| Issue |
A&A
Volume 408, Number 2, September III 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 559 - 579 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20030937 | |
| Published online | 17 November 2003 | |
Shells of dust around AGB stars: Effects on the integrated spectrum of Single Stellar Populations
Department of Astronomy, University of Padova, Vicolo dell'Osservatorio 2, 35122 Padova, Italy e-mail: tantalo@pd.astro.it; chiosi@pd.astro.it
Corresponding author: L. Piovan, piovan@pd.astro.it
Received:
20
January
2003
Accepted:
18
June
2003
In this paper we present models for Single Stellar
Populations (SSPs) of
intermediate and old ages where dust enshrouded Asymptotic Giant
Branch (AGB) stars
are introduced. As long known AGB stars are surrounded by dust-rich
shells of matter caused by their own stellar wind, which absorb the
radiation coming from the central object
and re-emit it in the far infrared (IR).
To this aim, particular care is devoted to
follow the evolution of the AGB stars throughout the quiet and
thermally pulsing
regimes, to evaluate the effect of self contamination in the outermost
layers by the
third dredge-up mechanism, to follow the transition from
oxygen-rich to carbon-rich objects (as appropriate to their
initial mass and chemical composition), and finally to estimate
the efficiency of mass-loss by stellar winds, all aspects that
concur to the formation and properties of the dusty shells around.
In addition to this, accurate physical models of the dusty shells
are presented in which the re-processing of radiation from the
central stars is calculated by solving the radiative transfer
equations in presence of dust particles of different chemical
composition. The resulting spectral energy distribution (SED) is
examined to show how important features, like the 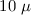 m
m 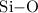 stretching mode feature and the
stretching mode feature and the 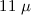 m SiC feature,
evolve with time. The SEDs are then convolved with the IRAS
filters to obtain the flux in various pass-bands, i.e. 12, 25 and 60 μm, for individual AGB stars of different mass, chemical
composition, and age. The comparison is made by means of SSPs
along which AGB stars of the same age but different initial masses
are located. This allows us to explore the whole range of masses
and ages spanned by AGB stars.
The theoretical results are compared
to the observational data for selected groups of stars. The same
is made for the
m SiC feature,
evolve with time. The SEDs are then convolved with the IRAS
filters to obtain the flux in various pass-bands, i.e. 12, 25 and 60 μm, for individual AGB stars of different mass, chemical
composition, and age. The comparison is made by means of SSPs
along which AGB stars of the same age but different initial masses
are located. This allows us to explore the whole range of masses
and ages spanned by AGB stars.
The theoretical results are compared
to the observational data for selected groups of stars. The same
is made for the 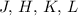 pass-bands of the Johnson system.
Finally, from the integrated SEDs of the SSPs, we derive the
integrated Johnson
pass-bands of the Johnson system.
Finally, from the integrated SEDs of the SSPs, we derive the
integrated Johnson 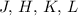 magnitudes and colors to be compared
to infrared data for star clusters of the Magellanic Clouds. In
general good agreement with the data is possible if the effects of
the circumstellar shells of dust are taken into account.
magnitudes and colors to be compared
to infrared data for star clusters of the Magellanic Clouds. In
general good agreement with the data is possible if the effects of
the circumstellar shells of dust are taken into account.
Key words: stars: AGB and post AGB / stars: mass-loss / stars: circumstellar matter / infrared: stars
© ESO, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


