Fig. 4
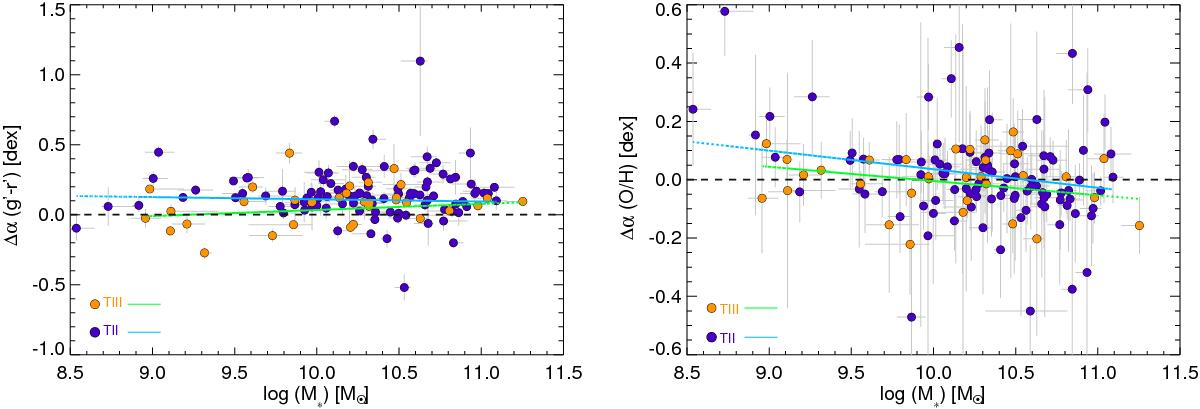
Left: change in the outer-disk color gradient as a function of the galaxy stellar mass, as derived by Walcher et al. (2014), along with the linear fits to the values derived for the Tii (cyan solid line) and Tiii-type (green solid line) galaxies. The p-value parameters in this case range between 0.1 and 0.2, although the dichotomy between Tii and Tiii at low stellar masses is quite clear. Right: the same as above but for the change in ionized-gas metallicity gradient. The correlation in the case of the Tii galaxies yields very low p-values, namely 0.003 (Pearson), 0.018 (Spearman), and 0.010 (Kendall), indicating that stellar mass might be one of the main drivers of the change in the ionized-gas metallicity in the outer disk of Tii galaxies.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.