Fig. 5
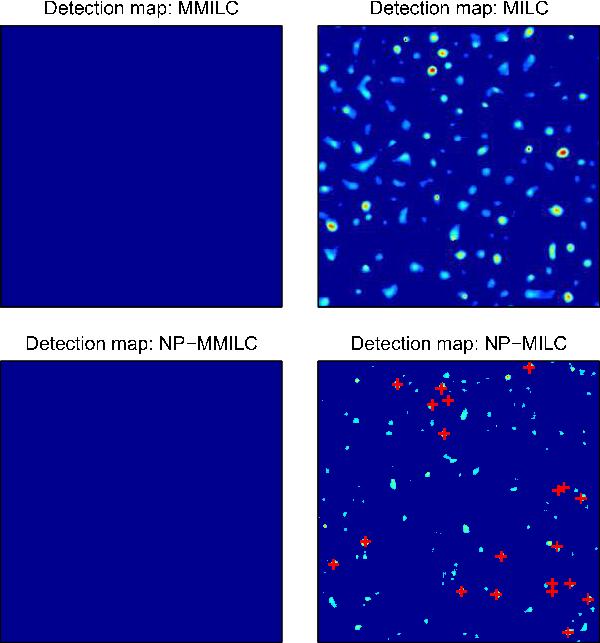
Results provided by MILC, MMILC, NP-MILC, and NP-MMILC when applied to the maps in Fig. 4. The detection threshold has been set to 4σL for all algorithms except for NP-MMILC for which a value of 3.5σL has been adopted (see text) and the background has been approximated by a two-dimensional polynomial of degree one. The top and bottom left panels clearly show that both MMILC and NP-MMILC are not able to retrieve point sources in this case. This happens because the spectrum of the point sources has a frequency-dependence similar to the CMB and SZ, and therefore the subtraction process gets rid of all of them. The top and bottom right panels show that both MILC and NP-MILC, on the contrary, retrieve all sources and the SZ point-like emissions, because it subtracts the underlying diffuse component with the polynomial approximation. For NP-MILC a greater noise contamination of the detection map is evident. Also notice the detection of two couples of overlapping point sources in the bottom-right and middle-right part of the map.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


