Fig. 3
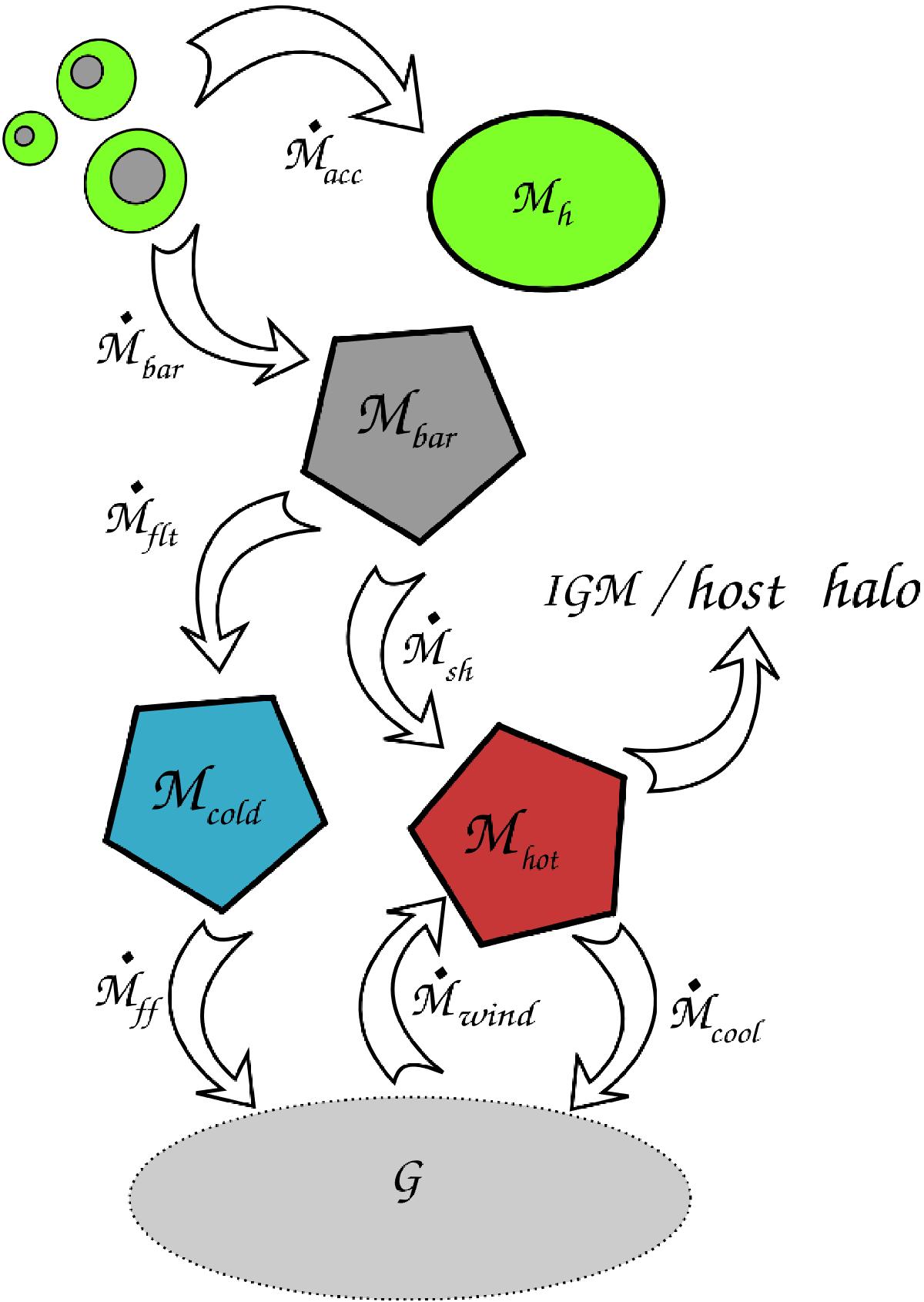
Large-scale exchanges. On a large scale, dark-matter and baryons are coupled. During the accretion process and while the dark-matter smooth accretion (Ṁacc) feeds the dark-matter halo (Mh), the associated baryons (Ṁbar) feed a baryonic reservoir (Mbar). In the context of bimodal accretion, this baryonic reservoir is divided into two parts: the hot reservoir representing the hot atmosphere (Ṁsh and Mhot), and the cold reservoir representing filamentary streams (Ṁflt and Mcold). The cold gas feeds the galaxy (Ṁff) directly. The hot gas follows radiative cooling process and then also feeds the galaxy (Ṁcool). As described in the text, a galaxy can eject material. The ejecta (Ṁwind) are continuously added to the hot-gas reservoir (Mhot) or definitively lost in the IGM according to their velocity distribution. Indeed, the gas stored in the IGM reservoir will never be considered.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


