Fig. 25
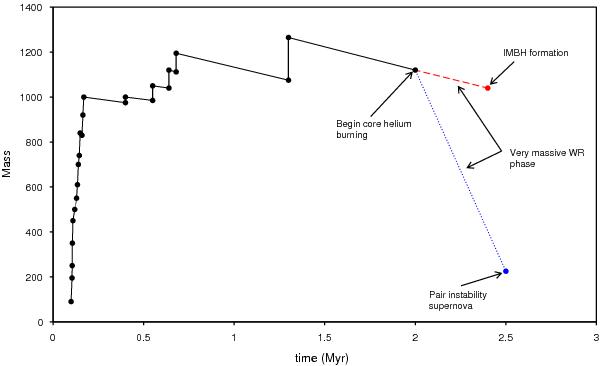
The figure illustrates the influence of the mass loss rate on the evolution of a massive merger object. The dashed line represents the mass evolution during the core helium burning phase (CHeB) if a constant mass loss rate of hydrogen-deficient WR stars is adopted that closely matches our computed rates. In this case the VMS will end its life with a mass greater than 1000 M⊙ and the formation of an intermediate-mass black hole (IMBH) takes place. In contrast, we also followed the CHeB evolution by using an extrapolation of the mass loss rates presented by Nugis & Lamers (2000) for hydrogen-deficient WR stars (dotted line). In this case the star loses much more mass and therefore the occurrence of a pair-instability supernova is more likely than the formation of an IMBH.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


