Fig. 1
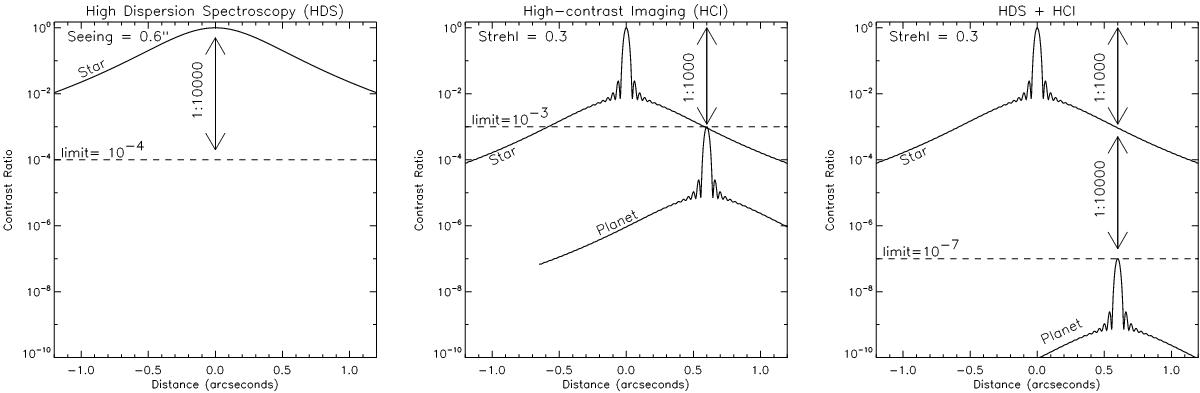
Toy model of the HDS+HCI method. Left panel: stellar point-spread function (PSF) for conventional, seeing-limited (seeing = 0.6 arcsec) HDS observations, with indicated a contrast of 1 × 10-4. This level of contrast has been readily achieved both in the optical (e.g. Leigh et al. 2003a) and infrared (e.g. Brogi et al. 2012), meaning that such planet signal can be detected at a 1:10 000 level in the spectrum of the star. Middle panel: model PSF for HCI observations for an adaptive-optics assisted 8 m telescope with a Strehl ratio of 0.3 at 0.5 μm, under the same seeing conditions. The PSF is modeled as the theoretical Airy profile of the telescope combined with a Moffat function as the non-AO-corrected seeing-limited contribution. A hypothetical planet is inserted at an angular distance of 0.6 arcsec from the star at a contrast of 1:1000 with respect to the stellar brightness at the position of the planet. The right panel illustrates that in this example HDS+HCI can achieve a contrast of 10-3 × 10-4 = 10-7 at the planet position.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


