Fig. 1
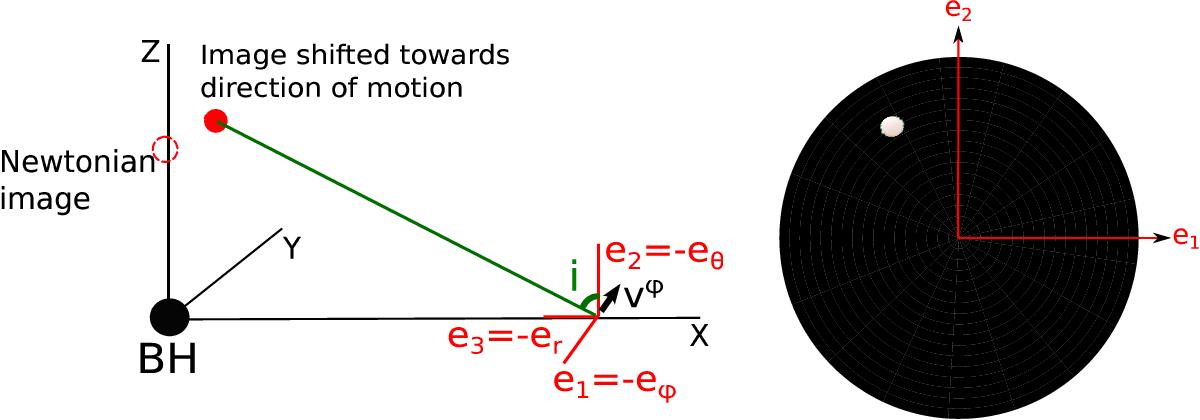
Left: geometry of the lamp post model. The velocity vϕ is the Keplerian velocity of the corotating observer. The triad (e1, e2, e3) is the local rest frame of the observer. The angle i lies between the direction of the local normal and direction of the lamp as seen by the observer. Right: image (map of the quantity g3 + α as defined in Eq. (2)) of the lamp as observed by a Keplerian observer rotating at r = 40 M. The total field of view is of 0.9 rad. The lamp is not strictly speaking point-like so the angle i is equal to the average of all the directions on sky connecting the observer to the lamp. Also, the lamp appears shifted with respect to the local normal because of the special relativistic effect linked to the high velocity of the observer. The displacement is in the direction of the observer’s motion.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


