Fig. 3
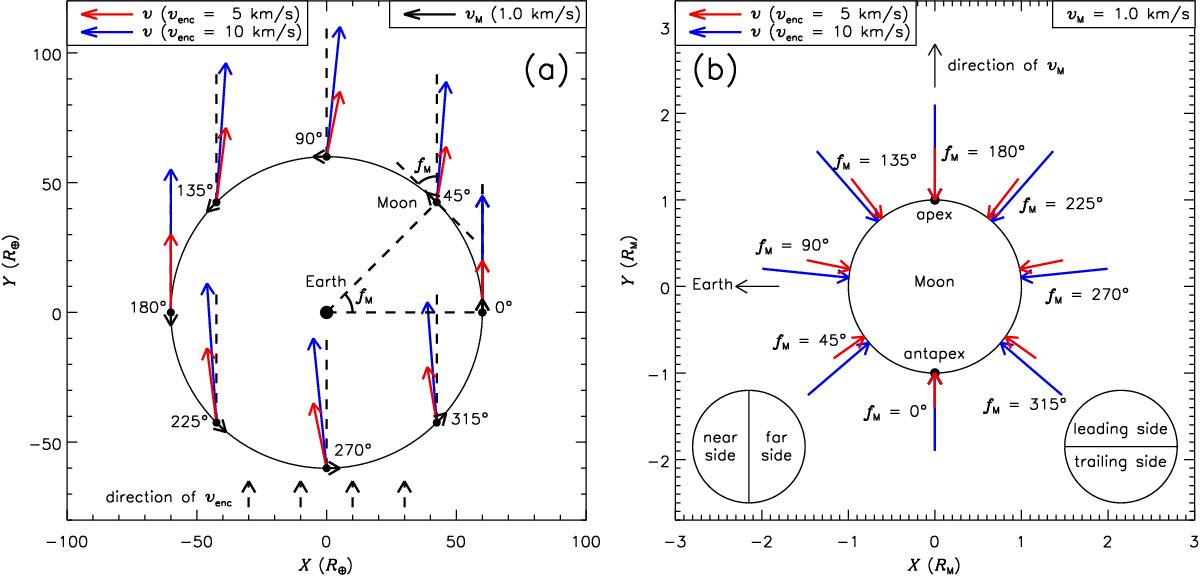
Impact geometry seen in the rest frame of Earth a) and Moon b). a) The Moon is assumed to be where aM = 60 R⊕, with vM = 1.0 km s-1. The impactors, distributed extensively enough to cover the lunar orbit (black circle), are in the common direction of venc (black dashed arrow). Where fM = 0°,45°,...,315°, the lunar velocity vM (black solid arrow) and the impact velocity v for venc = 5 or 10 km s-1 (red or blue solid arrows) are all plotted to the same scale. b) Under the same conditions, v is plotted pointing at the normal impact points on the lunar surface.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


