Fig. 4
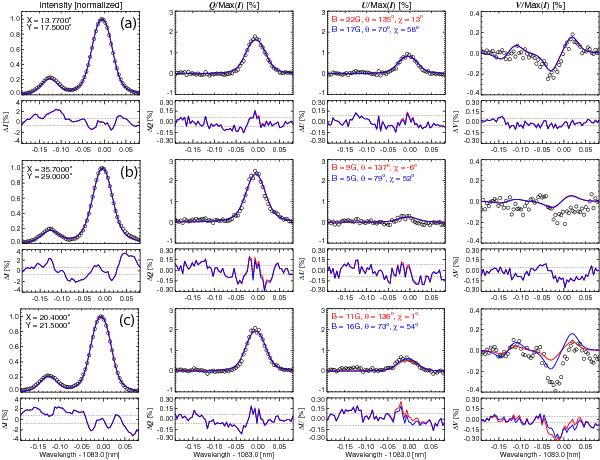
Observed and best-fit He1 1083.0 nm triplet Stokes profiles corresponding to different pixels in the prominence. Stokes I is normalized to unity, while Stokes Q, U, and V are normalized to their Stokes I maximum peak value. Open dots represent the observations and solid lines stand for the theoretical profiles obtained by HAZEL. Blue and red represent two different solutions. In this case, we plot the quasi-horizontal solution (blue) and the corresponding one to the 90° ambiguity (red), which corresponds to the quasi-vertical solution (see Sect. 4). The bottom subpanels display the difference between the observed and the synthetic profiles. The horizontal dashed lines in the subpanels stand for the mean standard deviation of the noise:  %. They were calculated by averaging the standard deviation at a single wavelength point in the continuum and over all pixels showing polarization signal amplitudes above three times their corresponding noise level, in Stokes Q, U, or V. The legend in the Stokes I panels gives the location of the pixel in arcseconds and the one in Stokes U/I gives the values of the field strength, inclination, and azimuth retrieved for each pixel and for the two 90° ambiguous solutions. The positive reference direction for Stokes Q is the parallel to the solar limb. Panels a), b), and c) represent a prototypical He1 1083.0 nm triplet profile with significant linear and circular polarization signals, a profile with noisy Stokes V signal, and one whose Stokes V signal shows an anomalous profile shape.
%. They were calculated by averaging the standard deviation at a single wavelength point in the continuum and over all pixels showing polarization signal amplitudes above three times their corresponding noise level, in Stokes Q, U, or V. The legend in the Stokes I panels gives the location of the pixel in arcseconds and the one in Stokes U/I gives the values of the field strength, inclination, and azimuth retrieved for each pixel and for the two 90° ambiguous solutions. The positive reference direction for Stokes Q is the parallel to the solar limb. Panels a), b), and c) represent a prototypical He1 1083.0 nm triplet profile with significant linear and circular polarization signals, a profile with noisy Stokes V signal, and one whose Stokes V signal shows an anomalous profile shape.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


