Fig. 6
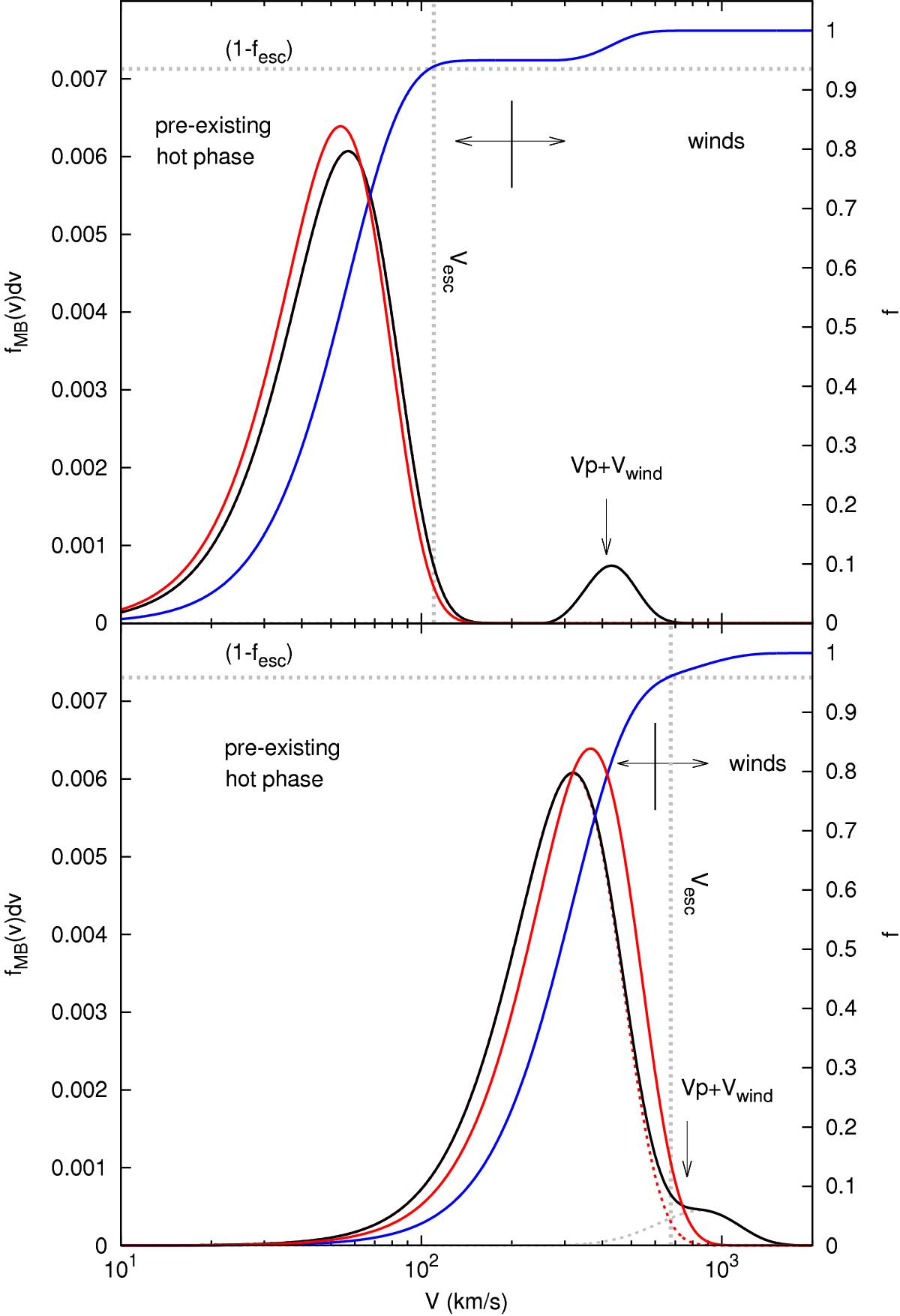
Distribution functions of the velocity in the pre-existing hot gas phase and in the wind. The upper and lower panels show the distributions for two different dark-matter haloes with Mvir = 1010 M⊙ and Mvir = 1013 M⊙, respectively. In the two cases, the wind speed is close to Vwind = 250 km s-1 but the temperature is close to ![]() K in the upper panel and
K in the upper panel and ![]() K in the lower panel. The total gas distribution, in black, is the sum of the pre-existing hot gas distribution (red dotted line) and the gas wind distribution (grey dotted line). The blue curve gives the mass fraction. The vertical dotted grey line indicates the escape velocity of the dark-matter structure. The intersection of the mass fraction and this velocity threshold allows us to determine the escape fraction. The red curve shows the new hot gas phase distribution recomputed with the new temperature
K in the lower panel. The total gas distribution, in black, is the sum of the pre-existing hot gas distribution (red dotted line) and the gas wind distribution (grey dotted line). The blue curve gives the mass fraction. The vertical dotted grey line indicates the escape velocity of the dark-matter structure. The intersection of the mass fraction and this velocity threshold allows us to determine the escape fraction. The red curve shows the new hot gas phase distribution recomputed with the new temperature ![]() (Eq. (42)) derived after accretion, cooling, and ejection processes have been taken into account during the previous time step Δt. In the low-mass case, all the mass contained in the wind leaves the structure. In the high-mass case, a fraction of the wind mass can be retained.
(Eq. (42)) derived after accretion, cooling, and ejection processes have been taken into account during the previous time step Δt. In the low-mass case, all the mass contained in the wind leaves the structure. In the high-mass case, a fraction of the wind mass can be retained.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


