| Issue |
A&A
Volume 468, Number 3, June IV 2007
Extended baselines for the IRAM Plateau de Bure interferometer: First results
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | L45 - L48 | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20066969 | |
| Published online | 05 March 2007 | |
Letter to the Editor
The nebula around the post-AGB star 89 Herculis *
1
Observatorio Astronómico Nacional (OAN-IGN), Apartado 112, 28803 Alcalá de Henares, Spain e-mail: v.bujarrabal@oan.es
2
Instituut voor Sterrenkunde, KU Leuven, Celestijnenlaan 200B, 3001 Leuven, Belgium e-mail: [Pieter.Deroo;Hans.VanWinckel]@ster.kuleuven.be
3
Institut de Radio Astronomie Millimétrique (IRAM), 300 rue de la Piscine, 38406 St. Martin d'Hères, France e-mail: [ccarrizo;neri]@iram.fr
4
Observatorio Astronómico Nacional (OAN-IGN), C/ Alfonso XII 3, 28014 Madrid, Spain e-mail: j.alcolea@oan.es
Received:
19
December
2006
Accepted:
24
February
2007
Aims.We aim to study the structure of the nebula around the post-AGB, binary star 89 Her. The presence of a rotating disk around this star had been proposed but not been yet confirmed by observations.
Methods.We present high-resolution PdBI maps of CO 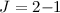 and 1-0.
Properties of the nebula are directly derived from the data and
model fitting. We also present N-band interferometric data on the
extent of the hot dust emission, obtained with the VLTI.
and 1-0.
Properties of the nebula are directly derived from the data and
model fitting. We also present N-band interferometric data on the
extent of the hot dust emission, obtained with the VLTI.
Results.Two nebular components are found: (a) an extended hour-glass-like
structure, with expansion velocities of ~7 km s-1 and a total mass
~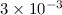
 , and (b) an unresolved very compact
component, smaller than ~0
, and (b) an unresolved very compact
component, smaller than ~0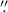 4 and with a low total
velocity dispersion of ~5 km s-1. We cannot determine the velocity
field in the compact component,
but we argue that it can hardly be in expansion, since
this would require too recent and too sudden an ejection of mass. On the
other hand, assuming that this component is a Keplerian disk, we
derive disk properties that are compatible with expectations for such
a structure; in particular, the size of the rotating gas disk should
be very similar to the extent of the hot dust component from
our VLTI data. Assuming that the equator of the extended nebula
coincides with the binary orbital plane, we provide new
results on the companion star mass and orbit.
4 and with a low total
velocity dispersion of ~5 km s-1. We cannot determine the velocity
field in the compact component,
but we argue that it can hardly be in expansion, since
this would require too recent and too sudden an ejection of mass. On the
other hand, assuming that this component is a Keplerian disk, we
derive disk properties that are compatible with expectations for such
a structure; in particular, the size of the rotating gas disk should
be very similar to the extent of the hot dust component from
our VLTI data. Assuming that the equator of the extended nebula
coincides with the binary orbital plane, we provide new
results on the companion star mass and orbit.
Key words: stars: AGB and post-AGB / stars: winds, outflows / radio lines: stars / stars: individual: 89 Her
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


