- ...
IGM
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The data
used in this study are based on public
data released from the VLT/UVES Commissioning and Science
Verification and from the OPC program 65.O-0296A (P.I.
S. D'Odorico) at the VLT/Kueyen
telescope, ESO,Paranal, Chile.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... (AMD)
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Schaye et al. (2000) adopted a
threshold of 1 AMD, which results in a power law fit with higher
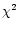 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...1996)
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The previous section suggests
there is a
contribution from sources other than QSOs to the UV background.
Estimates of contributions from galaxies depend on many factors,
such as the galaxy luminosity function and the galaxy emissivities.
Including a contribution from galaxies, Shull et al. (1999) derive
a UV background decreasing from
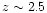 to
to 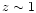 ,
similar to the
QSO-dominated
,
similar to the
QSO-dominated
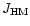 .
On the other hand, Bianchi et al.
(2001) find a non-decreasing J from
.
On the other hand, Bianchi et al.
(2001) find a non-decreasing J from 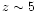 to
to 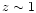 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.