Fig. 1
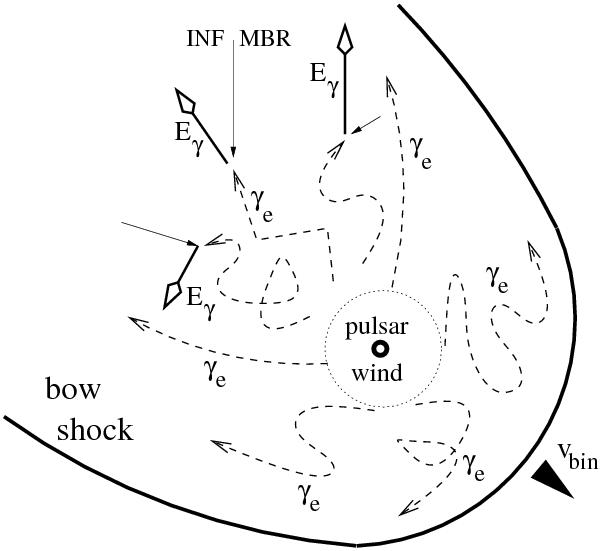
Schematic representation of the bow shock nebula around binary system containing the millisecond pulsar B1957+20. The bow shock is created due to the motion of the binary system through the interstellar space with the velocity of ~220 km s-1. Relativistic electrons with the Lorentz factors γe are accelerated by the pulsar itself or by the shocks due to the pulsar wind interactions. The electrons are collimated by the bow shock in the direction opposite to the motion of the binary system. These electrons comptonize the microwave background radiation (MBR) and the infrared radiation (INF) from the galactic disk. As a result γ-ray photons are produced (tagged as Eγ) at the region behind the pulsar.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


