Fig. B.1
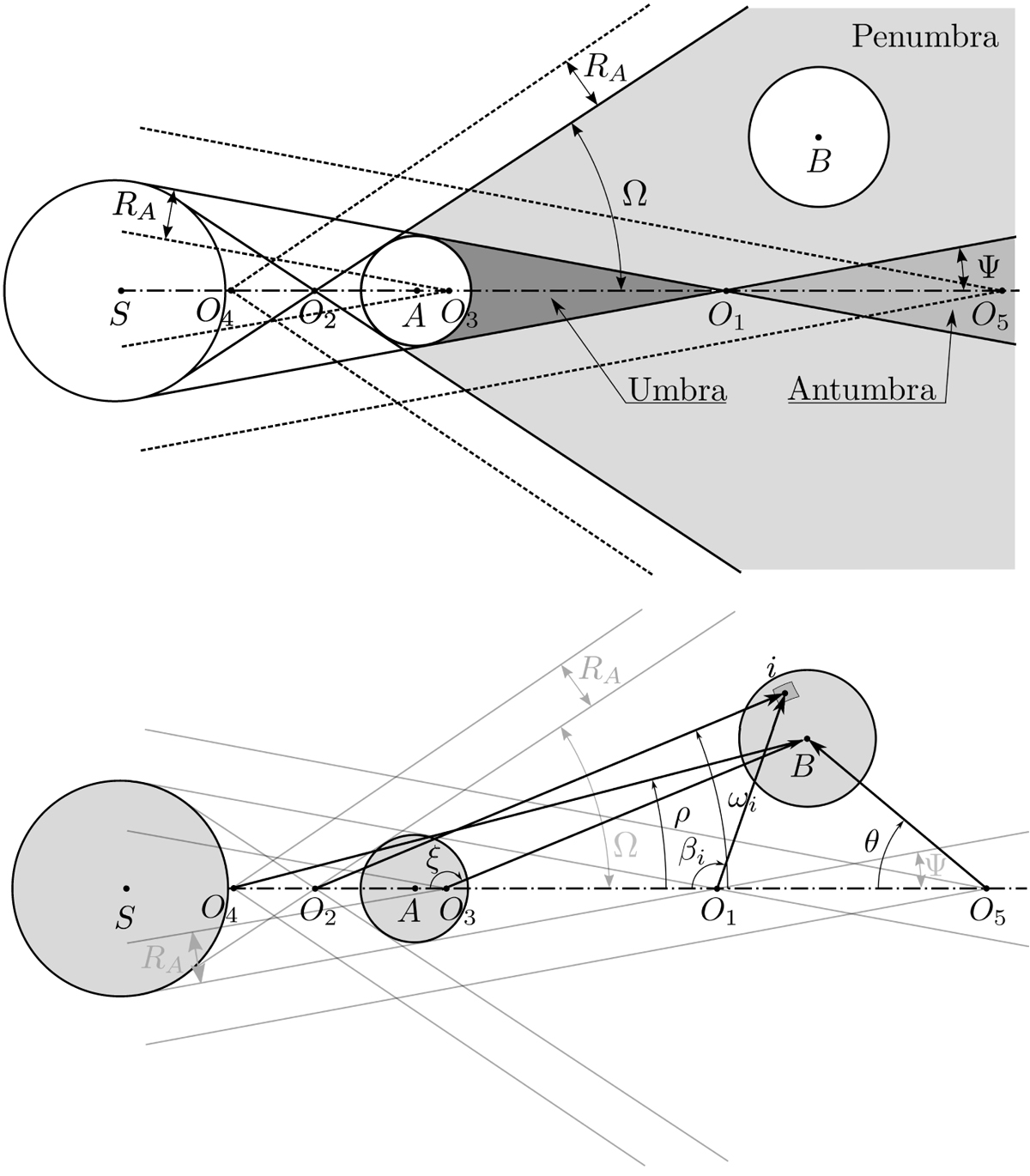
Geometry of the umbral, antumbral, and penumbral shadow cones, when star S is eclipsed by body A, casting a shadow on body B. The shadow cast by A into space is rotationally symmetric around the axis through the center of the star and body A. The radii of the star, body A, and body B are denoted by RS, RA, and RB, respectively. Points O1, O2, O3, O4, and O5 denote auxiliary points: the umbral and antumbral cones have apex O1 and aperture2Ψ and the penumbral cone has apex O2 and aperture2Ω. The lower figure also shows angles ζ, ρ, ωi, βi, and θ, that are used in the computation of the eclipse shadow depth. Distances between bodies and radii are not to scale in order to emphasize the geometry of the system.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


