Table 1
Summary of the different methods used to determine νmax and ⟨ Δν ⟩ .
| ID | COR | CAN | A2Z | SYD | DLB | OCT |
|
|
||||||
| ν max | centroid Gaussian | centroid Gaussian | centroid Gaussian | peak smoothed PS | centroid Gaussian | centroid Gaussian (I) |
| first moment (II) | ||||||
| smoothing | 3Δν Gauss | none | 4Δν box | 2Δν Gauss | 10 μHz Gauss | 2Δν box |
| Δν | autocor timeseries | fit to PS | PS ⊗ PS | autocor PS | autocor PS | PS ⊗ PS |
| freq interval | FWHM osc excess | 3 radial orders | νmax ± νmax/3 | νmax ± 5–7Δν | νmax ± νmax/4 | osc excess |
| background | a ν −β |
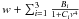
|
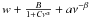
|
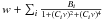
|
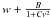
|
linear approx |
| Eq. (2) | yes | no | yes | yes | yes | yes |
Notes. We also mention the way the smoothing is applied to the power spectrum in the determination of νmax, the frequency interval over which ⟨ Δν ⟩ is computed, how the background is determined and whether Eq. (2) is used. For the background we indicate the general formulae with w indicating white noise, ν frequency, and a,B,C,α and β free parameters.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


