| Issue |
A&A
Volume 388, Number 2, June III 2002
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | L29 - L32 | |
| Section | Letters | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20020599 | |
| Published online | 31 May 2002 | |
Letter to the Editor
Pulsed radiation from neutron star winds
1
Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Postfach 10 39 80, 69029 Heidelberg, Germany
2
Service d'Astrophysique, CEA-Saclay, 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette, France
Corresponding author: J. G. Kirk, john.kirk@mpi-hd.mpg.de
Received:
22
February
2002
Accepted:
17
April
2002
The radiation of a pulsar wind is computed
assuming that at roughly 10 to 100 light cylinder radii
from the star, magnetic energy is dissipated into
particle energy. The synchrotron emission of heated
particles appears periodic, with, in general, both a pulse and an
interpulse. The predicted spacing agrees
well with the Crab and Vela pulse profiles.
Using parameters appropriate for
the Crab pulsar (magnetisation parameter at the light cylinder
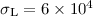 , Lorentz factor
, Lorentz factor
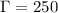 ) agreement is found with the
observed total pulsed luminosity.
This suggests that the high-energy pulses
from young pulsars originate not in the corotating magnetosphere
within the light cylinder (as in all other models) but from the
radially directed wind well outside it.
) agreement is found with the
observed total pulsed luminosity.
This suggests that the high-energy pulses
from young pulsars originate not in the corotating magnetosphere
within the light cylinder (as in all other models) but from the
radially directed wind well outside it.
Key words: pulsars: general / pulsars: Crab / MHD / radiation mechanisms: non-thermal
© ESO, 2002
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


