Fig. 6
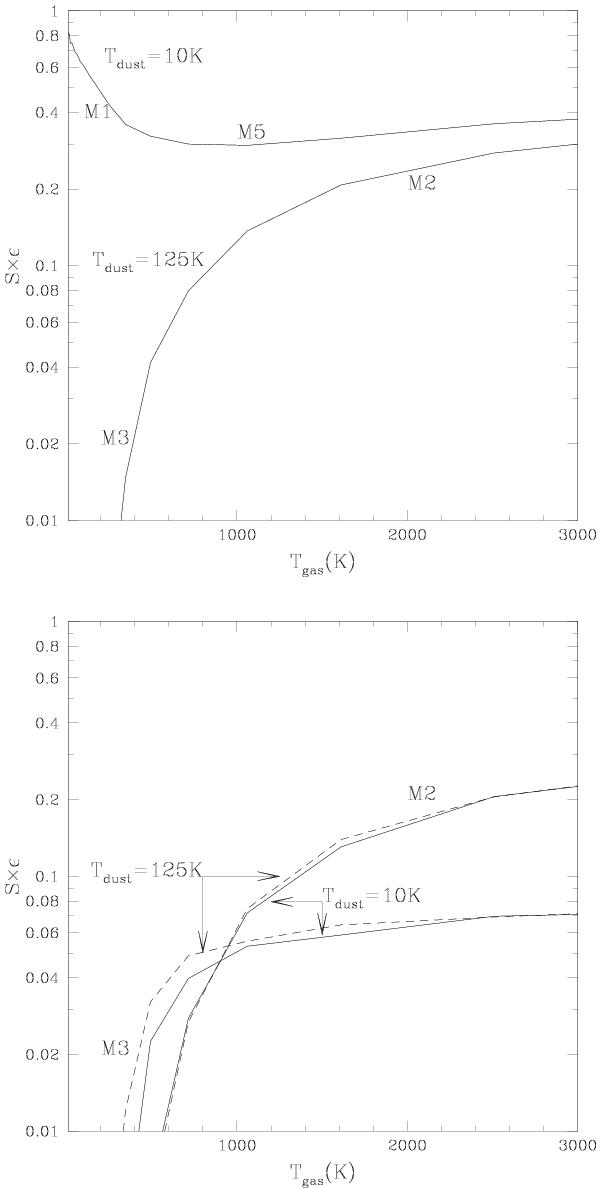
H2 formation efficiencies on 10 K and 125 K surfaces as a function of gas temperature, with the sticking in physisorbed sites Sphys taken as in Cuppen et al. (2010). Top: total H2 formation, governed by mechanisms M1 (2 physisorbed atoms) and M5 (physisorbed atom arriving in H dimer) for 10 K dust, and governed by mechanisms M3 (direct chemisorption with H dimer) and M2 (direct chemisorption with H monomer). Bottom: same as top panel but for H2 formation involving only chemisorbed atoms. At low gas temperatures, H2 is formed through mechanism M3 (direct chemisorption with H dimer). For Tgas > 1000 K, H2 is formed though mechamism M2 (direct chemisorption with H monomer).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.