Fig. 20
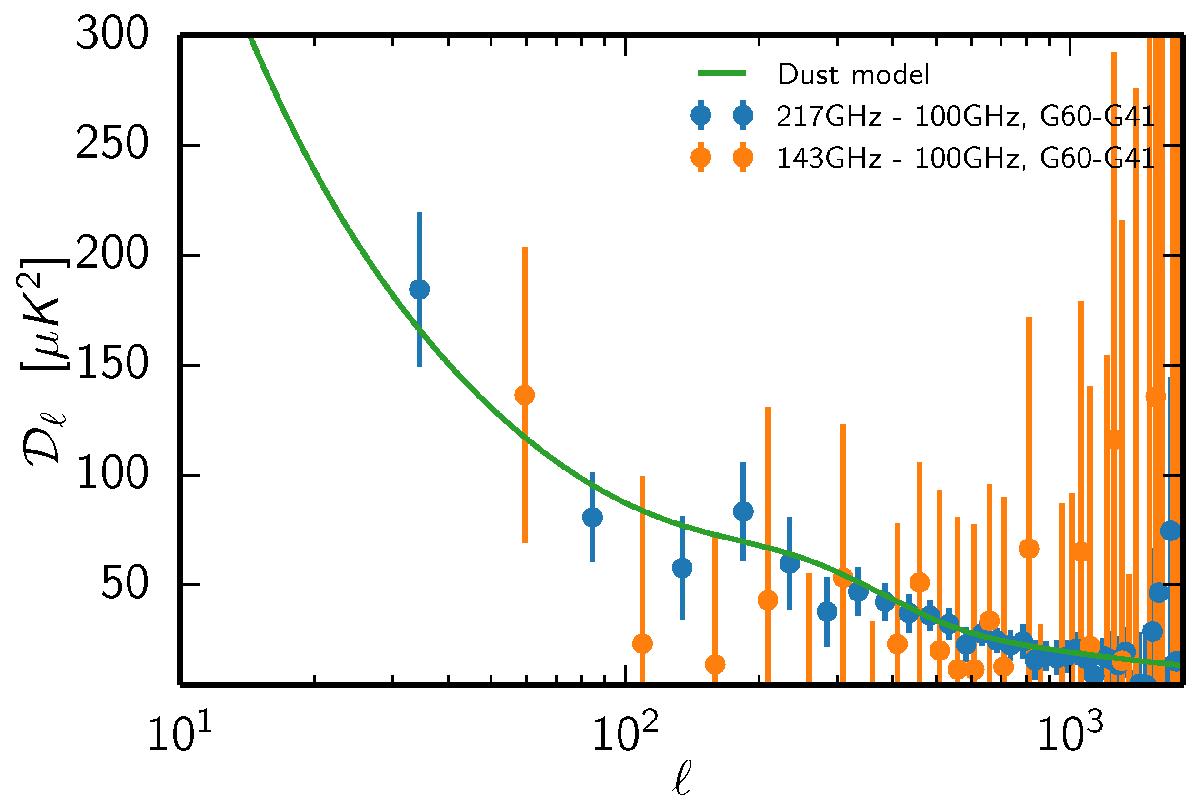
Dust model versus data. In blue, the power spectrum of the double mask difference between 217 GHz and 100 GHz half-mission cross-spectra in masks G60 and G41 (complemented by the joint masks for CO, extended objects, and point sources). In orange, the equivalent spectrum for 143 and 100 GHz. The mask difference enables us to remove the contribution from all the isotropic components (CMB, CIB, and point sources) in the mean. But simple mask differences are still affected by the difference of the CMB in the two masks due to cosmic variance. Removing the 100 GHz mask difference, which is dominated by the CMB, reduces the scatter significantly. The error bars are computed as the scatter in bins of size Δℓ = 50. The dust model (green) based on the 545 GHz data has been rescaled to the expected dust contamination in the 217 GHz mask difference using values from Table 11. The 143 GHz double mask difference is also rescaled to the level of the 217 GHz difference; i.e., it is multiplied by approximately 14. Different multipole bins are used for the 217 GHz and 143 GHz data to improve readability.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


