| Issue |
A&A
Volume 431, Number 2, February IV 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 757 - 771 | |
| Section | Astronomical instrumentation | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20042009 | |
| Published online | 04 February 2005 | |
Extracting clean supernova spectra*
Towards a quantitative analysis of high-redshift Type Ia supernova spectra
1
European Southern Observatory (ESO), Karl-Schwarzschild-Strasse 2, 85748 Garching bei München, Germany e-mail: [sblondin;bleibund]@eso.org
2
Space Telescope-European Coordinating Facility (ST-ECF), European Southern Observatory (ESO), Karl-Schwarzschild-Strasse 2, 85748 Garching bei München, Germany e-mail: jwalsh@eso.org
3
LPNHE CNRS/IN2P3, Université Paris VI & VII, 4 place Jussieu, 75252 Paris Cedex 05, France e-mail: sainton@in2p3.fr
Received:
14
September
2004
Accepted:
14
October
2004
We use a new technique to extract the spectrum of a supernova
from that of the contaminating background of its host galaxy, and apply it to
the specific case of high-redshift Type Ia supernova (SN Ia) spectroscopy. The
algorithm is based on a two-channel iterative technique employing the
Richardson-Lucy restoration method and is implemented in the IRAF code
specinholucy. We run the code both on simulated (SN Ia at 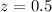 embedded in a bright host galaxy) and observed (SNe Ia at various phases up
to
embedded in a bright host galaxy) and observed (SNe Ia at various phases up
to 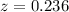 ) data taken with VLT+FORS1 and show the advantages of using such
a deconvolution technique in comparison with less elaborate methods. This
paper is motivated by the need for optimal supernova spectroscopic
data reduction in order to make meaningful comparisons between the low and
high-redshift SN Ia samples. This may reveal subtle evolutionary and
systematic effects that could depend on redshift, and bias the cosmological
results derived from comparisons of local and high-z SNe Ia in recent years.
We describe the various aspects of the extraction in some detail as
guidelines for the first-time user and present an optimal observing strategy
for successful implementation of this method in future high-z SN Ia
spectroscopic follow-up programmes.
) data taken with VLT+FORS1 and show the advantages of using such
a deconvolution technique in comparison with less elaborate methods. This
paper is motivated by the need for optimal supernova spectroscopic
data reduction in order to make meaningful comparisons between the low and
high-redshift SN Ia samples. This may reveal subtle evolutionary and
systematic effects that could depend on redshift, and bias the cosmological
results derived from comparisons of local and high-z SNe Ia in recent years.
We describe the various aspects of the extraction in some detail as
guidelines for the first-time user and present an optimal observing strategy
for successful implementation of this method in future high-z SN Ia
spectroscopic follow-up programmes.
Key words: stars: supernovae: general / stars: supernovae: individual: SN 2002bo, SN 2002go, SN 2002gr / instrumentation: spectrographs / methods: data analysis / techniques: spectroscopic
© ESO, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


