Fig. 10
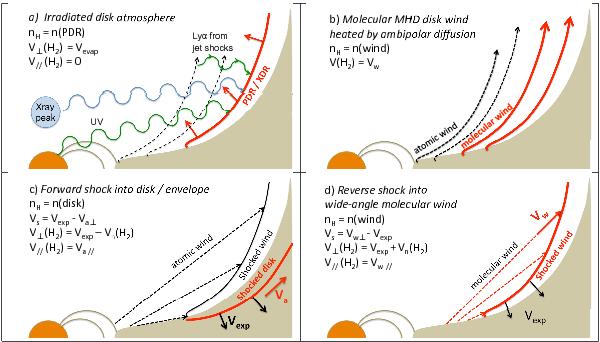
Schematic representation of the 4 scenarii discussed for the origin of the wide-angle rovibrational H2 emission in DG Tau. The layer of emitting H2 at 2000 K is drawn in solid red. Wide-angle wind streamlines are shown as dashed (black if atomic, red if molecular) lines. The velocity of the emitting gas perpendicular and parallel to the cavity wall (V⊥ and V∥), and the shock speed Vs and preshock density nH when applicable, are also listed as a function of the expansion proper motion of the cavity Vexp, the velocity of the H2 1–0 S(1) emitting layer in the frame of the shock wave, Vn(H2), and the initial velocity of the ambient gas (Va) or molecular wind (Vw).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


