Fig. 2
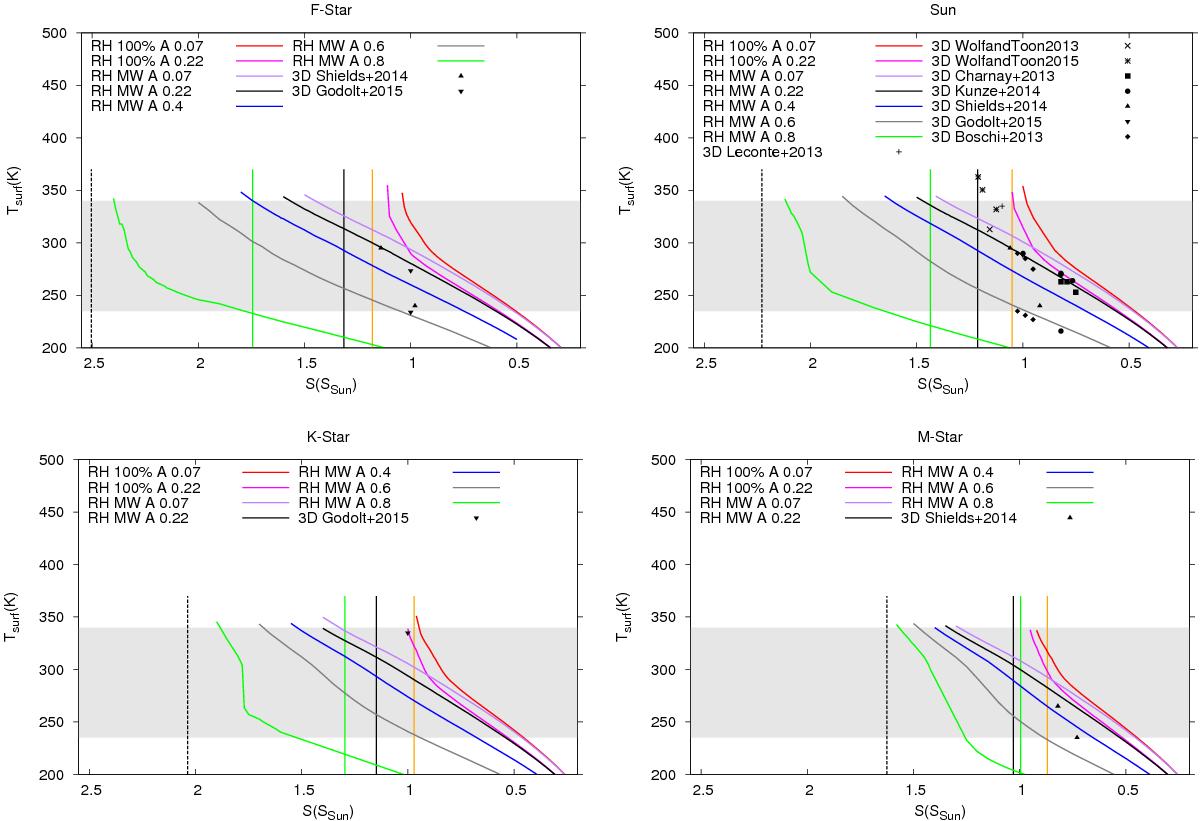
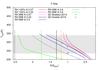
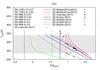
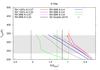
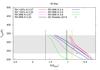
Surface temperatures of Earth-like planets around different stars at various stellar insolations (S) as computed with the 1D model for different assumptions of the relative humidity and surface albedo. Upper left panel: Earth-like planets around an F-type star; upper right panel: Earth-like planets around the Sun; lower left panel: Earth-like planets around a K-type star; and lower right panel: Earth-like planets around a M-type star. The vertical lines indicate the inner habitable zone boundaries as calculated by Kopparapu et al. (2013) (orange), Kasting et al. (1993) (green), and Yang et al. (2014) (solid black line for rapidly rotating planets and dashed black line for slowly rotating planets). Symbols indicate the results of 3D modeling studies by Boschi et al. (2013), Yang et al. (2013), Charnay et al. (2013), Godolt et al. (2015), Kunze et al. (2014), Leconte et al. (2013b), Shields et al. (2014), Wolf & Toon (2015, and 2013. Some of the 3D modeling scenarios of the early Earth (Charnay et al. 2013; Kunze et al. 2014) have larger CO2 volume mixing ratios than assumed for Earth-like planets.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.