- ...1
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Current address:
i). NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Code 661,
Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA ii). Universities
Space Research Association, 7501 Forbes Blvd. #206,
Seabrook, MD 20706-2253, USA.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... radioactivity
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- In the following, "primordial
radioactivity'' denotes unstable isotopes that already existed when
the Earth was formed.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
detector
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The D1 detector mass fraction of Fe, Cr, and Ni
relative to Al is about 20%, 5%, and 6%, respectively.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
passages
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The D1 detector mass fraction of Cu relative to Al
is about 13%.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... following
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- This veto rate is the number
of deadtime clock counts that occur during the presence of a veto
signal. For each veto dome the deadtime clock counts are accumulated
over the length of a telemetry packet (2.048 s) once during each
superpacket (16.384 s) and recorded in the house-keeping datasets in
units of [deadtime clock counts/2.048 s
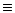 DT].
DT].
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... CDG
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- A
similar procedure consisting of four different fits was utilized in
the CDG analysis of Kappadath et al. (2000) to
determine the background contributions from the five isotopes (2D,
22Na, 24Na, 28Al, and 40K (fixed))
identified at that time.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... interval
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Ideally, the event rates due to these
isotopes would be determined by fitting the two-dimensional event
distribution in
E1-E2. However, at present
such two-dimensional fits are not feasible for two reasons. First, in
general the statistics is not sufficient in the CDG analysis, and
second, we do not yet have a reliable model of the
E1-E2 distribution of the continuum
background, which has a complex shape as it is a blend of various
components.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.