Table 1
Example results of SED fitting for all sources with far-IR data.
| Object | RA | Dec | RMS | # | Data |
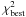
|
Δχ2 | # | Bolometric flux | Type | Ap. | Ap. |
| (J2000) | (J2000) | Ident. | Pts | Incl. | Fits | (10-11 W m-2) | Cor. | Type | ||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| G010.3844+02.2128 | 18:00:22.67 | −18:52:09.7 | YSO | 8 | YN I NN | 1.6 | 2.0 | 32 | 3.300 ± 0.371 | s | 1.00 | N |
| G010.5067+02.2285 | 18:00:34.58 | −18:45:17.6 | YSO | 7 | YN I NN | 2.0 | 2.0 | 183 | 0.618 ± 0.146 | s | 1.00 | N |
| G010.6207−00.3199 | 18:10:14.11 | −19:54:07.5 | DH ii | 5 | YNMNN | 4.8 | 4.0 | 11 | 1.350 ± 0.130 | s | 1.00 | N |
| G010.6291−00.3385 | 18:10:19.25 | −19:54:12.1 | H ii | 6 | YNMNN | 14.2 | 4.0 | 11 | 3.901 ± 0.319 | s | 1.00 | N |
| G010.8411−02.5919 | 18:19:12.09 | −20:47:30.9 | YSO | 11 | YN I Y3 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 30 | 20.660 ± 3.162 | s | 1.00 | N |
| G010.9657+00.0083 | 18:09:43.36 | −19:26:28.6 | H ii | 7 | YNMNN | 6.1 | 4.0 | 10 | 1.497 ± 0.155 | s | 1.00 | N |
| G011.1109−00.4001 | 18:11:32.28 | −19:30:40.6 | H ii | 6 | YNMNN | 11.1 | 12.0 | 15 | 5.433 ± 0.367 | s | 1.00 | N |
| G011.5001−01.4857 | 18:16:22.58 | −19:41:19.3 | H ii/YSO | 10 | YN I YN | 6.0 | 2.0 | 13 | 7.478 ± 1.030 | s | 1.00 | N |
| G011.9019+00.7265 | 18:08:58.78 | −18:16:29.8 | Y/O Str | 7 | YNMNN | 0.3 | 2.0 | 134 | 0.692 ± 0.163 | s | 0.88 | G |
| G011.9454−00.0373 | 18:11:53.20 | −18:36:21.8 | H ii | 8 | YNMN3 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 33 | 6.329 ± 2.001 | s | 1.00 | N |
| G013.0105−00.1267 | 18:14:22.17 | −17:42:48.8 | Y/O Str | 6 | YNMNN | 2.1 | 2.0 | 44 | 3.106 ± 1.220 | s | 1.00 | N |
| G013.1840−00.1069A | 18:14:38.57 | −17:33:05.8 | YSO | 5 | NNMNN | 4.0 | 2.0 | 15 | 0.308 ± 0.048 | s | 0.37 | G |
| G013.1840−00.1069B | 18:14:38.57 | −17:33:05.8 | H ii | 8 | YNMNN | 8.6 | 3.0 | 15 | 0.420 ± 0.061 | s | 0.37 | G |
| G013.2097−00.1436 | 18:14:49.94 | −17:32:46.6 | DH ii | 8 | YNMNN | 44.9 | 14.0 | 10 | 5.084 ± 0.504 | s | 1.00 | N |
| G015.0939+00.1913 | 18:17:20.87 | −15:43:45.9 | YSO | 6 | YNMNN | 2.8 | 3.0 | 28 | 0.372 ± 0.146 | s | 0.65 | G |
| G017.0332+00.7476A | 18:19:07.33 | −13:45:23.6 | YSO | 5 | NNMNN | 4.4 | 2.0 | 26 | 0.742 ± 0.243 | s | 0.29 | G |
| G017.0332+00.7476B | 18:19:07.22 | −13:45:30.2 | H ii | 8 | YNMNN | 9.2 | 2.0 | 12 | 0.710 ± 0.117 | s | 0.71 | S |
Notes. The columns are as follows – 1: MSX PSC name; 2: right
ascension; 3: declination; 4: RMS classification; 5: number of detected flux data
points, not including upper limits, included in the fit; 6: flags indicating which
data were included in the SED. These are from left to right 2MASS (Y or N), TIMMI2
(Y or N), far-IR IGA (I) or MIPSGAL (M), submillimetre (Y or N) and millimetre (N,
1 = Beuther et al. 2002, 2 = Faúndez et al. 2004, 3 = Hill et al. 2005, 4 = Beltrán
et al. 2006); 7: 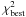 for the
fit; 8: Δχ2 at which at least 10 fits are found; 9: the
number of fits; 10: the bolometric flux with uncertainty, calculated using
Eqs. (1) and (2); 11: whether the kinematic distance
has been solved (s) or the near/far ambiguity remains unsolved (nf). Sources with
galactocentric radii ≥ 8.5 kpc or at the tangent point are also indicated as solved
(s); 12: the apportioning correction applied to large-beam fluxes, as discussed in
Sect. 2.1, with a value of 1 meaning that no
apportioning was performed; 13: type of apportioning used with “N” for none, “T” for
TIMMI2 data, “G” for GLIMPSE data and “S” for a simple split of the remaining
fraction between all multiple source components without TIMMI2 or GLIMPSE
detections. A full version of this table is available online at the CDS.
for the
fit; 8: Δχ2 at which at least 10 fits are found; 9: the
number of fits; 10: the bolometric flux with uncertainty, calculated using
Eqs. (1) and (2); 11: whether the kinematic distance
has been solved (s) or the near/far ambiguity remains unsolved (nf). Sources with
galactocentric radii ≥ 8.5 kpc or at the tangent point are also indicated as solved
(s); 12: the apportioning correction applied to large-beam fluxes, as discussed in
Sect. 2.1, with a value of 1 meaning that no
apportioning was performed; 13: type of apportioning used with “N” for none, “T” for
TIMMI2 data, “G” for GLIMPSE data and “S” for a simple split of the remaining
fraction between all multiple source components without TIMMI2 or GLIMPSE
detections. A full version of this table is available online at the CDS.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


