A&A 465, 825-838 (2007)
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20066185
Tracing the long bar with red-clump giants
A. Cabrera-Lavers1,2 -
P. L. Hammersley1 - C. González-Fernández1 - M.
López-Corredoira1 - F. Garzón1,3 -
T. J. Mahoney1
1 - Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, 38205 La Laguna, Tenerife, Spain
2 -
GTC Project Office, 38205 La Laguna, Tenerife, Spain
3 -
Departamento de Astrofísica, Universidad de La Laguna, 38205 La
Laguna, Tenerife, Spain
Received 4 August 2006 / Accepted 20 January 2007
Abstract
Context. Over the last decade a series of results have lent support to the hypothesis of the existence of a long thin bar in the Milky Way with a half-length of 4.5 kpc and a position angle of around 45 .
This is apparently a very different structure from the triaxial bulge of the Galaxy.
.
This is apparently a very different structure from the triaxial bulge of the Galaxy.
Aims. In this paper, we analyse the stellar distribution in the inner 4 kpc of the Galaxy to see if there is clear evidence for two triaxial or barlike structures, or whether there is only one.
Methods. By using the red-clump population as a tracer of the structure of the inner Galaxy we determine the apparent morphology of the inner Galaxy. Star counts from 2MASS are used to provide additional support for this analysis.
Results. We show that there are two very different large-scale triaxial structures coexisting in the inner Galaxy: a long thin stellar bar constrained to the Galactic plane (
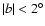 )
with a position angle of 43
)
with a position angle of 43
 0
0  1
1
 8, and a distinct triaxial bulge that extends to at least
8, and a distinct triaxial bulge that extends to at least
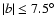 with a position angle of 12
with a position angle of 12
 6
6  3
3
 2. The scale height of the bar source distribution is around 100 pc, whereas for the bulge the value of this parameter is five times larger.
2. The scale height of the bar source distribution is around 100 pc, whereas for the bulge the value of this parameter is five times larger.
Key words: Galaxy: general - Galaxy: stellar content -
Galaxy: structure - infrared: stars
There is now a substantial consensus for there being a stellar bar in the
inner Galaxy. This was first suggested by de Vaucouleurs (1964) to explain the nonaxisymmetry in radio maps. The first evidence for a barlike distribution
in the stars was derived from the asymmetries
in the infrared (IR) surface brightness maps (e.g. Blitz & Spergel 1991;
Dwek et al. 1995) and in source counts (Weinberg 1992; Hammersley et al. 1994;
Stanek et al. 1994), which both show systematically more stars at positive
galactic longitudes l<30 close to the Galactic
plane (GP). The exact morphology of the inner Galaxy, however, is still controversial. While some authors refer to the bar as a fatter structure, around 2.5 kpc in length with a position angle of 15-30 degrees with respect to the Sun-Galactic Centre direction (Dwek et al. 1995;
Nikolaev & Weinberg 1997; Stanek et al. 1997; Binney et al. 1997;
Freudenreich 1998; López-Corredoira et al. 1999;
Bissantz & Gerhard 2002; Babusiaux & Gilmore 2005), other researchers
suggest that there is a long bar with a half length of 4 kpc and a position
angle of around 45 degrees. It is noteworthy that those authors supporting the 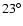 bar all
examine the region at
bar all
examine the region at
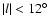 ,
whereas
those supporting the long bar with the larger angle are trying to explain counts for
,
whereas
those supporting the long bar with the larger angle are trying to explain counts for
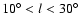 and
and
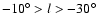 .
.
Hammersley et al. (2000) showed that there is a major over-density of
K2-3III (red-clump) stars on the GP at
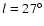 at a distance of about 6 kpc from the Sun. This over-density could also be
detected at smaller galactic longitudes, but
more reddened and at an increased distance from the observer. These
stars could not be seen a few degrees above
or below the GP at the same galactic longitudes, nor at greater longitudes.
This, when combined with the findings of Hammersley et al. (1994), was interpreted as
strong evidence for
the existence of a long in-plane bar with a half length
at a distance of about 6 kpc from the Sun. This over-density could also be
detected at smaller galactic longitudes, but
more reddened and at an increased distance from the observer. These
stars could not be seen a few degrees above
or below the GP at the same galactic longitudes, nor at greater longitudes.
This, when combined with the findings of Hammersley et al. (1994), was interpreted as
strong evidence for
the existence of a long in-plane bar with a half length 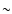 4 kpc and
position angle of 43
4 kpc and
position angle of 43 ,
clearly distinguishable from the triaxial
bulge, but
running into it near l = 12
,
clearly distinguishable from the triaxial
bulge, but
running into it near l = 12 .
This over-density of stars was also
analysed by
comparing near-infrared (NIR) counts with predictions of the
Besançon Galactic model (Robin et al. 2003)
with similar conclusions (Picaud et al. 2003).
This result has been further supported by
observations in the mid-infrared with GLIMPSE data (Benjamin et al.
2005) who did a similar analysis to that of
Hammersley et al. (2000) but at a wavelength range
in which the effects due to extinction are even lower than in the NIR, hence
reducing the uncertainty in the results.
.
This over-density of stars was also
analysed by
comparing near-infrared (NIR) counts with predictions of the
Besançon Galactic model (Robin et al. 2003)
with similar conclusions (Picaud et al. 2003).
This result has been further supported by
observations in the mid-infrared with GLIMPSE data (Benjamin et al.
2005) who did a similar analysis to that of
Hammersley et al. (2000) but at a wavelength range
in which the effects due to extinction are even lower than in the NIR, hence
reducing the uncertainty in the results.
There is also a noticeable difference in the luminosity function found in
the two regions. The majority of the work on the
short, fat bar (subtending an angle of 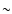 23
23 with the Sun-Galactic Centre line),
has been restricted to within a few degrees of the plane in regions
that are routinely used by other authors to
study the bulge, and what is seen is an older population. The on-plane
region between
with the Sun-Galactic Centre line),
has been restricted to within a few degrees of the plane in regions
that are routinely used by other authors to
study the bulge, and what is seen is an older population. The on-plane
region between
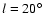 and 27
and 27 ,
however, has been shown to contain a large number of extremely luminous young stars (Hammersley et al. 1994;
Gazón et al. 1997; López-Corredoira et al.
1997), and a characteristic feature of long bars is a major star formation region
where they interact with the disc.
,
however, has been shown to contain a large number of extremely luminous young stars (Hammersley et al. 1994;
Gazón et al. 1997; López-Corredoira et al.
1997), and a characteristic feature of long bars is a major star formation region
where they interact with the disc.
These results suggest that the structure in the inner Galaxy
(
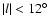 )
could be interpreted as
a triaxial bulge
)
could be interpreted as
a triaxial bulge![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif) rather than a bar, and certainly not a long straight bar. This triaxial bulge has
axial ratios of 1:0.5:0.4 (López-Corredoira
et al. 2005). Furthermore López-Corredoira et al.
(1999) showed that a triaxial bulge + disc model cannot reproduce
the observed counts in the Galactic plane
for
rather than a bar, and certainly not a long straight bar. This triaxial bulge has
axial ratios of 1:0.5:0.4 (López-Corredoira
et al. 2005). Furthermore López-Corredoira et al.
(1999) showed that a triaxial bulge + disc model cannot reproduce
the observed counts in the Galactic plane
for
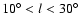 .
This is also suggested by NIR photometry of
red-clump stars (Nishiyama et al. 2005). It should be noted that the
possibility of there being even
smaller non-axisymmetric structures (e.g. a secondary bar) in The Milky Way
cannot be discounted (Unavane & Gilmore 1998; Alard 2001;
Nishiyama et al. 2005); thus, more observations are needed for a decisive conclusion to be reached.
.
This is also suggested by NIR photometry of
red-clump stars (Nishiyama et al. 2005). It should be noted that the
possibility of there being even
smaller non-axisymmetric structures (e.g. a secondary bar) in The Milky Way
cannot be discounted (Unavane & Gilmore 1998; Alard 2001;
Nishiyama et al. 2005); thus, more observations are needed for a decisive conclusion to be reached.
Many galaxies have triaxial bulges contained within a primary stellar bar,
and even a third, smaller-scale bar inside the bulge (Fiedli et al. 1996). More than
half of all disc galaxies have some kind of bar component (Buta et al. 1996) and as many as a third have a strong primary bar (Freeman
1996). Recent NIR observations by Beaton et al.
(2005) and N-body simulations by Athanassoula & Beaton (2006) provide strong
evidence in favour of the existence in our close neighbour M 31 of a boxy bulge contained
within a primary bar of semilength of 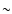 4 kpc. Such a high degree of morphological similarity
between two neighbouring galaxies is striking (even though the angular separation between the major axes of the primary bar and triaxial bulge is different for the two galaxies).
4 kpc. Such a high degree of morphological similarity
between two neighbouring galaxies is striking (even though the angular separation between the major axes of the primary bar and triaxial bulge is different for the two galaxies).
Bars are generally constrained to the
plane whereas bulges are shorter and more extended vertically.
Therefore, using data covering a wide range of longitudes and latitudes
is the only way to distinguish between the
two possible morphologies for the inner Milky Way: a short
inner bar or a triaxial bulge + long bar. In this paper we have used NIR data from the TCS-CAIN survey to analyse the spatial distribution of red-clump sources in
the inner Galaxy. This population of stars has been widely used as a standard candle in deriving distances to the inner Galaxy (Hammersley et al. 2000; Stanek et al. 1994; López-Corredoira et al. 2004; Babusiaux & Gilmore 2005; Nishiyama et al. 2005, 2006b). By observing how
these stars are distributed along different lines of sight towards the inner Galaxy we are able to explore the 3D morphology of our Galaxy.
TCS-CAIN catalogue is a NIR survey of the Milky Way that has
recently been completed at the Instituto
de Astrofísica de Canarias. This survey consists of more
than 500 fields distributed along or near the Galactic plane
(
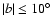 )
observed in J, H and
)
observed in J, H and 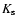 filters with a photometric accuracy of
filters with a photometric accuracy of 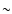 0.1 mag in the three bands and a positional accuracy of
0.1 mag in the three bands and a positional accuracy of 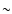 0.2'', based on the 2MASS catalogue as astrometric reference. Each field
covers approximately 0.07 deg2 on the sky, centred on the stated
galactic coordinates for that field. The nominal limiting magnitudes of the
survey (determined using growth curves of the differential star counts) are 17, 16.5 and 15.2 in J, H and
0.2'', based on the 2MASS catalogue as astrometric reference. Each field
covers approximately 0.07 deg2 on the sky, centred on the stated
galactic coordinates for that field. The nominal limiting magnitudes of the
survey (determined using growth curves of the differential star counts) are 17, 16.5 and 15.2 in J, H and 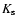 respectively; hence, TCS-CAIN is at least one magnitude
deeper than 2MASS, and even more in the inner Galaxy, where confusion is
important. A complete description of the catalogue and data reduction, and
details of its contents can be found in Cabrera-Lavers et al. (2006).
respectively; hence, TCS-CAIN is at least one magnitude
deeper than 2MASS, and even more in the inner Galaxy, where confusion is
important. A complete description of the catalogue and data reduction, and
details of its contents can be found in Cabrera-Lavers et al. (2006).
In this paper we have used all the available near plane fields in the inner Galaxy
(
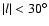 ,
|b|
,
|b| 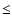 7.5
7.5 ), which gives a total number of 205 usable fields,
covering an area of approximately 14.2 deg2
of the sky (nearly 35% of the whole catalogue area).
), which gives a total number of 205 usable fields,
covering an area of approximately 14.2 deg2
of the sky (nearly 35% of the whole catalogue area).
Red-clump giants have long been proposed as standard candles. They have a very narrow luminosity
function and constitute a compact
and well-defined clump in an HR diagram, particularly in the infrared. Furthermore, as they are relatively luminous, they can
be identified even to large distances from the Sun.
López-Corredoira et al. (2002) developed a method
to obtain the star density and interstellar extinction along a line of
sight by extracting
the red-clump population from the NIR colour-magnitude diagrams (CMDs). This
method has proved very powerful for analysing the
structure of the thin (López-Corredoira et al. 2002, 2004) and
thick (Cabrera-Lavers et al. 2005) discs of the Milky Way, as well as in
the study of the distribution of interstellar extinction (Drimmel et al. 2003; Picaud et al. 2003; Duran & van Kerkwijk 2006).
The absolute magnitude (MK) and intrinsic colour,
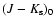 ,
of the red-clump giants are well established
(Alves 2000; Grocholski & Sarajedini 2002; Salaris & Girardi 2002;
Pietrzynski et al. 2003). Here, we consider an absolute magnitude
for the red
clump population of -1.62
,
of the red-clump giants are well established
(Alves 2000; Grocholski & Sarajedini 2002; Salaris & Girardi 2002;
Pietrzynski et al. 2003). Here, we consider an absolute magnitude
for the red
clump population of -1.62  0.03 mag and and an intrinsic colour of
0.03 mag and and an intrinsic colour of
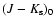 = 0.7 mag. These values are consistent with the results derived by Alves
(2000) from the
Hipparcos red-clump and also with the results obtained by Grocholski &
Sarajedini (2002)
for open clusters. The intrinsic colour of the red-clump stars
predicted by the
Padova isochrones in the 2MASS system (Bonatto et al. 2004) for a 10 Gyr
population of solar metallicity is (J-K)0 = 0.68 mag. As 2MASS
photometry is
nearly equivalent to the TCS-CAIN photometric system (Cabrera-Lavers et al.
2006) the value of
0.7 mag is sufficiently close to represent the red-clump population.
= 0.7 mag. These values are consistent with the results derived by Alves
(2000) from the
Hipparcos red-clump and also with the results obtained by Grocholski &
Sarajedini (2002)
for open clusters. The intrinsic colour of the red-clump stars
predicted by the
Padova isochrones in the 2MASS system (Bonatto et al. 2004) for a 10 Gyr
population of solar metallicity is (J-K)0 = 0.68 mag. As 2MASS
photometry is
nearly equivalent to the TCS-CAIN photometric system (Cabrera-Lavers et al.
2006) the value of
0.7 mag is sufficiently close to represent the red-clump population.
The absolute magnitude of the red-clump has a small dependence on metallicity
(Salaris & Girardi 2002). There is no large metallicity gradient in
the Galactic disc
(Ibata & Gilmore 1995a,b; Sarajedini et al. 1995); however, there is a slight difference between the solar neighborhood metallicity and those
of the bulge giants, which peaks at [Fe/H] = -0.25 dex (Ramírez et al. 2000;
Schultheis et al. 2003; Molla et al. 2000). According to Salaris &
Girardi (2002), a small correction of 0.03 mag should be applied to the
absolute magnitude of the red-clump stars for these ranges of metallicity.
However, this is
well within the uncertainty considered for the absolute magnitude used
here. The red-clump absolute magnitude in J is more sensitive to
metallicity
and age than the K filter, hence the intrinsic colour (J-K)0 also
depends on both
the metallicity and age (Salaris & Girardi 2002; Grocholski & Sarajedini
2002; Pietrzynski et al. 2003). The theoretical isochrones of Salaris
& Girardi (2002) and Bonatto et al. (2004) suggest that the de-reddened colour for the
range of metallicities expected for a bulge population is
(J-K)0=0.63  0.02.
Hence the metallicity dependences lead to a systematic
uncertainty of 0.03 mag in the absolute magnitude of the red-clump stars and
0.05 mag in the intrinsic colour, (J-K)0.
0.02.
Hence the metallicity dependences lead to a systematic
uncertainty of 0.03 mag in the absolute magnitude of the red-clump stars and
0.05 mag in the intrinsic colour, (J-K)0.
A recent study using NIR spectra of the inner Galaxy giants between
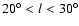 has shown that these stars have a well defined
metallicity (typically [Fe/H] between 0 and -0.2 dex) with a very small dispersion
(Cabrera-Lavers et al., in preparation).
By using the population of infrared carbon stars from the 2MASS survey,
Cole & Weinberg (2002) conclude that
the bar formed more recently than 3 Gyr ago and must be younger than
6 Gyr. For this age and metallicity, the corrections given by Salaris &
Girardi (2002) are even lower than for the older bulge. Hence, we have
assumed that uncertainties in absolute magnitude and intrinsic colour for this
population of red-clump stars are of the same order as in the case of the bulge stars.
has shown that these stars have a well defined
metallicity (typically [Fe/H] between 0 and -0.2 dex) with a very small dispersion
(Cabrera-Lavers et al., in preparation).
By using the population of infrared carbon stars from the 2MASS survey,
Cole & Weinberg (2002) conclude that
the bar formed more recently than 3 Gyr ago and must be younger than
6 Gyr. For this age and metallicity, the corrections given by Salaris &
Girardi (2002) are even lower than for the older bulge. Hence, we have
assumed that uncertainties in absolute magnitude and intrinsic colour for this
population of red-clump stars are of the same order as in the case of the bulge stars.
In this paper the TCS-CAIN survey data is analysed using the method
developed by Stanek et al. (1997) for
their data obtained by the Optical Gravitational
Lensing Experiment (OGLE; Udalski et al. 1993, 1994). This method
has also recently been used by Nishiyama et al. (2005, 2006b) and Babusiaux &
Gilmore (2005) to analyse
the red-clump population of the inner Galaxy.
To avoid extinction effects a reddening-independent magnitude (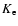 )
is used:
)
is used:
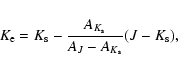 |
(1) |
adopting
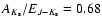 (Rieke & Lebofski 1985), a value
which agrees with that used in Babusiaux & Gilmore (2005)
and also with that obtained by Indebetouw et al. (2005) by
combining data from the Spitzer Space Telescope and 2MASS.
(Rieke & Lebofski 1985), a value
which agrees with that used in Babusiaux & Gilmore (2005)
and also with that obtained by Indebetouw et al. (2005) by
combining data from the Spitzer Space Telescope and 2MASS.
With the reddening-independent magnitudes, any compact structural feature in the CMD
would appear as a "clump'' of stars, as they will be located at
approximately the same distance from the Sun and hence they would have the same apparent
K-magnitude. As the red-clump stars are the dominant giant population
(Cohen et al. 2000; Hammersley et al. 2000), we can derive the
distance to the feature by a non-linear least-squares fit of the sum of a Gaussian
function and a second-order polynomial (Eq. (2)) to the histogram of red
giant stars (Stanek et al. 1994; Stanek & Garnavich 1998; Babusiaux & Gilmore 2005):
![\begin{displaymath}%
N(m)=a+bm+cm^2+ \frac{N_{\rm RC}}{\sigma_{\rm RC}\sqrt{2\pi...
...\left[-\frac{(m_{\rm RC}-m)^2}{2\sigma_{\rm RC}^2}\right]\cdot
\end{displaymath}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/img32.gif) |
(2) |
The Gaussian term corresponds to a fit of the red-clump population of the
bulge/bar, while the second-order polynomial reflects the contribution
of the background stars. The combined effect of distance plus extinction
produces an increase in
the mixture between faint dwarfs and giants. In order to subtract the
contribution of foreground dwarf
stars we have used the SKY extinction model (Wainscoat et al. 1992)
to derive the
theoretical traces in the diagrams for the giant population in each
field. With these theoretical
traces we can isolate the population of red-clump stars in each CMD;
thus, the
fit is made only after removing the contribution of dwarf stars in the
reddening-corrected counts (Fig. 1).
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.85cm,clip]{6185fig01.ps}\par\includegraphics[width=7.85cm,clip]{6185fig02.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg33.gif) |
Figure 1:
Two examples of the use of the theoretical traces for the giant
population by means of the SKY model. Stars isolated between
both traces (corresponding to the K0 and the M0 populations) are
assumed to be red-clump stars and are extracted to analyse their spatial
distribution. |
| Open with DEXTER |
To transform the derived extinction-corrected magnitudes into distances
from the Sun we use:
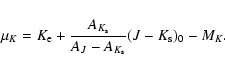 |
(3) |
To estimate an upper limit to the reddening-independent magnitude that
can be analysed reliably we
have followed the same procedure described in
Babussiaux & Gilmore (2005). First, an estimate of the completeness
limits in J and K (
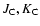 )
are derived by determining when the number
counts as function of magnitude stops increasing. The relative
completeness of
)
are derived by determining when the number
counts as function of magnitude stops increasing. The relative
completeness of 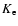 is then derived by combining these estimates with the
mean colour of the giants in the field
is then derived by combining these estimates with the
mean colour of the giants in the field
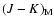 ,
and adding a 0.5 mag
safety margin to take into account the spread in the mean colour:
,
and adding a 0.5 mag
safety margin to take into account the spread in the mean colour:
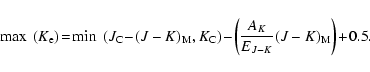 |
(4) |
Figure 2 shows all of the analysed fields used in this work. There are
three different kind of fields:
- Those (labelled "discarded'' fields) in which the completeness
made it impossible to fit the red-clump distribution accurately.
- Those (labelled "rejected'' fields) in which no
successful fit was possible, as no clear structural component was
present. In these cases, the counts increase
continuously with the distance modulus until reaching
the completeness limit for the field. These in-plane fields are purely
disc fields and are located too far above or below the galactic plane for
either the bulge or the bar components to be observed, so that no "hump'' in
the red-clump counts is expected (Fig. 3).
- Those marked as "used'' in Fig. 2 where it was possible to derive a distance to the red-clump population. After discarding all those fields which were not
useful, we obtained results in 49 of the total sample of 205 fields.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,clip]{6185fig03.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg39.gif) |
Figure 2:
Summary of the 205 TCS-CAIN fields analysed in this work. |
| Open with DEXTER |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.7cm,clip]{6185fig04.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg40.gif) |
Figure 3:
Example of a field where no peak in the counts of the red-clump distribution
is observed, as we are observing a field where only the disc component
is present, hence the star counts increase up to the completeness limit
of the field (shown as a vertical dashed line). |
| Open with DEXTER |
Some fields were observed only in the J and H bands, since far from the Galactic plane the counts in the K and H bands are nearly equivalent due to the low extinction. For
this reason some of the fields in this work use
H-band extinction-corrected magnitudes (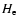 ):
):
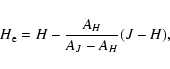 |
(5) |
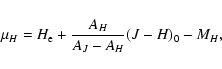 |
(6) |
using
(J-H)0=0.5, MH =-1.5 (Wainscoat et al. 1992) and
AH/EJ-H=1.41, following Rieke & Lebofsky (1985) and in agreement
with the result of Nishiyama et al. (2006a). These values were used
in eight fields, those with
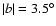 and
and
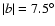 ,
and three additional fields at
,
and three additional fields at 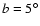 (those at
(those at 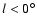 ).
).
To test the reliability of deriving distances using either K- or H-band
corrected magnitudes, the results for the fields with
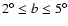 were compared where
were compared where
 photometry was available; also, there are no
effects of completeness in either
photometry was available; also, there are no
effects of completeness in either 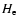 or
or 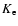 .
In general, the fits using
the two different reddening-independent magnitudes are all consistent to
within 0.2 mag, with a mean difference of 0.05 mag (
.
In general, the fits using
the two different reddening-independent magnitudes are all consistent to
within 0.2 mag, with a mean difference of 0.05 mag (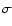 = 0.11 mag)
for a total of 18 fields (see Figs. 4 and 5). Hence, the
derived distances using (J-H,H) data can be compared with those obtained
using (J-K,K) data.
= 0.11 mag)
for a total of 18 fields (see Figs. 4 and 5). Hence, the
derived distances using (J-H,H) data can be compared with those obtained
using (J-K,K) data.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.85cm,clip]{6185fig05.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg51.gif) |
Figure 4:
Comparison between the distance modulus obtained with H-band
data with that obtained with K-band data for the same
fields. The solid line shows the 1:1 ratio. The two quantities are well correlated and give similar distances. |
| Open with DEXTER |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.65cm,clip]{6185fig06.eps}\par\includegraphics[width=7.65cm,clip]{6185fig07.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg52.gif) |
Figure 5:
Spatial distribution of red-clump stars obtained with either H-
or K-band corrected magnitudes for the
fields 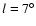 , ,
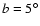 (above) and
(above) and 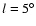 , ,
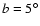 (below). The distributions are very similar, and the maxima are nearly
coincident. Vertical lines show the limiting magnitude derived using the K(solid) and H (dashed) bands, respectively. (below). The distributions are very similar, and the maxima are nearly
coincident. Vertical lines show the limiting magnitude derived using the K(solid) and H (dashed) bands, respectively. |
| Open with DEXTER |
The distances to the bar/bulge red-clump cluster of stars
are summarized in Table 1 and examples of the fits are shown in
Fig. 6. Error estimates for the distances
have been obtained as a combination of the systematic uncertainties in the
intrinsic colour and absolute magnitude of the red-clump population and the fitting error
of Eq. (2), added in quadrature. The dispersion in distance is represented in each
case by 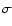 .
This is estimated from a simple deconvolution:
.
This is estimated from a simple deconvolution:
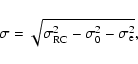 |
(7) |
where
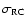 is the dispersion of the Gaussian fitted to the
histograms by Eq. (2),
is the dispersion of the Gaussian fitted to the
histograms by Eq. (2), 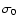 is the intrinsic dispersion of the red-clump
luminosity, which has been estimated in the range 0.15-0.2 mag (Alves 2000;
López-Corredoira et al. 2002) and finally,
is the intrinsic dispersion of the red-clump
luminosity, which has been estimated in the range 0.15-0.2 mag (Alves 2000;
López-Corredoira et al. 2002) and finally,
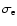 is the photometric
error, which for TCS-CAIN is of the order
is the photometric
error, which for TCS-CAIN is of the order 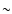 0.08 mag
(Cabrera-Lavers et al. 2006).
0.08 mag
(Cabrera-Lavers et al. 2006).
Table 1:
Distance modulii and distances derived with the red-clump stars for
the 49 fields used along this work, with each field covering 0.07 deg2 on the sky centred on the Galactic coordinates given in Cols. (1) and (2). The last eight fields are those in which H-band data were used to derive distances.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6cm,clip]{6185fig08.eps}\par\includegr...
...p]{6185fig09.eps}\par\includegraphics[width=6cm,clip]{6185fig10.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg58.gif) |
Figure 6:
Histograms of the distance modulus in three of the fields used in this work.
Fits of Eq. (2) to the histograms are shown as
solid curves, while vertical lines show the limiting magnitude estimates up to which the fits were performed. |
| Open with DEXTER |
Although we have used the theoretical traces from the SKY model to isolate the red-clump population to avoid contamination due to other populations in the counts (Fig. 1), there will be some contamination from other
sources and the effect of this on the overall shape of the reddening-corrected counts should be estimated. For this, we have used the SKY model to predict the relative
number of dwarf stars that will fall into the red-clump region of the CMDs (between the dashed lines in Fig. 1). The dwarfs predicted by the SKY model that fell into the red-clump area on the CMD were subtracted from the measured counts to give a new "corrected'' distribution. A full description of this
procedure can be found in Sect. 3.3.3 of López-Corredoira et al. (2002). What is found is that for mK<12.5 only 2.5-5% of the detected sources are dwarfs, but that this rises to 10-40% for 13<mK<14.
As shown in Fig. 7, both for an in-plane and an off-plane field, there is no significant difference in between the corrected and uncorrected
distribution. The effect of dwarfs is more important for fainter magnitudes
(hence for apparently more distant sources), so the distributions overestimate the number of sources for higher values of the distance modulus. However, the peak location is dominated by the red-clump population, and any possible contamination
does not affect its location. We fitted Eq. (2) to the "corrected'' distributions and obtained a mean difference in the distance modulus derived from either
the uncorrected or corrected data of 0.05 mag (which, translated into distances, yields to a difference of around 100 pc in this case),
which is lower than the accuracy of the fit itself. This calculation was done only for a test sample of four randomly selected fields. Since we did not find any significant difference in the results, correction was not attempted for with the remaining fields.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6.75cm,clip]{6185fig11.eps}\par\includegraphics[width=6.75cm,clip]{6185fig12.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg59.gif) |
Figure 7:
Histograms of the distance modulus for two of the observed fields. Points/solid lines show the histograms derived directly from the data, while dotted/dashed lines show the distributions once corrected for dwarf contamination (using the
predictions of the SKY model). Vertical dashed lines stand for the completeness-induced limits for each field. |
| Open with DEXTER |
López-Corredoira et al. (2002) demonstrated that the effect of
contamination is more severe off the plane, as extinction helps to separate the populations.
The results for off-plane fields show a much better correction of the counts, giving a slightly narrower distribution around the peak.
Although applying this could in theory improve the fit, the effect is small and
introduces another factor based on models, hence we decided not to apply this correction.
5.1 In-plane fields (
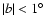 )
)
Results for in-plane fields in the range
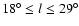 show a narrow distribution of distances from the Sun. This is consistent with a high-density feature seen in the red-clump stars
with position angle 40
show a narrow distribution of distances from the Sun. This is consistent with a high-density feature seen in the red-clump stars
with position angle 40
 5
5  3
3
 9 (after a linear fit through the points)
with respect to the Sun-Galactic Centre direction. First panel in Fig. 8 shows the distribution of red-clump density maxima for a face-on view of the Galaxy, with the
Galactic Centre at (0, 8000 pc). The solid line shows a position angle of 45
9 (after a linear fit through the points)
with respect to the Sun-Galactic Centre direction. First panel in Fig. 8 shows the distribution of red-clump density maxima for a face-on view of the Galaxy, with the
Galactic Centre at (0, 8000 pc). The solid line shows a position angle of 45 (consistent with the 43 degrees given for the bar in Hammersley et al. 2000). The dashed line
shows a position angle of 25
(consistent with the 43 degrees given for the bar in Hammersley et al. 2000). The dashed line
shows a position angle of 25 ,
which is consistent with the results of
Dwek et al. (1995), López-Corredoira et al. (2005), Stanek et al. (1997) and,
more recently, Babusiaux & Gilmore (2005). The range of longitudes covered
in these fields (
,
which is consistent with the results of
Dwek et al. (1995), López-Corredoira et al. (2005), Stanek et al. (1997) and,
more recently, Babusiaux & Gilmore (2005). The range of longitudes covered
in these fields (
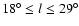 ), however, is very different
from those which obtain the smaller position angle. Only a single point at
), however, is very different
from those which obtain the smaller position angle. Only a single point at
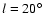 ,
,
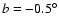 ,
is
observed near the latter position angle. This point
could be due to local highly anomalous extinction (see Sect. 5.3), as this line of sight does run close to
a major star formation region (Garay et al. 1998; Sridharan et al. 2005).
Furthermore, the over-density is is apparently somewhat
inhomogeneous, as was noted by Picaud et al. (2003) at
,
is
observed near the latter position angle. This point
could be due to local highly anomalous extinction (see Sect. 5.3), as this line of sight does run close to
a major star formation region (Garay et al. 1998; Sridharan et al. 2005).
Furthermore, the over-density is is apparently somewhat
inhomogeneous, as was noted by Picaud et al. (2003) at
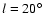 and
and
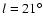 .
.
The gap in the longitude range
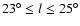 is due to the
very high extinction that
extends up to
is due to the
very high extinction that
extends up to
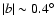 ,
which is noticeable also in the mid-infrared
range (see Fig. 1 of Benjamin et al. 2005). This makes it impossible to obtain
an accurate fit for the fields located in this region. The same problem applies
to the in-plane data for
,
which is noticeable also in the mid-infrared
range (see Fig. 1 of Benjamin et al. 2005). This makes it impossible to obtain
an accurate fit for the fields located in this region. The same problem applies
to the in-plane data for
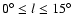 .
In these fields the
completeness limit is far brighter than the apparent magnitude of the K giants for any structure that would be
present, that is significantly fainter than the completeness limit. Hence, the above method cannot be applied.
However, in the CMD the giant branch from the feature is still visible but its distance cannot be measured.
.
In these fields the
completeness limit is far brighter than the apparent magnitude of the K giants for any structure that would be
present, that is significantly fainter than the completeness limit. Hence, the above method cannot be applied.
However, in the CMD the giant branch from the feature is still visible but its distance cannot be measured.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=5.15cm,clip]{6185fig13CMJN.eps}\par\in...
...5CMJN.eps}\par\includegraphics[width=5.15cm,clip]{6185fig16CMJN.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg66.gif) |
Figure 8:
Spatial distribution of red-clump giants maxima in the
XY-plane at different latitude intervals, with the Sun at (0, 0) and the Galactic Center at (0, 8 kpc) marked with a big circle. Two possible configurations for
the observed distribution are also shown: a feature with a position angle of 45 (solid line), and another one with a position angle of 25
(solid line), and another one with a position angle of 25 (dashed line). Dot-dashed lines define two circles with radii 4.5 kpc and 3 kpc, respectively, while different lines of sight
towards the inner Galaxy are also shown in intervals of 10 (dashed line). Dot-dashed lines define two circles with radii 4.5 kpc and 3 kpc, respectively, while different lines of sight
towards the inner Galaxy are also shown in intervals of 10 in longitude. Error bars have been estimated from the distance
uncertainties, assuming these divided equally in both the X- and Y-axes.
in longitude. Error bars have been estimated from the distance
uncertainties, assuming these divided equally in both the X- and Y-axes. |
| Open with DEXTER |
The results for
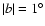 (second panel in Fig. 8) show that there are two distance regimes for the red-clump population, one that follows approximately the
43
(second panel in Fig. 8) show that there are two distance regimes for the red-clump population, one that follows approximately the
43
 4
4  3
3
 5 angle (nine points) and a second with a smaller angle of
21
5 angle (nine points) and a second with a smaller angle of
21
 9
9  1
1
 0 (six points). Most of the points in this latter
feature are at
0 (six points). Most of the points in this latter
feature are at
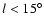 ,
while the points associated with the former are
mostly located at
,
while the points associated with the former are
mostly located at
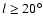 .
Nishiyama et al. (2005) also
observed the red-clump stars at
.
Nishiyama et al. (2005) also
observed the red-clump stars at
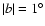 over the range
over the range
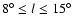 and there is good agreement between
their distribution of red-clump maxima and ours (Fig. 9), even in the central regions of the Galaxy.
and there is good agreement between
their distribution of red-clump maxima and ours (Fig. 9), even in the central regions of the Galaxy.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6.85cm,clip]{6185fig17CMJN.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg70.gif) |
Figure 9:
Spatial distribution of red-clump giants maxima presented face on
for data at
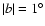 and the results obtained for Nishiyama et al. (2005) for comparison (shown as open circles).
and the results obtained for Nishiyama et al. (2005) for comparison (shown as open circles). |
| Open with DEXTER |
For
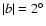 the results are less conclusive (third panel in Fig. 8).
This is because we are not deep enough to be complete in the red-clump giants
in the innermost Galaxy (
the results are less conclusive (third panel in Fig. 8).
This is because we are not deep enough to be complete in the red-clump giants
in the innermost Galaxy (
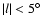 )
and this makes it difficult to observe
the peak in the red-clump counts. Also, for fields
)
and this makes it difficult to observe
the peak in the red-clump counts. Also, for fields
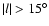 there is no red-clump cluster observed in the modulus distance
histograms, i.e. there is no feature there. Only one point is detected with
there is no red-clump cluster observed in the modulus distance
histograms, i.e. there is no feature there. Only one point is detected with
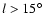 and this has the highest dispersion in distance of any field.
The remainder of the fields lie where there is little difference in
distance between the two position angles, making it difficult
to clearly assign the red-clump density maxima to one of them. A linear fit to
those data yields a global position angle of 36
and this has the highest dispersion in distance of any field.
The remainder of the fields lie where there is little difference in
distance between the two position angles, making it difficult
to clearly assign the red-clump density maxima to one of them. A linear fit to
those data yields a global position angle of 36
 6
6  5
5
 8
(after discarding those at
8
(after discarding those at
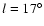 ), although if the points are assigned
to the position angle that runs closer to that position, and are then averaged separately
we obtain position angles of 44
), although if the points are assigned
to the position angle that runs closer to that position, and are then averaged separately
we obtain position angles of 44
 1
1  2
2
 8 and
25
8 and
25
 1
1  2
2
 7, respectively.
7, respectively.
Farther away from the plane (
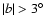 )
it is possible to
sample the innermost Galaxy as the incompleteness effect disappears; however,
there are no observable features in the histograms for
)
it is possible to
sample the innermost Galaxy as the incompleteness effect disappears; however,
there are no observable features in the histograms for 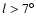 as
the disc component dominates and there is no dense structure at a specific distance.
The distribution of red-clump peaks
shows in this case a position angle of 30
as
the disc component dominates and there is no dense structure at a specific distance.
The distribution of red-clump peaks
shows in this case a position angle of 30
 7
7  5
5
 2 with
respect to the Sun-Galactic Centre line (lower panel in Fig. 8).
These results are compatible
with the position angle of 29
2 with
respect to the Sun-Galactic Centre line (lower panel in Fig. 8).
These results are compatible
with the position angle of 29
 8
8 derived in
López-Corredoira et al. (2005) for the bulge of the Milky Way
using 2MASS data. Also, this result is consistent with the position angle of
22
derived in
López-Corredoira et al. (2005) for the bulge of the Milky Way
using 2MASS data. Also, this result is consistent with the position angle of
22
 5
5
 5 recently derived
by Babusiaux & Gilmore analysing their private in-plane data at
5 recently derived
by Babusiaux & Gilmore analysing their private in-plane data at
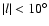 .
.
Table 2:
Fitted position angles and mean dispersion in distances for
the different latitude ranges.
5.3 The effect of extinction on the results
A global extinction law is assumed when deriving the reddening-independent
magnitudes. However, recent
results show that there are noticeable differences in the
extinction law derived in different directions towards the inner Galaxy
(Nishiyama et al. 2006a) and even very small variations in the ratio of
total to selective extinction are present on very small scales (Gosling
et al. 2006), so care must be taken when applying reddening
corrections. The combination of this plus the possible mixture of
sources coming from the two position angles would broaden
in the distance histograms, hence giving a higher dispersion in
distances, 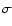 .
.
To examine this effect, we have calculated the
mean dispersion in distances in the four latitude ranges showed in Fig. 8 (Table 2). There is clearly less
dispersion at
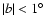 and at
and at
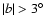 than at
intermediate latitudes, where the mixture of sources becomes more
important (error bars shown in Table 2 account only for the
standard deviation of values). The mean values all cluster around 0.5 kpc,
but again, with slightly
larger values at
than at
intermediate latitudes, where the mixture of sources becomes more
important (error bars shown in Table 2 account only for the
standard deviation of values). The mean values all cluster around 0.5 kpc,
but again, with slightly
larger values at
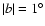 and
and
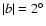 .
Hence, if we consider the results only for those fields that present
.
Hence, if we consider the results only for those fields that present
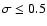 kpc we obtain the red-clump peak
distributions shown in Fig. 10.
kpc we obtain the red-clump peak
distributions shown in Fig. 10.
It is noticeable that in all the cases those points that were
originally located at positions intermediate between the two position angles
have been removed. Furthermore, only one point has disappeared from the fields at
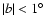 and
and
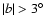 as a reflection of the lower dispersion values obtained in those latitude
ranges. The point removed is that noted in Sect. 5.1 at
as a reflection of the lower dispersion values obtained in those latitude
ranges. The point removed is that noted in Sect. 5.1 at
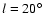 ,
,
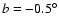 suggesting that extinction is
responsible for its discrepant location.
suggesting that extinction is
responsible for its discrepant location.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=5.25cm,clip]{6185fig18CMJN.eps}\par\in...
...5fig20CMJN.eps}\par\includegraphics[width=5.25cm,clip]{6185fig21.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg84.gif) |
Figure 10:
Same as in Fig. 8, but considering only those fields
where dispersion in distances is less than 0.5 kpc. |
| Open with DEXTER |
The above shows that:
The position angles are derived by a weighted mean of the values summarized in
Table 2 for both features.
Sevenster et al. (1999) found a similar effect when comparing N-body models with their
sample of OH/IR stars and noted that the position angle changed from 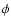 = 44
= 44 when
using in-plane fields to
when
using in-plane fields to 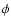 = 25
= 25 when only high latitude
fields were considered. They also noted in the literature that lower values for the viewing angles determined from stellar data
were found when low-latitude fields were excluded from
the fit, which is in agreement with the work presented here.
when only high latitude
fields were considered. They also noted in the literature that lower values for the viewing angles determined from stellar data
were found when low-latitude fields were excluded from
the fit, which is in agreement with the work presented here.
The feature seen on the plane
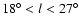 in the red-clump stars can have
no direct link with the Scutum spiral arm. The tangential point to the stars in this arm is at
in the red-clump stars can have
no direct link with the Scutum spiral arm. The tangential point to the stars in this arm is at
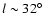 ,
and it would be expected that any features associated with an arm would be strongest there.
However, there is no red-clump cluster seen at that location
(Hammersley et al. 2000), and inwards of the this point the effect of the arm would
become less (Hammersley et al. 1994). Furthermore, a spiral arm would not form a feature that appeared to run directly towards the Galactic Centre.
,
and it would be expected that any features associated with an arm would be strongest there.
However, there is no red-clump cluster seen at that location
(Hammersley et al. 2000), and inwards of the this point the effect of the arm would
become less (Hammersley et al. 1994). Furthermore, a spiral arm would not form a feature that appeared to run directly towards the Galactic Centre.
Extinction can also be discounted. There are a range of extinctions covered
between 18
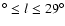 and in no field is the extinction less
than is predicted by the simple extinction model used in Wainscoat et al. (1992). In any case,
the method used corrects for extinction. Furthermore, our result is in extremely
good agreement with the result of Benjamin et al. (2005) (see Fig. 11), where the effects of extinction are significantly reduced. Also, in Fig. 11
we show how the concentration of data
seen at
and in no field is the extinction less
than is predicted by the simple extinction model used in Wainscoat et al. (1992). In any case,
the method used corrects for extinction. Furthermore, our result is in extremely
good agreement with the result of Benjamin et al. (2005) (see Fig. 11), where the effects of extinction are significantly reduced. Also, in Fig. 11
we show how the concentration of data
seen at
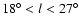 is not an isolated
feature, and how it is consistent with other estimates for this
structure obtained with
deeper data than ours in different lines of sight to
the inner Galaxy. In fact, it is
clear that this feature runs to the inner Galaxy, at least up to 1.5-2 kpc from the
Galactic Centre, where it merges with the bulge.
is not an isolated
feature, and how it is consistent with other estimates for this
structure obtained with
deeper data than ours in different lines of sight to
the inner Galaxy. In fact, it is
clear that this feature runs to the inner Galaxy, at least up to 1.5-2 kpc from the
Galactic Centre, where it merges with the bulge.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6.2cm,clip]{6185fig22.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg93.gif) |
Figure 11:
Spatial distribution of red-clump giants maxima for in-plane fields in the XY-plane, with some of the more recent estimates for this feature (H00: Hammersley et al. 2000; P03: Picaud et al. 2003; B05: Benjamin et al. 2005). Note there is an excellent agreement between the different sets of data. The long bar with a position angle of 43
 0 derived in this work is
represented by a solid line (and a width of 1 kpc is represented by dashed lines). 0 derived in this work is
represented by a solid line (and a width of 1 kpc is represented by dashed lines). |
| Open with DEXTER |
The only scenario that readily fits the star count data and CMDs, those presented both here and elsewhere, is that of a triaxial bulge plus a long bar. The bulge has a position angle of about 25 and dominates the counts to
and dominates the counts to
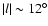 and up to
and up to
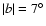 or farther off the plane. The in-plane bar has a position angle of 43
or farther off the plane. The in-plane bar has a position angle of 43 with a half-length of some 4 kpc but is only detected close to the plane. This bulge + bar picture is not so unreasonable.
Recent N-body simulations on the secular evolution of disc galaxies predict that in
a bar-driven evolution, the bar has a thick inner part of shorter extent and a thin outer
part of larger extent (Athanassoula 2006), a fact that is in good
agreement with observations (Athanassoula 2005; Bureau et al. 2006). Also,
the ratio of the thin bar
size to the inner bulge length that is derived from our data (between 2.2-2.8 assuming a bulge length of 1.5-2 kpc) is in completely agreement with that was
observed in external galaxies (2.7
with a half-length of some 4 kpc but is only detected close to the plane. This bulge + bar picture is not so unreasonable.
Recent N-body simulations on the secular evolution of disc galaxies predict that in
a bar-driven evolution, the bar has a thick inner part of shorter extent and a thin outer
part of larger extent (Athanassoula 2006), a fact that is in good
agreement with observations (Athanassoula 2005; Bureau et al. 2006). Also,
the ratio of the thin bar
size to the inner bulge length that is derived from our data (between 2.2-2.8 assuming a bulge length of 1.5-2 kpc) is in completely agreement with that was
observed in external galaxies (2.7  0.3, L
0.3, L
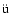 tticke et al. 2000).
tticke et al. 2000).
In order to illustrate this, Fig. 12 shows the results from Babusiaux & Gilmore (2005; hereafter BG05). Also shown on the plot are the results from this work and position angles of 45 and 25
and 25 degrees.
The BG05 data set is deeper than ours (as a result of a pixel scale five times smaller),
permitting them to reach the inner Galaxy with in-plane data. It is noticeable that the BG05 points at
degrees.
The BG05 data set is deeper than ours (as a result of a pixel scale five times smaller),
permitting them to reach the inner Galaxy with in-plane data. It is noticeable that the BG05 points at
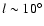 and
and
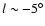 coincide with positions for the triaxial bulge obtained here; however, the point
at
coincide with positions for the triaxial bulge obtained here; however, the point
at
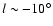 lies on the 45
lies on the 45 position angle and is well away from the position required for the triaxial bulge.
position angle and is well away from the position required for the triaxial bulge.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6.6cm,clip]{6185fig23.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg100.gif) |
Figure 12:
Distribution of positions for the red-clump sources obtained in
this work at
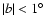 and
and
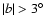 compared with the
results of Babusiaux & Gilmore (2005) by using in-plane NIR data.
Dot dashed lines delimite circles with radii 4.3 kpc, 3 kpc and
2 kpc, respectively.
compared with the
results of Babusiaux & Gilmore (2005) by using in-plane NIR data.
Dot dashed lines delimite circles with radii 4.3 kpc, 3 kpc and
2 kpc, respectively. |
| Open with DEXTER |
From the histograms of the red-clump sources an estimate can be made of the mean scale height
of the sources associated with the long thin bar. We have used only those
fields with
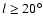 and
and
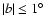 ,
as
at
,
as
at 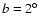 there are not sufficient bar sources for a reliable extraction.
For each field the space densities along different lines of sight were determined by selecting the stars within one
there are not sufficient bar sources for a reliable extraction.
For each field the space densities along different lines of sight were determined by selecting the stars within one 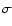 of the maximum of the histograms of the distance modulus (see Table 1). Combining the distances along the line of sight
to the features (d) and the Galactic coordinates of the fields (l,b) allows these space densities to be expressed with
respect to the galactocentric distance (R) and the height (z) above the plane, taking into
account the location of the Sun 15 pc above the mean plane (Hammersley et al. 1995).
The result is shown in Fig. 13. It can be observed that the mid-point of the distribution is at z=-41 pc. Hence, we have
represented in Fig. 14 the space density with respect to a vertical distance to the
plane z*, defined as
z*=|z+41|. This means that the location of this hypothetical long thin bar is
of the maximum of the histograms of the distance modulus (see Table 1). Combining the distances along the line of sight
to the features (d) and the Galactic coordinates of the fields (l,b) allows these space densities to be expressed with
respect to the galactocentric distance (R) and the height (z) above the plane, taking into
account the location of the Sun 15 pc above the mean plane (Hammersley et al. 1995).
The result is shown in Fig. 13. It can be observed that the mid-point of the distribution is at z=-41 pc. Hence, we have
represented in Fig. 14 the space density with respect to a vertical distance to the
plane z*, defined as
z*=|z+41|. This means that the location of this hypothetical long thin bar is 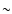
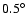 tilted with respect to the mean plane, a result that is compatible
with the values found in Picaud & Robin (2004) for the orientation of the outer bulge.
tilted with respect to the mean plane, a result that is compatible
with the values found in Picaud & Robin (2004) for the orientation of the outer bulge.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,clip]{6185fig24.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg104.gif) |
Figure 13:
Variation of the space density as a function of distance from the Galactic plane. For
comparison, the best fit of an exponential law (solid line) and a sech2 law (dashed line) are shown. |
| Open with DEXTER |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,clip]{6185fig25.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg105.gif) |
Figure 14:
Vertical dependence of the density of bar stars. The best exponential fit, with a scale
height of 99.28  3.13 pc, is also shown as a solid line.
3.13 pc, is also shown as a solid line. |
| Open with DEXTER |
We have also tested a sech2 profile to compare with the observed space density for a simple exponential. The two equations used are:
where hz is the scale height of the bar sources and 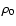 is the space density in the Galactic plane. The exponential gives hz = 99.3
is the space density in the Galactic plane. The exponential gives hz = 99.3  3.1 pc and
3.1 pc and 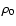 = 0.022
= 0.022  0.014 pc-3, whereas the sech2 profile yields hz = 105.4
0.014 pc-3, whereas the sech2 profile yields hz = 105.4  5.3 pc and
5.3 pc and
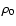 = 0.018
= 0.018  0.013 pc-3. Both fits are shown in Fig. 13.
0.013 pc-3. Both fits are shown in Fig. 13.
An exponential scale height for the bar of around 100 pc is a factor 2 higher than that previously
obtained by López-Corredoira et al. (2001) or Hammersley et al. (1995) from NIR star counts.
However, it should be noted that here we are looking at a very different star type than in the previous studies. In both of those cases the stars observed were considerably more luminous, and spectra of a selection of these sources (Garzón et al. 1997)
showed that there were a large number of young sources at
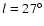 and
and
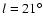 .
The red-clump sources observed here probably represent
an older population and hence the larger scale height would be expected. However, the scale height for the red-clump stars in other
Galactic components is far higher. For the thin disc it is
.
The red-clump sources observed here probably represent
an older population and hence the larger scale height would be expected. However, the scale height for the red-clump stars in other
Galactic components is far higher. For the thin disc it is 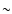 260 pc (Cabrera-Lavers et al. 2005) and applying the same method used above to the
bulge for the fields at
260 pc (Cabrera-Lavers et al. 2005) and applying the same method used above to the
bulge for the fields at
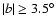 gives a scale height of
hz=488
gives a scale height of
hz=488  28 pc (see Fig. 15). Hence the scale height is a further clear indication that on the plane between
28 pc (see Fig. 15). Hence the scale height is a further clear indication that on the plane between
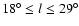 there is a geometric component that is very different to the bulge or thin disc.
there is a geometric component that is very different to the bulge or thin disc.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,clip]{6185fig26.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg108.gif) |
Figure 15:
Vertical dependence of the density of inner bulge stars. The best exponential fit shown as a solid line now has a scale height 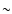 5 times higher than that of the thin bar. 5 times higher than that of the thin bar. |
| Open with DEXTER |
The distances to the red-clump population were obtained by fitting Eq. (2) to the
distance modulus histograms. However, the maximum of star counts vs. magnitude is not strictly coincident with the maximum in density along the line of sight, which is proportional to the
first multiplied by a factor 1/d3. Hence the magnitude histogram counts, N(m), should be transformed into density along the line of sight, 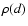 ,
and Eq. (2) then fitted to the resultant distribution. From the relationship between
,
and Eq. (2) then fitted to the resultant distribution. From the relationship between 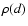 and N(m) it can be shown that the difference between the corrected distance to the maximum in the density distribution (
and N(m) it can be shown that the difference between the corrected distance to the maximum in the density distribution (
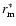 )
and the distance obtained to the maximum in the counts histograms (
)
and the distance obtained to the maximum in the counts histograms (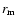 )
is:
)
is:
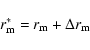 |
(8) |
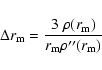 |
(9) |
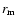 being the distance to the maximum in the N(m) histogram (hence,
being the distance to the maximum in the N(m) histogram (hence,
![$N'(m[r_{\rm m}])=0$](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/img114.gif) )
and
)
and
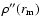 the second derivative of
the second derivative of 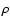 with
respect to the distance, measured at
with
respect to the distance, measured at 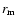 .
As
.
As
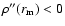 ,
then
,
then
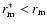 ,
thus the corrected distances are
slightly lower than those obtained from the maximum of the magnitude histograms.
,
thus the corrected distances are
slightly lower than those obtained from the maximum of the magnitude histograms.
This effect is more noticeable for the bulge component than for the long thin bar, as
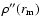 is very large for this latter. We have estimated the range of values for
is very large for this latter. We have estimated the range of values for
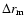 for the bulge and for the long bar, obtaining the true density distributions
along the line of sight. We have used those fields with
for the bulge and for the long bar, obtaining the true density distributions
along the line of sight. We have used those fields with
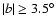 as representative of the bulge, while those in-plane fields with
as representative of the bulge, while those in-plane fields with
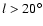 are representative of
the long bar. It is found that
are representative of
the long bar. It is found that
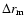 is in the range 100-300 pc in bulge fields, whereas for long bar fields the effect
is far smaller, in the order of 25-50 pc. Figure 16 shows two examples of the change in the overall shape of the density distribution compared to the number count histograms used to derive the distances to the red-clump population.
The effect on the determined geometries for either the bulge and the long bar is not large in either case. For the long bar it is ten times lower than the
uncertainties in the fit itself (see Table 1) and even for the bulge it is only about 50% of the uncertainty in the fit.
is in the range 100-300 pc in bulge fields, whereas for long bar fields the effect
is far smaller, in the order of 25-50 pc. Figure 16 shows two examples of the change in the overall shape of the density distribution compared to the number count histograms used to derive the distances to the red-clump population.
The effect on the determined geometries for either the bulge and the long bar is not large in either case. For the long bar it is ten times lower than the
uncertainties in the fit itself (see Table 1) and even for the bulge it is only about 50% of the uncertainty in the fit.
The position of the maximum density
along the line of sight is not coincident with the
the position of the major axis of a triaxial structure unless
the structure is very thin along the line of sight (a bar). There are two effects:
- The more important one
is that the density along the line of sight reaches a maximum at the tangential
point of the innermost ellipsoid along it and this is not in general
on the major axis (see Fig. 17).
- For off-plane regions, the lines of sight are not parallel to the
 and so the larger the distance the greater the height above the plane, and hence the lower the density. Therefore, the maximum density along the line of sight is
closer than the real maximum in a plane parallel to
and so the larger the distance the greater the height above the plane, and hence the lower the density. Therefore, the maximum density along the line of sight is
closer than the real maximum in a plane parallel to  .
.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6.85cm,clip]{6185fig27.ps}\par\includegraphics[width=6.85cm,clip]{6185fig28.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg122.gif) |
Figure 16:
Comparison between the density (solid line) and the number count (dashed line) distributions with respect to the distance along the
line of sight for long bar (above) and bulge (below) fields as examples. Density distributions are arbitrarily displaced along the Y-axis in order to
make both distributions comparable. |
| Open with DEXTER |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=3.6cm,clip]{6185fig29.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg123.gif) |
Figure 17:
Schematic representation of the difference between the
maximum density position along the line of sight (filled square) for
triaxial ellipsoids and the intersection of their major axis with the line of
sight (filled circle). |
| Open with DEXTER |
We can derive analytically the difference (
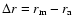 )
between the
maximum density position along the line of sight (
)
between the
maximum density position along the line of sight (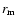 )
and the
intersection of the line of sight with the major axis (
)
and the
intersection of the line of sight with the major axis (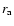 )
for a triaxial structure with monotonically density decreasing outwards.
The isodensity contours are defined by the points in space
with the same value of t:
)
for a triaxial structure with monotonically density decreasing outwards.
The isodensity contours are defined by the points in space
with the same value of t:
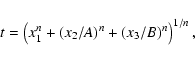 |
(10) |
that in the n=2 case corresponds to isodensity ellipsoids. A and B are the axial ratios of the second and the third axes with respect to the major axis of the ellipsoids,
and xi are the Cartesian coordinates with the axis of the ellipsoids
concentric with the centre of the Galaxy (see Fig. 17). We assume that the minor axis is perpendicular to the Galactic plane (x3=z). x, y, z are the Cartesian coordinates with XY defining the plane of the Galaxy with the
y-axis in the Sun-Galactic Centre line and 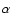 is the angle between
the major axis of the ellipsoid and this y-axis (Fig. 17).
is the angle between
the major axis of the ellipsoid and this y-axis (Fig. 17).
The tangential point of the line of sight with the maximum density (filled square in Fig. 17), follows:
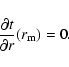 |
(11) |
Equation (11), together with Eq. (10), lead to
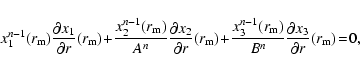 |
(12) |
which finally lead to
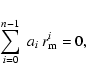 |
(13) |
where
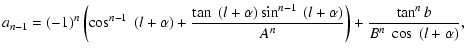 |
|
|
(14) |
and
while the position of the major axis (simple geometry with the application
of the sine rule, see Fig. 17) is
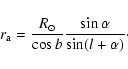 |
(16) |
In the simplest case, for n=2, Eq. (13) yields
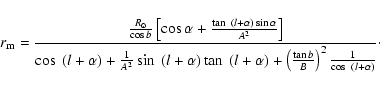 |
(17) |
Both of the expressions for 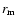 and
and 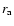 are coincident for
are coincident for 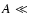 (very
elongated ellipsoids) and
(very
elongated ellipsoids) and 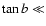 (in the plane), but other cases
are affected by a significant systematic error
(in the plane), but other cases
are affected by a significant systematic error 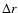 .
Two triaxial structures were examined in order to estimate this effect:
.
Two triaxial structures were examined in order to estimate this effect:
- A=0.5, B=0.4,
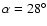 ,
typical of the bulge
(López-Corredoira et al. 2005): Fig. 18;
,
typical of the bulge
(López-Corredoira et al. 2005): Fig. 18;
- A=0.11, B=0.04,
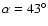 ,
typical of a long bar:
Fig. 19. The low depth in the line of sight of the bar (around 1 kpc)
is justifiable because of the low dispersion of the red-clump
giants.
,
typical of a long bar:
Fig. 19. The low depth in the line of sight of the bar (around 1 kpc)
is justifiable because of the low dispersion of the red-clump
giants.
The result is that 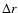 is negligible for the bar,
with less than
is negligible for the bar,
with less than 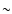 150 pc of systematic error; however, it is not negligible
for the bulge, which reaches a discrepancy of up to 1000 pc.
150 pc of systematic error; however, it is not negligible
for the bulge, which reaches a discrepancy of up to 1000 pc.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.4cm,clip]{6185fig30.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg142.gif) |
Figure 18:
Difference between the maximum density position along the line of sight for triaxial
ellipsoids of axial ratios 1:0.5:0.4, oriented with respect to the Sun-Galactic
Centre at an angle of 28 (expected for the thick bulge)
and the intersection of their major axes with the line of sight.
(expected for the thick bulge)
and the intersection of their major axes with the line of sight. |
| Open with DEXTER |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.55cm,clip]{6185fig31.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg143.gif) |
Figure 19:
Difference between the maximum density position along the line of sight for triaxial
ellipsoids of axial ratios 1:0.11:0.04, orientated with respect to the Sun-Galactic
Centre line at an angle of 43 (expected for the long bar) and the intersection of
their major axes with the line of sight.
(expected for the long bar) and the intersection of
their major axes with the line of sight. |
| Open with DEXTER |
To avoid this effect in deriving the real parameters of the bulge we performed a chi-squared fit
to the observed distances of the red-clump density
maxima by means of Eq. (17), which contains only three free parameters (A, B and  ). We have selected only those points at
). We have selected only those points at
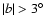 ,
as they are more representative of this component. For each set of model parameters we calculate
,
as they are more representative of this component. For each set of model parameters we calculate
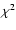 .
Once this was calculated for all sets in the parameter space, we select that one
which gives a minimum
.
Once this was calculated for all sets in the parameter space, we select that one
which gives a minimum 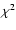 .
Again, for n=2 the values which give the minimum
.
Again, for n=2 the values which give the minimum 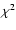 are:
are:
The result for 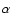 is notably smaller than that directly derived from the fit to the red-clump density peak, but it is consistent with other estimates found in previous works (Freudenreich 1998; Lépine & Leroy 2000; Picaud & Robin 2004). The axial ratios
of the bulge are more or less coincident with those
considered in López-Corredoira et al. (2005) and others (e.g. Stanek et al. 1997; Bissantz & Gerhard 2002; Picaud & Robin 2004). It should be noted, however, that Eq. (17) is valid only for a series of triaxial ellipsoids,
and so will not be correct if the bulge has a different geometry. However, when we use the general formula given by Eq. (13) the
results do not change noticeably (see Table 3), all of them being
compatible with a structure with a position angle of 10-15
is notably smaller than that directly derived from the fit to the red-clump density peak, but it is consistent with other estimates found in previous works (Freudenreich 1998; Lépine & Leroy 2000; Picaud & Robin 2004). The axial ratios
of the bulge are more or less coincident with those
considered in López-Corredoira et al. (2005) and others (e.g. Stanek et al. 1997; Bissantz & Gerhard 2002; Picaud & Robin 2004). It should be noted, however, that Eq. (17) is valid only for a series of triaxial ellipsoids,
and so will not be correct if the bulge has a different geometry. However, when we use the general formula given by Eq. (13) the
results do not change noticeably (see Table 3), all of them being
compatible with a structure with a position angle of 10-15 (with a weighted mean of 12
(with a weighted mean of 12
 6
6  3
3
 2).
2).
Table 3:
Parameters derived for different assumed bulge geometries.
In summary, the position angle we have derived in this work for the bulge (23
 1
1  0
0
 9) by using the distribution of red-clump density maxima might be overestimating the real position angle by around 8-10
9) by using the distribution of red-clump density maxima might be overestimating the real position angle by around 8-10 .
So
the real position angle of the
inner bulge is around 13-15
.
So
the real position angle of the
inner bulge is around 13-15 with respect to the Sun-Galactic Centre line (nearly coincident with the value of 12
with respect to the Sun-Galactic Centre line (nearly coincident with the value of 12
 6
6  3
3
 2
obtained via chi-squared fitting). In the case of the long thin bar, the effect analysed
in this section is less significant and so do not alter the geometry of this component.
2
obtained via chi-squared fitting). In the case of the long thin bar, the effect analysed
in this section is less significant and so do not alter the geometry of this component.
The 2MASS survey (Skrustkie et al. 2006) provides a complete coverage of the
Galactic Plane in the
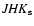 .
Unfortunately, the 2MASS data
are not deep enough to reach the red-clump stars in the
inner Galaxy, hence the 2MASS data cannot be analysed using the above method.
However, the 2MASS star counts can be
useful to confirm the proposed morphologies in the inner
Galaxy, as they are a powerful tool when searching for asymmetries in
the stellar distribution. While the bulge
is observed in off-plane regions up to
.
Unfortunately, the 2MASS data
are not deep enough to reach the red-clump stars in the
inner Galaxy, hence the 2MASS data cannot be analysed using the above method.
However, the 2MASS star counts can be
useful to confirm the proposed morphologies in the inner
Galaxy, as they are a powerful tool when searching for asymmetries in
the stellar distribution. While the bulge
is observed in off-plane regions up to
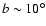 and at
and at
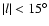 ,
the long bar is visible only in the
in-plane regions,
,
the long bar is visible only in the
in-plane regions,
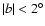 and up to
and up to
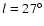 at positive
longitudes and but only to
at positive
longitudes and but only to
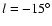 at negative longitudes (from the length and position angle). For this study, counts up to mK = 9 mag will be used as this gives a high inner Galaxy-to-disc contrast (Garzón et al. 1993)
whilst still providing sufficient sources to give good statistics. A similar analysis was performed in López-Corredoira et al. (2001) with the combination of DENIS (Epchtein et al. 1997)
and TMGS (Garzón et al. 1993) K-band counts. The advantage of using 2MASS is that it covers the whole region homogeneously and so makes testing the model simpler.
at negative longitudes (from the length and position angle). For this study, counts up to mK = 9 mag will be used as this gives a high inner Galaxy-to-disc contrast (Garzón et al. 1993)
whilst still providing sufficient sources to give good statistics. A similar analysis was performed in López-Corredoira et al. (2001) with the combination of DENIS (Epchtein et al. 1997)
and TMGS (Garzón et al. 1993) K-band counts. The advantage of using 2MASS is that it covers the whole region homogeneously and so makes testing the model simpler.
Figure 20 shows the 2MASS star counts with mK < 9 mag (averaged over
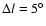 )
at three different latitude slices:
)
at three different latitude slices:
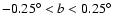 ,
,
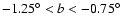 and
and
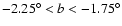 .
At the distance of the Galactic Centre (7.9 kpc), the heights above the Galactic plane are 0 pc, -140 pc and -280 pc respectively.
.
At the distance of the Galactic Centre (7.9 kpc), the heights above the Galactic plane are 0 pc, -140 pc and -280 pc respectively.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6.45cm,clip]{6185fig32.ps}\par\include...
...{6185fig33.ps}\par\includegraphics[width=6.45cm,clip]{6185fig34.ps} \end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg156.gif) |
Figure 20:
2MASS star counts with mK < 9 mag in three different latitude
ranges. Counts have been averaged over
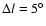 to obtain
a large number stars in each region, in this way minimizing the
Poissonian error.
to obtain
a large number stars in each region, in this way minimizing the
Poissonian error. |
| Open with DEXTER |
At 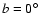 there is a large-scale asymmetry about
there is a large-scale asymmetry about 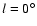 with far more counts at positive
longitudes than at negative longitudes. Farther from the plane
young inner Galaxy features with very small scale heights should not be significant and the effect of extinction is reduced. Hence, although the contrast with the disc is reduced there should still be sufficient bar counts to see something and
the accuracy of model should be massively improved as it cannot deal with the patchy extinction on the plane. In López-Corredoira et al. (2001) it was shown that inner
Galactic star counts are more or less symmetric in latitude, with small
differences attributed to the Sun being about 15 pc above the Galactic plane
(Hammersley et al. 1995) and differences in the extinction above and
below the plane. Here, we concentrate our analysis only
on those slices at negative latitudes and we assume that the structure of the inner
Galaxy is more or less symmetric about the Galactic plane.
with far more counts at positive
longitudes than at negative longitudes. Farther from the plane
young inner Galaxy features with very small scale heights should not be significant and the effect of extinction is reduced. Hence, although the contrast with the disc is reduced there should still be sufficient bar counts to see something and
the accuracy of model should be massively improved as it cannot deal with the patchy extinction on the plane. In López-Corredoira et al. (2001) it was shown that inner
Galactic star counts are more or less symmetric in latitude, with small
differences attributed to the Sun being about 15 pc above the Galactic plane
(Hammersley et al. 1995) and differences in the extinction above and
below the plane. Here, we concentrate our analysis only
on those slices at negative latitudes and we assume that the structure of the inner
Galaxy is more or less symmetric about the Galactic plane.
We have constructed a very simple Galactic model that includes the
contributions of the Galactic disc, a bulge, and a long thin bar to
reproduce the 2MASS counts at
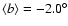 .
For the Galactic disc we have used the luminosity function of Eaton et al. (1984) and an exponential density for the outer Galaxy
with a scale height of 285 pc and a scale length of 2.1 kpc (López-Corredoira et al. 2002).
The inner 4 kpc of the disc, however, has a constant density (López-Corredoira et al. 2004). It has has been shown that continuing the exponential disc to the Galactic Centre leads to a significant overestimation of the K-band star counts (López-Corredoira et al. 2001; Benjamin et al. 2005). This result is consistent with
the disc being a Freeman type II disc, which are common in galaxies with long bars.
The triaxial bulge has ratios 1:0.5:0.4 and a position angle of the major axis with respect to the
Sun-Galactic Centre line of 27
.
For the Galactic disc we have used the luminosity function of Eaton et al. (1984) and an exponential density for the outer Galaxy
with a scale height of 285 pc and a scale length of 2.1 kpc (López-Corredoira et al. 2002).
The inner 4 kpc of the disc, however, has a constant density (López-Corredoira et al. 2004). It has has been shown that continuing the exponential disc to the Galactic Centre leads to a significant overestimation of the K-band star counts (López-Corredoira et al. 2001; Benjamin et al. 2005). This result is consistent with
the disc being a Freeman type II disc, which are common in galaxies with long bars.
The triaxial bulge has ratios 1:0.5:0.4 and a position angle of the major axis with respect to the
Sun-Galactic Centre line of 27 (López-Corredoira et al.
2005). The bulge luminosity function and density law
have been also taken from this work. Finally, a simple bar model in
agreement with Hammersley et al. (2000) was added. The bar has a depth along the line of sight
of 500 pc, a half-length of 4 kpc and a position angle of 43
(López-Corredoira et al.
2005). The bulge luminosity function and density law
have been also taken from this work. Finally, a simple bar model in
agreement with Hammersley et al. (2000) was added. The bar has a depth along the line of sight
of 500 pc, a half-length of 4 kpc and a position angle of 43 .
The distribution was assumed to be constant along the bar, but
exponential in height above the plane and the luminosity function used
was the same as for the disc although the density was then normalized
to make the total counts match those at
.
The distribution was assumed to be constant along the bar, but
exponential in height above the plane and the luminosity function used
was the same as for the disc although the density was then normalized
to make the total counts match those at
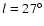 .
In all the cases,
the extinction model used is as described in Wainscoat et al. (1992).
.
In all the cases,
the extinction model used is as described in Wainscoat et al. (1992).
Whilst the model is simple, it can be shown from Fig. 21 that
it does reproduce the counts fairly well at
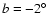 .
The model predicts:
.
The model predicts:
- The increasing counts with decreasing longitudes for
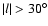 due to the exponential disc.
due to the exponential disc.
- The sharp jump in the counts at
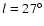 due to the bar.
due to the bar.
- The basically flat region between
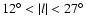 due to exponential disc not continuing into the centre and the bar.
due to exponential disc not continuing into the centre and the bar.
- The steep rise inwards of
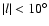 as the bulge dominates. The bar/bulge ratio in
this region is below 0.025.
as the bulge dominates. The bar/bulge ratio in
this region is below 0.025.
There are, however, some other features not
well predicted by the simple model. As no ring was included in the model there are excess counts
for the region
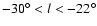 .
Sevenster et al. (1999) also observed an excess of OH/IR stars at
.
Sevenster et al. (1999) also observed an excess of OH/IR stars at
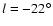 .
The possible implications for an elliptical ring are described in Sect. 6.1 of López-Corredoira et al. (2001) but are beyond the scope of this paper, so will not be repeated here. Similarly, the model does not include the Scutum
spiral arm so near the tangential point (
.
The possible implications for an elliptical ring are described in Sect. 6.1 of López-Corredoira et al. (2001) but are beyond the scope of this paper, so will not be repeated here. Similarly, the model does not include the Scutum
spiral arm so near the tangential point (
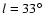 )
there could also be problems.
A fuller analysis of the inner Galactic star counts can be found
in López-Corredoira et al. (2001; Sect. 3). Here, we are only interested in testing the plausibility of the bulge + thin bar scenario when reproducing the observed counts.
)
there could also be problems.
A fuller analysis of the inner Galactic star counts can be found
in López-Corredoira et al. (2001; Sect. 3). Here, we are only interested in testing the plausibility of the bulge + thin bar scenario when reproducing the observed counts.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.6cm,clip]{6185fig35.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg165.gif) |
Figure 21:
2MASS star counts to K<9 mag and the predictions of a model
that includes the contribution of disc (solid line), bulge (dot-dashed
line) and a long thin bar (dashed line). The sum of all the components
(strong solid line) reproduces the observed counts very accurately. |
| Open with DEXTER |
It is, however, clear from the above that a disc + thin bar + triaxial bulge can
account for the a large part of the observedcounts, in particular all of the large-scale Galactic features. Were the bar not to be included, the
fit would not be as good; in particular the asymmetry in longitude would not be reproduced.
By analysing the distribution of red-clump sources along different lines of sight towards the inner Galaxy, we have demonstrated that the Milky Way has two different structures coexisting in the inner R < 5 kpc: a long thin bar with a half length of 4 kpc constrained to the plane and a position angle of 43 ,
and a thicker bulge with a position angle of 13-15
,
and a thicker bulge with a position angle of 13-15 .
.
In the TCS-CAIN data, each structure dominates at different ranges of longitude and latitude.
At
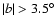 ,
,
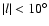 the bulge is the only component
that is observed whereas at
the bulge is the only component
that is observed whereas at
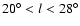 and
and
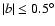 the long thin bar dominates. The scale heights of these structures are also very different. The red-clump giants of long-bar sources have a scale height of
the long thin bar dominates. The scale heights of these structures are also very different. The red-clump giants of long-bar sources have a scale height of  100 pc,
whereas the disc is over 2.6 times this thick and the bulge sources
have a scale height
100 pc,
whereas the disc is over 2.6 times this thick and the bulge sources
have a scale height  5 times larger still. Hence the long bar is geometrically a different structure to the triaxial bulge or disc,
although this does not necessarily mean that they are not related.
5 times larger still. Hence the long bar is geometrically a different structure to the triaxial bulge or disc,
although this does not necessarily mean that they are not related.
We have also checked how there are some systematic uncertainties in deriving distances from the red-clump population peaks that have not been taken into account in other
similar analyses (e.g. Stanek et al. 1994, 1997; Nishiyama et al. 2005; Babusiaux & Gilmore 2005).
Those uncertainties make the position angles
derived in those works around 10 larger than the real ones.
larger than the real ones.
We have shown that the large-scale 2MASS star counts in the inner Galaxy can be accurately described by a combination of a triaxial bulge, a bar and a disc. Hence, discussion as to the angle of the bar should be separated into two separate discussions: the form of the triaxial bulge and the form of the long bar.
Acknowledgements
This publication makes use of data products from TCS-CAIN (based on observations made at Carlos Sánchez Telescope operated
by the IAC at Teide Observatory on the island of Tenerife) and 2MASS (which is
a joint project of the University of Massachusetts and the Infrared Processing
and Analysis Center (IPAC), funded by NASA and the NSF).
- Alard, C. 2001,
A&A, 379, L44 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] (In the text)
- Alves, D. R. 2000, ApJ,
539, 732 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Athanassoula, E. 2005,
MNRAS, 358, 1477 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Athanassoula, E. 2006
[arXiv:astro-ph/0610113]
(In the text)
- Athanassoula, E.,
& Beaton, R. L. 2006, MNRAS, 693
(In the text)
- Beaton, R. L.,
Athanassoula, E., Majewski, S. R., et al. 2005, BAAS, 37, 1387 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Benjamin, R. A.,
Churchwell, E., Babler, B. L., et al. 2005, ApJ, 630, L149 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Blitz, L., &
Spergel, D. N. 1991, ApJ, 379, 631 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Binney, J., Gerhard, O.
E., & Spergel, D. 1997, MNRAS, 288, 365 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Bissantz, N., &
Gerhard, O. E. 2002, MNRAS, 330, 591 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Bonatto, C., Bica., E.,
& Girardi, L. 2004, A&A, 415, 571 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] (In the text)
- Bureau, M., Aronica,
G., Athanassoula, E., et al. 2006, MNRAS, 370, 753 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Buta, R., Crocker, D.
A., & Elmegreen, B. G. 1996, Barred Galaxies, IAU Coll., 157,
ASP Conf. Ser., 91
(In the text)
- Cabrera-Lavers, A.,
Garzón, F., & Hammersley, P. L. 2005, A&A, 433,
173 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] (In the text)
- Cabrera-Lavers, A.,
Garzón, F., Hammersley, P. L., Vicente, B., &
González-Fernández, C. 2006, A&A, 453, 371 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] (In the text)
- Cohen, M., Hammersley,
P. L., & Egan, M. P. 2000, AJ, 120, 3362 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Cole, A. A., &
Weinberg, M. D. 2002, ApJ, 574, L43 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- de Vaucouleurs, G.
1964, in The Galaxy and the Magellanic Clouds Interpretation of
velocity distribution of the inner regions of the Galaxy, IAU
Symp., 20, 195
(In the text)
- Drimmel, R.,
Cabrera-Lavers, A., & López-Corredoira, M. 2003, A&A,
409, 205 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] (In the text)
- Duran, M., & van
Kerkwijk, M. H. 2006 [arXiv:astro-ph/0606027]
(In the text)
- Dwek, E., Arendt, R.
G., Hauser, M. G., et al. 1995, ApJ, 445, 716 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Eaton, N., Adams, D. J,
& Giles, A. B. 1984, MNRAS, 208, 241 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Epchtein, N. 1997, in
The Impact of Large Scale Near-IR Sky Surveys, ed. F. Garzón,
N. Epchtein, A. Omont, B. Burton, & P. Persi (Dordrecht:
Kluwer), 15
- Freeman, K. C. 1996,
Barred Galaxies, IAU Coll., 157, ASP Conf. Ser., 91, 1
(In the text)
- Freudenreich, H. T.
1998, ApJ, 492, 495 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Friedli, D., Wozniak,
H., Rieke, M., Martinet, L., & Bratschi, P. 1996, A&AS,
118, 461 [NASA ADS]
- Garay, G., Moran, J.
M., Rodríguez, L. F., & Reid, M. J. 1998, ApJ, 492,
635 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Garzón, F.,
Hammersley, P. L., Mahoney, T., et al. 1993, MNRAS, 264, 773 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Garzón, F.,
López-Corredoira, M., Hammersley, P. L., Mahoney, T., &
Calbet, X. 1997, ApJ, 491, 31 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Gosling, A., Blundell,
K., & Bandyopadhyay, R. 2006, ApJ, 640, L171 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Grocholski, A. J.,
& Sarajedini, A. 2002, AJ, 123, 1603 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Hammersley, P. L.,
Garzón, F., Mahoney, T., & Calbet, X. 1994, MNRAS, 269,
753 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Hammersley, P. L.,
Garzón, F., Mahoney, T., & Calbet, X. 1995, MNRAS, 273,
206 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Hammersley, P. L.,
Garzón, F., Mahoney, T. J., López-Corredoira, M., &
Torres, M. A. P. 2000, MNRAS, 317, L45 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Ibata, R., &
Gilmore, G. 1995a, MNRAS, 275, 591 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Ibata, R., &
Gilmore, G. 1995b, MNRAS, 275, 605 [NASA ADS]
- Indebetouw, R., et al.
2005, ApJ, 619, 931 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Lépine, J. R. D.,
& Leroy, P. 2000, MNRAS, 313, 263 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- López-Corredoira,
M., Garzón, F., Hammersley, P. L., Mahoney, T. J., &
Calbet, X. 1997, MNRAS, 292, 15 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- López-Corredoira,
M., Garzón, F., Beckman, J. E., et al. 1999, AJ, 118, 381 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- López-Corredoira,
M., Hammersley, P. L., Garzón, F., Simonneau, E., &
Mahoney, T. J. 2000, MNRAS, 313, 392 [NASA ADS]
- López-Corredoira,
M., Hammersley, P. L., Garzón, F., et al. 2001, A&A, 373,
139 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] (In the text)
- López-Corredoira,
M., Cabrera-Lavers, A., Garzón, F., & Hammersley, P. L.
2002, A&A, 394, 883 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] (In the text)
- López-Corredoira,
M., Cabrera-Lavers, A., Gerhard, O., & Garzón, F. 2004,
A&A, 421, 953 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] (In the text)
- López-Corredoira,
M., Cabrera-Lavers, A., & Gerhard, O. E. 2005, A&A, 439,
107 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] (In the text)
- L
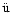 tticke, R., Dettmar, R.-J., & Pohlen, M. 2000,
A&A, 362, 435 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
tticke, R., Dettmar, R.-J., & Pohlen, M. 2000,
A&A, 362, 435 [NASA ADS] (In the text) - Molla, M., Ferrini, F.,
& Gozzi, G. 2000, MNRAS, 316, 345 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Nikolaev, S., &
Weinberg, M. D. 1997, ApJ, 487, 885 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Nishiyama, S., Nagata,
T., Baba, D., et al. 2005, ApJ, 621, L105 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Nishiyama, S.,
Nagata, T., Kusakabe, N., et al. 2006a, ApJ, 638, 839 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Nishiyama, S.,
Nagata, T., Sato, S., et al. 2006b, ApJ, 647, 1093 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Picaud, S.,
Cabrera-Lavers, A., & Garzón, F. 2003, A&A, 408,
141 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] (In the text)
- Picaud, S., &
Robin, A. C. 2004, A&A, 428, 891 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] (In the text)
- Pietrzynski, G.,
Gieren, W., & Udalski, A. 2003, AJ, 125, 2494 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Ramírez, S. V.,
Stephens, A. W., Frogel, J. A., & DePoy, D. L. 2000, AJ, 120,
833 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Rieke, G. H., &
Lebovsky, M. J. 1985, ApJ, 288, 618 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Robin, A. C.,
Reylé, C., Derriére, S., & Picaud, S. 2003, A&A,
409, 523 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] (In the text)
- Salaris, M., &
Girardi, L. 2002, MNRAS, 337, 332 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Sarajedini, A., Lee, Y.
W., & Lee, D. H. 1995, ApJ, 450, 712 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Schultheis, M.,
Lançon, A., Omont, A., Schuller, F., & Ojha, D. K. 2003,
A&A, 405, 531 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] (In the text)
- Sevenster, M.,
Prasenjit, S., Valls-Gabaud, D., & Fux, R. 1999, MNRAS, 307,
584 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Skrutskie, M. F.,
Cutri, R. M., Stiening, R., et al. 2006, AJ, 131, 1163 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, T. K.,
Beuther, H., Saito, M., Wyrowski, F., & Pchilke, P. 2005, ApJ,
634, L57 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Stanek, K. Z., &
Garnavich, P. M. 1998, ApJ, 503, L131 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Stanek, K. Z., Mateo,
M., Udalski, A., et al. 1994, ApJ, 429, L73 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Stanek, K. Z., Mateo,
M., Udalski, A., et al. 1997, ApJ, 477, 163 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Udalski, A., Symanski,
M., Kaluzny, J., Kubiak, M., & Mateo, M. 1993, Acta Astron.,
43, 69 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Udalski, A., et al.
1994, Acta Astron., 44, 165 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Unavane, M., &
Gilmore, G. 1998, MNRAS, 295, 145 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Wainscoat, R. J.,
Cohen, M., Volk, K., Walzer, H. J., & Schwartz, D. E. 1992,
ApJS, 83, 111 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Weinberg, M. D. 1992,
ApJ, 384, 81 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
Copyright ESO 2007
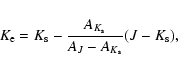
![\begin{displaymath}%
N(m)=a+bm+cm^2+ \frac{N_{\rm RC}}{\sigma_{\rm RC}\sqrt{2\pi...
...\left[-\frac{(m_{\rm RC}-m)^2}{2\sigma_{\rm RC}^2}\right]\cdot
\end{displaymath}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/img32.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.85cm,clip]{6185fig01.ps}\par\includegraphics[width=7.85cm,clip]{6185fig02.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg33.gif)
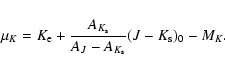
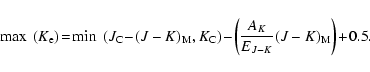
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,clip]{6185fig03.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg39.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.7cm,clip]{6185fig04.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg40.gif)
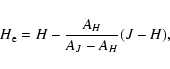
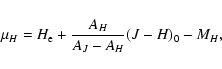
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.85cm,clip]{6185fig05.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg51.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.65cm,clip]{6185fig06.eps}\par\includegraphics[width=7.65cm,clip]{6185fig07.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg52.gif)
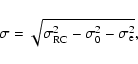
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6cm,clip]{6185fig08.eps}\par\includegr...
...p]{6185fig09.eps}\par\includegraphics[width=6cm,clip]{6185fig10.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg58.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6.75cm,clip]{6185fig11.eps}\par\includegraphics[width=6.75cm,clip]{6185fig12.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg59.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=5.15cm,clip]{6185fig13CMJN.eps}\par\in...
...5CMJN.eps}\par\includegraphics[width=5.15cm,clip]{6185fig16CMJN.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg66.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6.85cm,clip]{6185fig17CMJN.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg70.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=5.25cm,clip]{6185fig18CMJN.eps}\par\in...
...5fig20CMJN.eps}\par\includegraphics[width=5.25cm,clip]{6185fig21.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg84.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6.2cm,clip]{6185fig22.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg93.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6.6cm,clip]{6185fig23.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg100.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,clip]{6185fig24.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg104.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,clip]{6185fig25.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg105.gif)
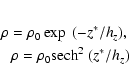
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,clip]{6185fig26.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg108.gif)
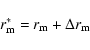
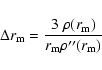
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6.85cm,clip]{6185fig27.ps}\par\includegraphics[width=6.85cm,clip]{6185fig28.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg122.gif)
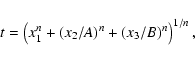
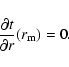
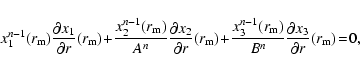
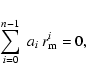
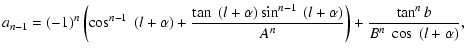
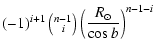
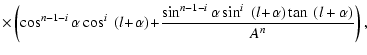
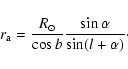
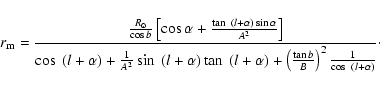
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.4cm,clip]{6185fig30.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg142.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.55cm,clip]{6185fig31.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg143.gif)
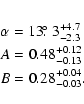
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=6.45cm,clip]{6185fig32.ps}\par\include...
...{6185fig33.ps}\par\includegraphics[width=6.45cm,clip]{6185fig34.ps} \end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg156.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.6cm,clip]{6185fig35.ps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2007/15/aa6185-06/Timg165.gif)