Table 1
Experimental details for hydrocarbon samples.
| Sample | Evaporation method(1) | Laser power | Atmosphere | Pressure | Product(2) |
(Wcm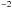 ) ) |
(mbar) | ||||
|
|
|||||
| #1 | laser ablation (for HACs) | 2.8 × 10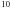 |
He:H (90:10) | 4.5 | PAH+HAC |
| laser-induced pyrolysis (for PAHs) | 480 | Ar:C H H (1500:40) (1500:40) |
750 | ||
|
|
|||||
| #2 | laser ablation | 2.8 × 1010 | He:H (90:10) | 4.5 | HAC |
| #3 (3) | HAC (703 K) | ||||
|
|
|||||
| #4 | laser-induced pyrolysis | 480 | Ar:C H H (1500:40) (1500:40) |
750 | PAH |
Notes. For the laser ablation method, the second harmonic of a pulsed Nd:YAG laser (at 532 nm) was used. Samples were produced in a deposition chamber at (5 ± 3) × 10-6 Torr (Jäger et al. 2008; Gadallah et al. 2011). For the laser-induced pyrolysis method, a high-power continuous-wave (cw) CO2 laser was used with 60 W radiation power at a wavelength of 10.6 μm (Jäger et al. 2006, 2009; Steglich et al. 2010, 2012). Samples were deposited on CaF substrates. Sample #3 was heated to 703 K.
substrates. Sample #3 was heated to 703 K.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


