Table 2
Properties derived from the IRS spectra of our ULIRGs.
| Galaxy | S Si9.7μm |
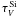
|
EW6.2/μm | |
| (a) | (b) | (c) | ||
|
|
||||
| IRAS 00199-7426 | −1.149 | 27.11 | 0.377 | |
| IRAS 01494-1845 | −1.396 | 32.95 | 0.394 | |
| IRAS Z02376-0054 | −0.697 | 16.44 | 0.332 | |
| IRAS 04114-5117 | −1.500 | 35.40 | 0.345 | |
| IRAS 06009-7716 | −1.262 | 29.78 | 0.429 | |
| IRAS F08208+3211 | −1.424 | 33.60 | 0.346 | |
| IRAS F10156+3705 | −1.072 | 25.30 | 0.659 | |
| IRAS 10565+2448 | −1.139 | 26.89 | 0.429 | |
| IRAS 12112+0305 | −1.629 | 38.43 | 0.289 | |
| IRAS 13120-5453 | −1.475 | 34.82 | 0.373 | |
| IRAS 16334+4630 | −1.367 | 32.27 | 0.349 | |
| IRAS 17208-0014 | −1.856 | 43.80 | 0.329 | |
| IRAS 19297-0406 | −1.600 | 37.77 | 0.317 | |
| IRAS 19458+0944 | −1.810 | 42.71 | 0.414 | |
| IRAS 20414-1651 | −1.705 | 40.23 | 0.423 | |
| IRAS 22491-1808 | −1.624 | 38.33 | 0.382 | |
Notes. (a) strength of the silicate absorption feature; (b) V-band optical depth computed using the ULIRG silicate model of Sirocky et al. (2008) assuming a cold dust screen; (c) We have measured the 6.2-μm PAH feature equivalent width by, firstly, fitting the continuum emission close to the feature with a linear function anchored at 5.8 and 6.6 μm. Then, we computed the feature emission by integrating the continuum-subtracted spectrum from 5.9 to 6.5 μm, and finally we divided this by the continuum emission interpolated at 6.2 μm.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


