a SWS observing mode used
(see de Graauw et al. 1996). Numbers in brackets correspond to
the scanning speed.
b TDT number which uniquely identifies each ISO observation.
 These spectra have been obtained by co-adding the separate
SWS spectra also listed in the table, see text.
These spectra have been obtained by co-adding the separate
SWS spectra also listed in the table, see text.
Effective temperatures from 1Mendez et al. (1992),
2Perinotto (1991), 3Kaler & Jacoby (1991),
4Quigley & Bruhweiler (1995) and 5Latter et al. (2000).
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.8cm,clip]{h3527f01.eps} \end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/29/aah3527/Timg13.gif) |
Figure 1:
The IRAS two-colour diagram for the sources studied in this
sample. The triangles represent the C-stars, the squares are the
post-AGB objects, the stars are the PNe and the diamonds are the
C-stars without a "30''  m feature detected. The dashed line
represents the position of blackbodies of different
temperatures. The dotted line sketches the evolution of a C-star
with a detached, expanding and cooling circumstellar shell. m feature detected. The dashed line
represents the position of blackbodies of different
temperatures. The dotted line sketches the evolution of a C-star
with a detached, expanding and cooling circumstellar shell. |
We present observations obtained with ISO of a sample of bright IR
sources at different stages along the evolutionary track from C-star
via post-AGB object to PN. The observations presented here consist of
data obtained with the ISO/SWS using astronomical observing template
06 and 01 at various speeds. These observing modes produces
observations from 2.3 to 45

m with a resolving
power (
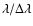
)
ranging from 500 to 1500. The sample
consists of all carbon-rich evolved objects in the ISO archive which
exhibit a "30''

m feature stronger than 8 Jy peak intensity and
have been observed over the full 2.3-45.2

m wavelength range of
the ISO/SWS. This peak intensity and the typical noise level of SWS
band 4 (29-45.2

m) allows to extract a reasonably reliable
feature strength and profile. The complete wavelength coverage is
needed in order to provide a sufficient baseline to estimate the
continuum. We have further completed the sample with all observed
C-stars with an IRAS 25

m flux over 13 Jy. These sources serve as
a control group since we would expect to detect the "30''

m
feature based on this brightness, the typical noise levels and the
typical feature over continuum level. These sources without the "30''

m feature detected are listed separately in
Table
1. It should be emphasised that the ISO archive
does not contain a statistically representative sample of objects. The
database of observations for the carbon stars provides a reasonable
sampling over stellar properties (e.g. mass-loss rates or colour
temperatures). However the post-AGB sample is heavily biased towards
the "21''

m objects; a peculiar type of C-rich post-AGB object.
The sample of PNe contains a collection of either bright, well-known
or well-studied objects without a proper statistical selection. It
also contains a relatively large proportion of PNe with hydrogen-poor
central stars. The total sample of 75 sources contains 48 C-stars, 14
post-AGB objects and 13 PNe. We have detected the "30''

m
feature in 36 out of 48 C-stars.
We present in Fig. 1 the IRAS two-colour diagram
for the sources in our sample following van der Veen & Habing (1988).
There are four sources in our sample without an entry in the IRAS
point source catalogue. For these sources we have used ISO/SWS and LWS
observations at 12, 25, 60 and 100  m to calculate the IRAS
colours. For IRAS Z02229, no measurements at 60 and 100
m to calculate the IRAS
colours. For IRAS Z02229, no measurements at 60 and 100  m are
available. In Fig. 1, the warmest sources are
located in the lower left corner. These are the optically visible
carbon stars with a low present-day mass-loss rate
(
m are
available. In Fig. 1, the warmest sources are
located in the lower left corner. These are the optically visible
carbon stars with a low present-day mass-loss rate
(
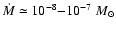 ). With increasing mass loss
the stars become redder and move up and to the right. After the AGB,
when the mass loss has terminated, the dust moves away from the star
and cools; i.e., these sources move further to the top-right corner of
the diagram. The C-stars located above the main group of C-stars have
a clear 60
). With increasing mass loss
the stars become redder and move up and to the right. After the AGB,
when the mass loss has terminated, the dust moves away from the star
and cools; i.e., these sources move further to the top-right corner of
the diagram. The C-stars located above the main group of C-stars have
a clear 60  m excess. This is evidence for an additional cool dust
component. Some of these sources are known to have an extended or
detached dust shell around them (Young et al. 1993). The empty
region between the C-stars and the post-AGBs is physical. When the
mass loss stops the star quickly loses its warmest dust and within a
short time span (<1000 yr) the star moves to the right in the
two-colour diagram. Notice how the sources without a detected "30''
m excess. This is evidence for an additional cool dust
component. Some of these sources are known to have an extended or
detached dust shell around them (Young et al. 1993). The empty
region between the C-stars and the post-AGBs is physical. When the
mass loss stops the star quickly loses its warmest dust and within a
short time span (<1000 yr) the star moves to the right in the
two-colour diagram. Notice how the sources without a detected "30''  m feature cluster on the left of the diagram, i.e., among the
warmest C-stars.
m feature cluster on the left of the diagram, i.e., among the
warmest C-stars.
2.1 Data reduction
The SWS data were processed using SWS interactive analysis product;
IA
3 (see de Graauw et al.
1996) using calibration files and
procedures equivalent with pipeline version 10.1. Further data
processing consisted of extensive bad data removal primarily
to remove the effects of cosmic ray hits and rebinning on a fixed
resolution wavelength grid. If a source has been observed multiple
times and these observations are of similar quality and of comparable
flux-level these data are co-added after the pipeline reduction. These
sources are indicated in Table
1 with a dagger
(
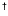
). Since the features we discuss here are fully resolved
in all observing modes, we combine the data obtained in all different
modes to maximise the
S/
N. Although the wavelength coverage of the
SWS instrument is well suited to study the profile of the "30''

m feature, there are some important instrumental effects which
hamper the unbiased extraction of the emission profiles. We discuss
these below.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.8cm,clip]{h3527f02.eps} \end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/29/aah3527/Timg16.gif) |
Figure 2:
Examples of the splicing of the SWS band 3D (19.5-27.5  m) and 4 (28.9-45.2 m) and 4 (28.9-45.2  m) data. We show the data before
(grey line) and after splicing (black line). All data have been
scaled to form a continuous spectrum. As can be seen; after
splicing, the slope of band 3D and band 4 match. We do not show
the band 3E data. The sharp rise at 27 m) data. We show the data before
(grey line) and after splicing (black line). All data have been
scaled to form a continuous spectrum. As can be seen; after
splicing, the slope of band 3D and band 4 match. We do not show
the band 3E data. The sharp rise at 27  m in R Scl and
IRC+40 450 is an instrumental artifact (see text for details). m in R Scl and
IRC+40 450 is an instrumental artifact (see text for details). |
One complete SWS AOT01 spectrum is obtained in 12 different subbands.
These subbands are observed through 3 different rectangular apertures
which range in size from
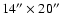
at the shortest
wavelengths to
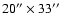
at the longest
wavelengths. All these data are independently flux calibrated and need
to be combined to form one continuous spectrum for one source. We
apply scaling factors to combine the different subbands to obtain the
continuous spectra. The C-stars and post-AGB objects we present in
this study all have a small angular extent even compared to the
smallest aperture used. Therefore we don't expect large jumps to be
present due to the differences between the apertures used. The angular
extent of some PNe can be large compared to the sizes of the
apertures. If there is a clear indication of flux jumps due to
aperture changes we have not included the source in our sample.
At wavelengths longer than between 26 and 27.5

m the data of SWS
subband 3D are affected by leakage adding flux from the 13

m
region. The sources used to derive the instrumental response function
are all stellar sources without circumstellar material. These
calibration sources are all very blue and emit much more flux at 13

m relative to 26

m than the cool, red sources we present in
this study. Therefore these calibrators are more affected by the
leakage than our sources. The instrumental response function derived
in this way has been implicitly corrected for leakage for the blue
sources. This resulted in fluxes in red sources to be systematically
underestimated. More recent calibrations (
OLP 10.0), have been
corrected for this effect. With the improved calibrations, the
resulting slopes of the spectra beyond 26

m have been checked and
are in general agreement with the slope of subband 4.
At wavelengths longer than 27.0

m the data of subband 3D show a
sharp increase which is found throughout the complete database of
ISO/SWS observations independent of source type. The data of subband
3E (27.5-29.0

m) are generally unreliable both in shape and
absolute flux level. These combined instrumental effects make it
inherently difficult to interpret the 27-29

m spectra. Any
substructure detected solely in this region alone should be
distrusted.
The instrumental effects between 27 and 29  m and the fact that
each of the subbands is independently flux calibrated make it
necessary to devise a strategy for splicing the band 3D, 3E and 4
data. There is unfortunately no objective way to choose this strategy.
We choose to assume minimal spectral structure between the end of
subband 3D and the beginning of band 4, i.e. to splice the subband
3D-4 data in such a way that the matching slopes of 3D and 4 also
match in flux level. Some examples are shown in
Fig. 2. The observed discontinuities between
subbands are relatively small (<20 per cent) and can be understood
as the result of absolute flux calibration uncertainties alone.
m and the fact that
each of the subbands is independently flux calibrated make it
necessary to devise a strategy for splicing the band 3D, 3E and 4
data. There is unfortunately no objective way to choose this strategy.
We choose to assume minimal spectral structure between the end of
subband 3D and the beginning of band 4, i.e. to splice the subband
3D-4 data in such a way that the matching slopes of 3D and 4 also
match in flux level. Some examples are shown in
Fig. 2. The observed discontinuities between
subbands are relatively small (<20 per cent) and can be understood
as the result of absolute flux calibration uncertainties alone.
2.2 Full spectra
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=17.1cm,clip]{h3527f03.eps} \end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/29/aah3527/Timg21.gif) |
Figure 3:
Overview of the spectra of carbon stars exhibiting the
"30''  m feature. The spectra are ordered according to
continuum temperature from high to low temperature, bottom to top,
left to right. The dashed line marks m feature. The spectra are ordered according to
continuum temperature from high to low temperature, bottom to top,
left to right. The dashed line marks
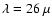 m. m. |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=17cm,clip]{h3527f04.eps} \end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/29/aah3527/Timg22.gif) |
Figure 4:
Overview of the spectra of post-AGB objects (left panel) and
PNe (right panel) exhibiting the "30''  m feature. The
spectra are ordered according to continuum temperature from high
to low temperature, bottom to top. The dashed line marks m feature. The
spectra are ordered according to continuum temperature from high
to low temperature, bottom to top. The dashed line marks
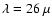 m. The spectrum of RAFGL 618 although warmer
than NGC 3918 is shown at the top of the PNe for clarity. m. The spectrum of RAFGL 618 although warmer
than NGC 3918 is shown at the top of the PNe for clarity. |
The resultant spectra for the sources that exhibit a "30''  m
feature are shown in Figs. 3, 4. The SWS spectra of this
large group of objects show a spectacular range in colour temperature,
molecular absorption bands and solid state features. The C-stars have
molecular absorption bands of C2H2 at 3.05, 7-8 and 14
m
feature are shown in Figs. 3, 4. The SWS spectra of this
large group of objects show a spectacular range in colour temperature,
molecular absorption bands and solid state features. The C-stars have
molecular absorption bands of C2H2 at 3.05, 7-8 and 14  m,
of HCN at 7 and 14
m,
of HCN at 7 and 14  m, CO at 4.7
m, CO at 4.7  m and C3 at 4.8-6
m and C3 at 4.8-6
 m. The sharp absorption band at 14
m. The sharp absorption band at 14  m is due to C2H2and HCN. There is an emission feature due to solid SiC at 11.4
m is due to C2H2and HCN. There is an emission feature due to solid SiC at 11.4  m.
In the reddest C-stars, we find the SiC in absorption. We also find
evidence for a weak depression in the 14-22
m.
In the reddest C-stars, we find the SiC in absorption. We also find
evidence for a weak depression in the 14-22  m range in the
reddest objects. This depression could be due to aliphatic chain
molecules like those found in RAFGL 618 (Cernicharo et al. 2001).
m range in the
reddest objects. This depression could be due to aliphatic chain
molecules like those found in RAFGL 618 (Cernicharo et al. 2001).
The post-AGBs and PNe exhibit many, sometimes broad solid state
emission features. In many sources we find emission due to polycyclic
aromatic hydrocarbons in the 3-15  m range. There is a broad
plateau feature from 10-15
m range. There is a broad
plateau feature from 10-15  m which may be due to hydrogenated
amorphous carbon (Guillois et al. 1996; Kwok et al. 2001).
Many post-AGBs and two PNe in the sample have a feature peaking at
20.1
m which may be due to hydrogenated
amorphous carbon (Guillois et al. 1996; Kwok et al. 2001).
Many post-AGBs and two PNe in the sample have a feature peaking at
20.1  m, called the "21''
m, called the "21''  m feature in the literature.
Recently the carrier of this feature has been identified with TiC
(von Helden et al. 2000). The feature at 23
m feature in the literature.
Recently the carrier of this feature has been identified with TiC
(von Helden et al. 2000). The feature at 23  m found in IRAS 18240 and
PN K3-17 is likely due to FeS (Hony et al. 2002). These absorption
and emission features have to be taken into account when determining
the profile of the "30''
m found in IRAS 18240 and
PN K3-17 is likely due to FeS (Hony et al. 2002). These absorption
and emission features have to be taken into account when determining
the profile of the "30''  m feature or the shape of the
underlying continuum.
m feature or the shape of the
underlying continuum.
Focusing on the "30''  m feature we can see variations in the
strength and shape of the band. The most marked difference is however
a shift in the peak position going from 26
m feature we can see variations in the
strength and shape of the band. The most marked difference is however
a shift in the peak position going from 26  m in some of the AGB
stars to 38
m in some of the AGB
stars to 38  m in the PNe. The dashed line in
Figs. 3 and 4 indicates
m in the PNe. The dashed line in
Figs. 3 and 4 indicates
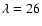
 m. There are systematic changes in the appearance of the "30''
m. There are systematic changes in the appearance of the "30''
 m feature from the C-stars to the PNe. The feature in the
C-stars almost exclusively peaks at 26
m feature from the C-stars to the PNe. The feature in the
C-stars almost exclusively peaks at 26  m. There are some
exceptions like R Scl. In the post-AGB sample, the feature is broader
and in some sources the feature peaks long ward of 26
m. There are some
exceptions like R Scl. In the post-AGB sample, the feature is broader
and in some sources the feature peaks long ward of 26  m. In the
PNe sample, there are no sources that peak at 26
m. In the
PNe sample, there are no sources that peak at 26  m.
However, the appearance of a broad feature like the "30''
m.
However, the appearance of a broad feature like the "30''  m
feature is sensitive to the shape of the underlying dust continuum,
especially since we have a sample with such a wide range of continuum
colour temperatures.
m
feature is sensitive to the shape of the underlying dust continuum,
especially since we have a sample with such a wide range of continuum
colour temperatures.

 Up: The carrier of the stars
Up: The carrier of the stars
Copyright ESO 2002
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.8cm,clip]{h3527f01.eps} \end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/29/aah3527/Timg13.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.8cm,clip]{h3527f02.eps} \end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/29/aah3527/Timg16.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=17.1cm,clip]{h3527f03.eps} \end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/29/aah3527/Timg21.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=17cm,clip]{h3527f04.eps} \end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/29/aah3527/Timg22.gif)