Fig. 4
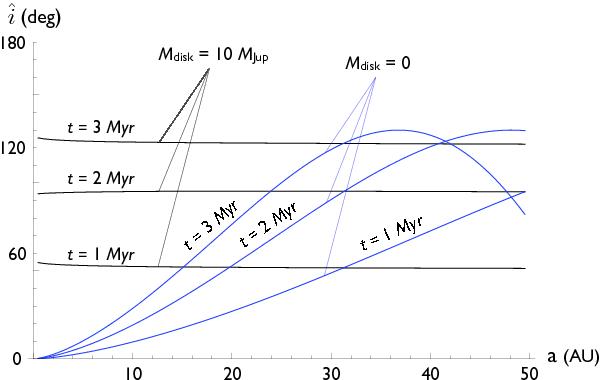
Inclination structure of a mass-less (blue) and a self-gravitating Mdisk = 10 MJup disks. Here the inclination is measured relative to the original plane of the disk. The inclination is shown as a function of semi major axis a at t = 1,3, and 5 Myr. Note that the mass-less disk is considerably warped due to the perturbations from the companion star, while the self-gravitating disk maintains a uniform inclination. in this case, the growth of inclination with time is due to the rigid precession of the disk relative to the binary star plane. The inclination returns back to zero after a precession period.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


