Fig. 1
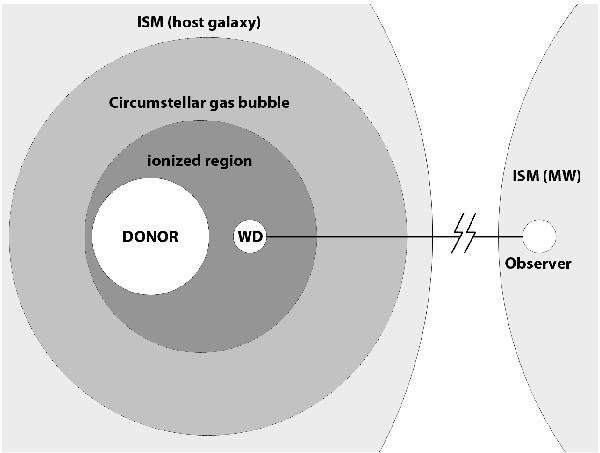
Schematic drawing of the model used in this study. The SSS system consists of a WD accreting material from a donor. The supersoft X-ray emission is the result of steady thermonuclear burning on the surface of the WD. The WD and donor are surrounded by a circumbinary configuration of gas and possibly dust. The radiation from the nuclear-burning WD may ionize a region around the system; in this sketch, the ionized region is localized narrowly around the binary, but for certain configurations the ionized region may extend to or beyond the edge of the circumbinary gas bubble. Before reaching an observer at Earth, photons from the SSS pass through the circumbinary material, the ISM in the host galaxy, the IGM, and the ISM in the Milky Way.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


