All Tables
- Table 1:
Observational data of the PMS stars. The spectral classifications based on
different criteria are separated by (/) to distinguish them from the given
spectral ranges (-).
Additional information on the double stars (denoted by in Col. 2) is
given in Table B.1. Uncertain values are indicated with (:).
The foreground colour-excess
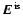 is labelled with (*) if
is labelled with (*) if
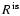
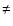 3.1
(Appendix B.4).
The h in Col. 7 denotes Hipparcos values (ESA 1997),
see Appendix C for supplementary information on each star.
Column 9 indicates if Walraven photometry was obtained for the star.
The inclination is indicated with E or P based on the methods (X, Y, Z)
described in Appendices B.5 and D.
3.1
(Appendix B.4).
The h in Col. 7 denotes Hipparcos values (ESA 1997),
see Appendix C for supplementary information on each star.
Column 9 indicates if Walraven photometry was obtained for the star.
The inclination is indicated with E or P based on the methods (X, Y, Z)
described in Appendices B.5 and D.
- Table 2:
Data of the analysed stars (Part 1),
 see Table 3,
see Table 3, 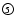 see Table 5.
see Table 5.
- Table 3:
Additional extinction data of BF Ori; (07-01 top) and
(07-02 bot).
See Table 2 for the other parameters.
- Table 4:
Extinction parameters for 11 observed brightness stages of UX Ori with a
photospheric spectral type of A2 III.
See Table 2 for the other parameters.
- Table 5:
Additional data of HR 5999. The
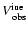 -value marked with () is uncertain, as
the brightness is underestimated due to the degradation of the FES counter
after 1990 (Sect. B.1).
See Table 2 for the other input parameters.
The apparently good agreement of the 3 faint spectra (#10-12) at the long
wavelength is caused by the fact that we used the same (overexposed) image
LWR14027 in these cases.
-value marked with () is uncertain, as
the brightness is underestimated due to the degradation of the FES counter
after 1990 (Sect. B.1).
See Table 2 for the other input parameters.
The apparently good agreement of the 3 faint spectra (#10-12) at the long
wavelength is caused by the fact that we used the same (overexposed) image
LWR14027 in these cases.
- Table 6:
Data of the double stars, p for
primary, s for secondary,
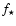 is the relative V-flux of the component.
is the relative V-flux of the component.
- Table 7:
Data used for the SED-calculations,
V-magnitude with references for each photometric observation.
Observations on the WULBV (Walraven) photometric system can be found in
deWinter et al. (2001) with the exception of HD 139614 and SU Aur.
Observations in the 4 IRAS bands (11.8, 24.4, 58.6 and 101
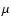 m) can be
found in NASA RP-1190 (1988).
m) can be
found in NASA RP-1190 (1988).
- Table 8:
Comparison of the determined stellar masses (
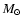 )
and relative ages,
spectral type z indicates ZAMS.
)
and relative ages,
spectral type z indicates ZAMS.
- Table A.1:
Absorption features in the UV spectra (Fig. A.1) of some
PMS Ae/Fe stars, SX Cas, U Cep and
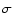 Cyg.
(n = narrow, b = broad, d = deep, s = shallow, e = emission instead
of absorption, : = uncertain value.)
Cyg.
(n = narrow, b = broad, d = deep, s = shallow, e = emission instead
of absorption, : = uncertain value.)
- Table B.1:
Published double-star parameters and spectral types, see also
Sect. 5.9 and Appendix C.
- Table C.1:
Data for HD 199143 from Neuhäuser et al. (2002).
- Table C.2:
Derived distances (pc) for KK Oph depending on the spectral
classification and the
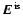 -value (in brackets).
-value (in brackets).
- Table D.1:
Review of inclination angles (in degrees) from Ly
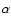 -emission-line profiles,
see Blondel et al. (1993) for details.
-emission-line profiles,
see Blondel et al. (1993) for details.
- Table E.1:
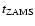 values Bernasconi (1996), see also Fig. 43.
values Bernasconi (1996), see also Fig. 43.
- Table E.2:
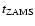 values Siess B (1999).
values Siess B (1999).
- Table E.3:
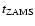 values Siess NG (2000).
values Siess NG (2000).
- Table F.1:
- Table F.2:
- Table F.3:
- Table F.4:
- Table F.5:
The (sparse) LW-images marked with
** are used for a range of SW-images to complete the spectrum.
- Table F.6:
Comments and notes to the Tables 1-5.
The first number of the image denotes IUE camera: 3 = SWP, 2 = LWR, 1 = LWP,
images not observed on the same run, but combined as they have acomparable
magnitude, are marked with (*).
The "notes'' refer to images used to complete the spectrum and applied flux
normalisation factors.
- Table G.1:
B stars, HD 202850 is
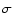 Cyg.
Cyg.
- Table G.2:
A stars.
- Table G.3:
F stars.
- Table G.4:
G stars.
- Table G.5:
K stars.
- Table G.6:
References to Col. 2.