Table 1
Characteristics of the dynamic model atmospheres for pulsating and mass-losing C-rich AGB stars used for the photometric modelling.
| Model: | T | R | S | C1 | C2 | ||
|
|
|||||||
| (i) | L⋆ | [L⊙] | 5200 | 7000 | 10 000 | 10 000 | 10 000 |
| M⋆ | [M⊙] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| T⋆ | [K] | 3000 | 2800 | 2600 | 2400 | 2400 | |
| [Fe/H] | [dex] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| C/O | by number | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.69 | 2.38 | |
|
|
|||||||
| (ii) | R ⋆ | [R⊙] | 268 | 355 | 493 | 580 | 580 |
| [AU] | 1.24 | 1.65 | 2.29 | 2.70 | 2.70 | ||
| log (g⋆ [cm s-2]) | – 0.42 | – 0.66 | – 0.94 | – 0.91 | – 0.91 | ||
|
|
|||||||
| (iii) | P | [d] | 295 | 390 | 490 | 640 | 640 |
| Δup | [km s-1] | 4 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 6 | |
| f L | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Δmbol | [mag] | 0.41 | 0.53 | 0.86 | 1.49 | 1.49 | |
|
|
|||||||
| (iv) | ⟨ Ṁ ⟩ | [M⊙ yr-1] | – | 3.5 × 10-6 | 4.3 × 10-6 | 9.1 × 10-6 | 1.4 × 10-5 |
| ⟨ u ⟩ | [km s-1] | – | 15 | 15 | 17 | 28.6 | |
| ⟨ fc⟩ | – | 0.33 | 0.28 | 0.43 | 0.58 | ||
| ⟨ ρd/ρg ⟩ | [10-3] | – | 0.75 | 0.63 | 1.22 | 3.23 | |
|
|
|||||||
| (v) | τdust (0.55 μm) | – | 3.26 | 4.00 | 11.06 | 19.45 | |
| τdust (1.6 μm) | – | 1.01 | 1.24 | 3.42 | 6.02 | ||
| τdust (3.8 μm) | – | 0.37 | 0.45 | 1.25 | 2.20 | ||
Notes.Listed are (i) parameters of the hydrostatic initial models; (ii) quantities derivable from these parameters; (iii) attributes of the inner boundary conditions (piston) used to simulate the pulsating stellar interiors as well as the resulting bolometric amplitudes Δmbol; (iv) properties of the resulting wind; and (v) dust optical depths of the formed circumstellar envelope. The notation follows previous papers (Höfner et al. 2003; Nowotny et al. 2010, 2011a): R⋆ – stellar radius of the hydrostatic initial model calculated from the luminosity L⋆ and temperature T⋆ via the relation L⋆ = 4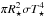 ; P, Δup – period and velocity amplitude of the piston at the inner boundary; fL – free parameter to adjust the luminosity amplitude at the inner boundary; ⟨ Ṁ ⟩, ⟨ u ⟩ – mean mass-loss rate and outflow velocity at the outer boundary; ⟨ fc ⟩ – mean degree of condensation of the element carbon into amC dust grains at the outer boundary; ⟨ ρd/ρg ⟩ – mean dust-to-gas ratio at the outer boundary (cf. Eq. (2) of Höfner & Dorfi 1997); τdust – optical depth of the dust envelope at the specified wavelength (V-, H-, L′-band) based on radial structures at φbol ≈ 0.25 (see Sect. 4.2). The radial coordinates in this work are plotted in units of the corresponding stellar radii R⋆ of the hydrostatic initial models, calculated from their luminosities L⋆ and temperatures T⋆ (as given in the table) via the relation L⋆ = 4
; P, Δup – period and velocity amplitude of the piston at the inner boundary; fL – free parameter to adjust the luminosity amplitude at the inner boundary; ⟨ Ṁ ⟩, ⟨ u ⟩ – mean mass-loss rate and outflow velocity at the outer boundary; ⟨ fc ⟩ – mean degree of condensation of the element carbon into amC dust grains at the outer boundary; ⟨ ρd/ρg ⟩ – mean dust-to-gas ratio at the outer boundary (cf. Eq. (2) of Höfner & Dorfi 1997); τdust – optical depth of the dust envelope at the specified wavelength (V-, H-, L′-band) based on radial structures at φbol ≈ 0.25 (see Sect. 4.2). The radial coordinates in this work are plotted in units of the corresponding stellar radii R⋆ of the hydrostatic initial models, calculated from their luminosities L⋆ and temperatures T⋆ (as given in the table) via the relation L⋆ = 4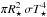 .
.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


