All Tables
- Table 1:
Estimated numerical error in longitude in INPOP06 (step size 0.055 day)
for all planets i (i=3 stands for the Earth-Moon Barycenter, and i=10 for the Moon).
The error
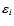 is given in microarcseconds (
is given in microarcseconds (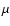 as) or micrometers (
as) or micrometers (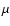 m)
over 100 years and over 10 000 years.
m)
over 100 years and over 10 000 years.
- Table 2:
Maximum difference between DE405 and INPOP05 (with the
same initial conditions) in range (r), latitude (
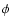 )
and
longitude (
)
and
longitude (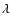 ). If (x,y,z) are the heliocentric (geocentric
for the Moon) coordinates of the planet in the equatorial reference
frame of the ICRF, then
). If (x,y,z) are the heliocentric (geocentric
for the Moon) coordinates of the planet in the equatorial reference
frame of the ICRF, then
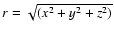 ,
,
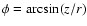 and
and
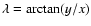 .
EMB is the Earth-Moon
Barycenter. For the librations of the Moon,
.
EMB is the Earth-Moon
Barycenter. For the librations of the Moon, 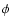 ,
,
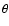 and
and 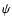 are the usual Euler's angles (see Newhall et al. 1983, Sect. II.D).
Comparisons are made over the whole time interval of
DE405 (-400 yr to 200 yr with origin at J2000); Col. 1: from -30 yr
to +30 yr; Col. 2: from -100 yr to +100 yr; Col. 3: from -400 yr to
200 yr.
are the usual Euler's angles (see Newhall et al. 1983, Sect. II.D).
Comparisons are made over the whole time interval of
DE405 (-400 yr to 200 yr with origin at J2000); Col. 1: from -30 yr
to +30 yr; Col. 2: from -100 yr to +100 yr; Col. 3: from -400 yr to
200 yr.
- Table 3:
INPOP05 (Col. 5) residuals for each type of observations. Column 3 gives the time interval of
observations and Col. 4 the number N of observations used in the fit and in the residual computations.
For optical observations, the residuals are given respectively in right ascension and declination (
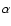 ;
;
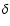 ). The given
uncertainties are at 1-sigma.
). The given
uncertainties are at 1-sigma.
- Table 4:
Maximum difference between DE405 and INPOP06 in range (r), latitude (
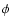 )
and
longitude (
)
and
longitude (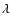 ). (x,y,z) are the heliocentric (geocentric
for the Moon) coordinates of the planet in the equatorial reference
frame of the ICRF, and
). (x,y,z) are the heliocentric (geocentric
for the Moon) coordinates of the planet in the equatorial reference
frame of the ICRF, and
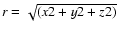 ,
,
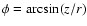 and
and
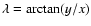 .
EMB is the Earth-Moon
Barycenter. For the librations of the Moon,
.
EMB is the Earth-Moon
Barycenter. For the librations of the Moon, 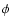 ,
,
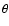 and
and 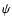 are the usual Euler's angles (see Newhall et al., section II.D).
Comparisons are made over the whole time interval of
DE405 (-400 yr to 200 yr with origin at J2000); Col. 1: from -30 yr
to +30 yr; Col. 2: from -100 yr to +100 yr; Col. 3: from -400 yr to
200 yr.
are the usual Euler's angles (see Newhall et al., section II.D).
Comparisons are made over the whole time interval of
DE405 (-400 yr to 200 yr with origin at J2000); Col. 1: from -30 yr
to +30 yr; Col. 2: from -100 yr to +100 yr; Col. 3: from -400 yr to
200 yr.
- Table 5:
Parameters used in DE405 (and INPOP05) (Col. 2), and in INPOP06 (Col. 3), to compute the tidal effects (see Sects. 2.3.3 and 2.3.5) and the Earth orientation.
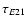 and
and
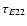 are respectively the Earth's time delays for harmonics (2, 1) and (2, 2), and
are respectively the Earth's time delays for harmonics (2, 1) and (2, 2), and
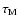 is the time delays for the Moon. They are expressed in days and rounded to 10-10. C, M and R are respectively the maximum moment of inertia, the mass and the mean equatorial radius of the Earth.
is the time delays for the Moon. They are expressed in days and rounded to 10-10. C, M and R are respectively the maximum moment of inertia, the mass and the mean equatorial radius of the Earth.
- Table 6:
INPOP06 (Col. 5) residuals for each type of observation. Column 3 gives the observational time interval and Col. 4 the number of observations N used in the fit and in the residual computations. For optical observations, the residuals are given respectively in right ascension and declination (
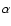 ;
;
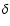 ). The uncertainties are at 1-sigma.
). The uncertainties are at 1-sigma.
- Table 7:
Physical parameters fitted in INPOP06. Other values deduced from planetary ephemerides
are presented for comparisons.The given
uncertainties are given at 1-sigma.
- Table 8:
Solar oblateness and the PPN parameter
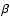 determinations based on INPOP06 fit to observations. In the first column, the publications from where the values are extracted and the methods used to estimate the Sun
J2 and the PPN parameters
determinations based on INPOP06 fit to observations. In the first column, the publications from where the values are extracted and the methods used to estimate the Sun
J2 and the PPN parameters 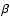 are given. In Cols. 2, 3 and 4, computed values of these parameters can be found.
are given. In Cols. 2, 3 and 4, computed values of these parameters can be found.