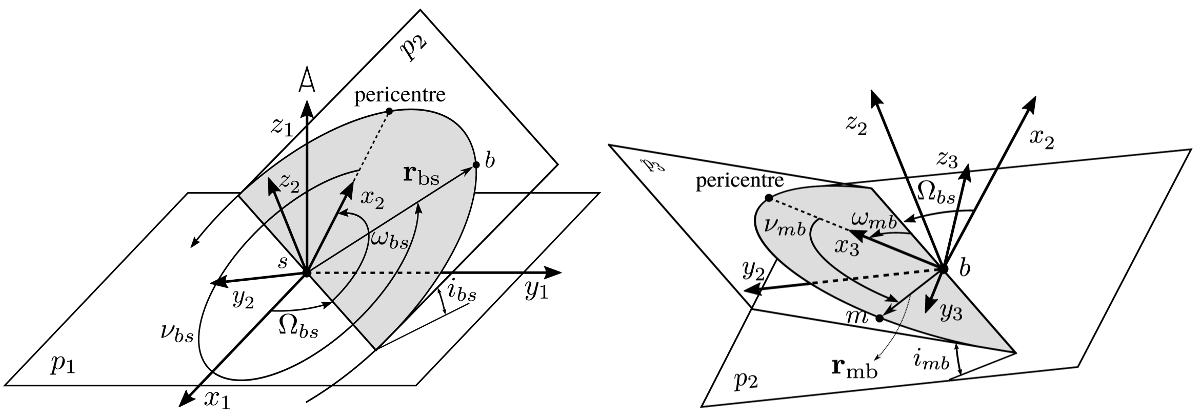
(a) The planet–moon barycenter orbit around the star (b) The moon orbit around the barycenter. The reference frames and angles used to describe the Keplerian orbits of the planet–moon system barycenter around the parent star (panel a) and the Keplerian orbit of the moon around the planet-moon system barycenter (panel b). Plane p1 (panel a) is the plane of the sky as seen by the observer on the positive z1 -axis. Plane p2 (panels a and b) is the barycenter’s orbital plane, and plane p3 (panel b) is the orbital plane of the moon around the barycenter. Angle i is the orbitalinclination angle, ω the argument of periastron, Ω the right ascension of the ascending node, and ν the true anomaly. Subscript bs refers to the barycenter of the planet–moon system around the star, and mb to the moon around the barycenter. Vectors rbs and rmb are the position vectors of the barycenter and the moon, respectively. The barycenter and the moon are indicated by b and m, respectively.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.