The Hubble Deep Field North (HDF-N) catalog (Williams et al. 1996) was chosen to test the evolution factor. Spectroscopic redshifts were measured carefully by Cohen et al. (2000), with some additions and corrections in Cohen (2001). FSLY give photometric data for the HDF-N objects and Fernández-Soto et al. (2001a) give a correspondence between their objects and the objects in Cohen et al. (2000). We exclude from the sample galaxies with negative fluxes. The remaining selected sub-sample contains 136 galaxies with redshifts distributed from 0 to 5.6.
The HDF-N sample presents a series of advantages
to explore the accuracy of our method and to compare it
to others. With a large redshift range
(
![]() ), the sample data acquired with
the WFPC2/HST camera is one
of the deepest (down to B=29) with an extent
over the wavelength range from about 3000 Å to 8000 Å
with the filters F300W, F450W, F606W, and F814W (hereafter called
U, B, V, I).
Moreover the near-infrared standard Johnson-Cousins J, H and
), the sample data acquired with
the WFPC2/HST camera is one
of the deepest (down to B=29) with an extent
over the wavelength range from about 3000 Å to 8000 Å
with the filters F300W, F450W, F606W, and F814W (hereafter called
U, B, V, I).
Moreover the near-infrared standard Johnson-Cousins J, H and ![]() (hereafter K)
colors listed in FSLY from Dickinson (1998) were observed at the KPNO/4 m telescope.
The calibration used is AB magnitudes.
(hereafter K)
colors listed in FSLY from Dickinson (1998) were observed at the KPNO/4 m telescope.
The calibration used is AB magnitudes.
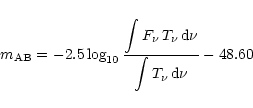
A further advantage is the benefit of spectroscopic redshifts of the selected sub-sample, as given by Cohen (2001). This allows a statistical comparison with our photometric redshifts and an estimation of the dispersion. Another advantage of this sample is the possibility of measuring the type-dependent evolution factor by comparing our results with the FSLY's results, since the latter authors propose photometric redshift determinations based on a maximum likelihood analysis and 4 spectral types without any evolution effect.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.3cm,clip]{MS2109f3.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/17/aa2109/Timg66.gif) |
Figure 2:
Comparison of photometric redshifts (points with error bars)
predicted by the model Z-PEG.1 to
spectroscopic redshifts of the selected HDF-N sample. The solid line of slope = 1 shows
the case of equality
for comparison. The dotted line is the linear regression of our photometric redshifts
if we exclude the points with
|
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[clip,width=8.3cm,clip]{MS2109f4.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2002/17/aa2109/Timg73.gif) |
Figure 3:
Crosses are differences
|
| Z-PEG Model | IGM abs. | UBVI | JHK | age constraint | z<1.5 | all z | Fig. | ||
| 1 | x | x | x | x |
| -0.0214 | -0.0844 | 2 | |
|
|
|
||||||||
| 2 | x | x | x |
| 0.0251 | -0.0621 | 5 | ||
|
|
|
||||||||
| 3 | x | x |
| 0.0252 | -0.0589 | 5 | |||
| 0.1156 | 0.5738 | ||||||||
| 4 | x | x |
| 0.1273 | -0.0040 | 7 | |||
| 0.3179 | 0.5840 | ||||||||
| FSLYa | x | x | x |
| -0.0037 | -0.0579 | |||
| 0.1125 | 0.2476 | ||||||||
| MIBVb | x | x | x |
| 0.026 | ||||
| 0.074 |
Copyright ESO 2002