Fig. 8
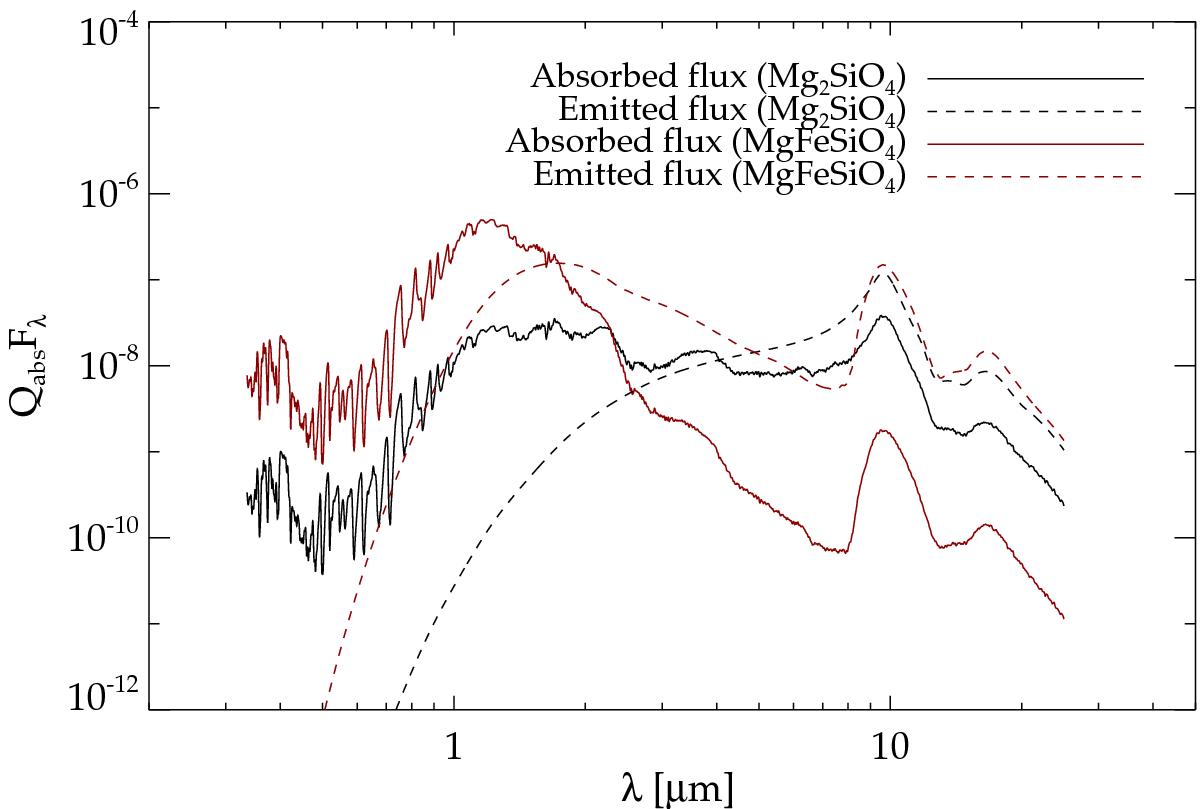
Absorbed and emitted flux, Qabs(λ)Fλ and Qabs(λ)Bλ, for two different grain materials, Mg2SiO4 (black) and MgFeSiO4 (red). The absorbed light is calculated using a geometrically diluted radiation field from a hydrostatic atmosphere (at 2 R∗ for Mg2SiO4 and at 10 R∗ for MgFeSiO4) with stellar parameters typical of an M-type AGB star (M = 1 M⊙, L = 5000 L⊙ and T∗ = 2800 K). The emitted light is calculated using a Planckian source function at a grain temperature of Td = 1000 K. The optical data for Mg2SiO4 is from Jäger et al. (2003) and the optical data for MgFeSiO4 is from Dorschner et al. (1995). We note that the local radiation field in the wind-acceleration zone will be more pronounced in the mid-IR region than what is shown here because of the addition of the emitted light from the dust component.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


