Fig. 5
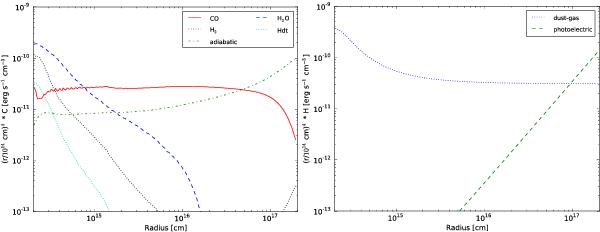
Gas cooling (left) and heating (right) rates determined in the best-fit CO model. The cooling includes contributions from CO, H2O and H2 line cooling, adiabatic cooling, and cooling due to non-collisional interactions of gas and dust (Hdt). The heating includes some CO line heating (when the cooling is negative), heating from dust-gas collisions, and photoelectric heating from the interstellar radiation field. There is a slight “wiggle” in the CO cooling function due to unavoidable Monte-Carlo noise. This does not have an impact on our results.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.