Fig. 1
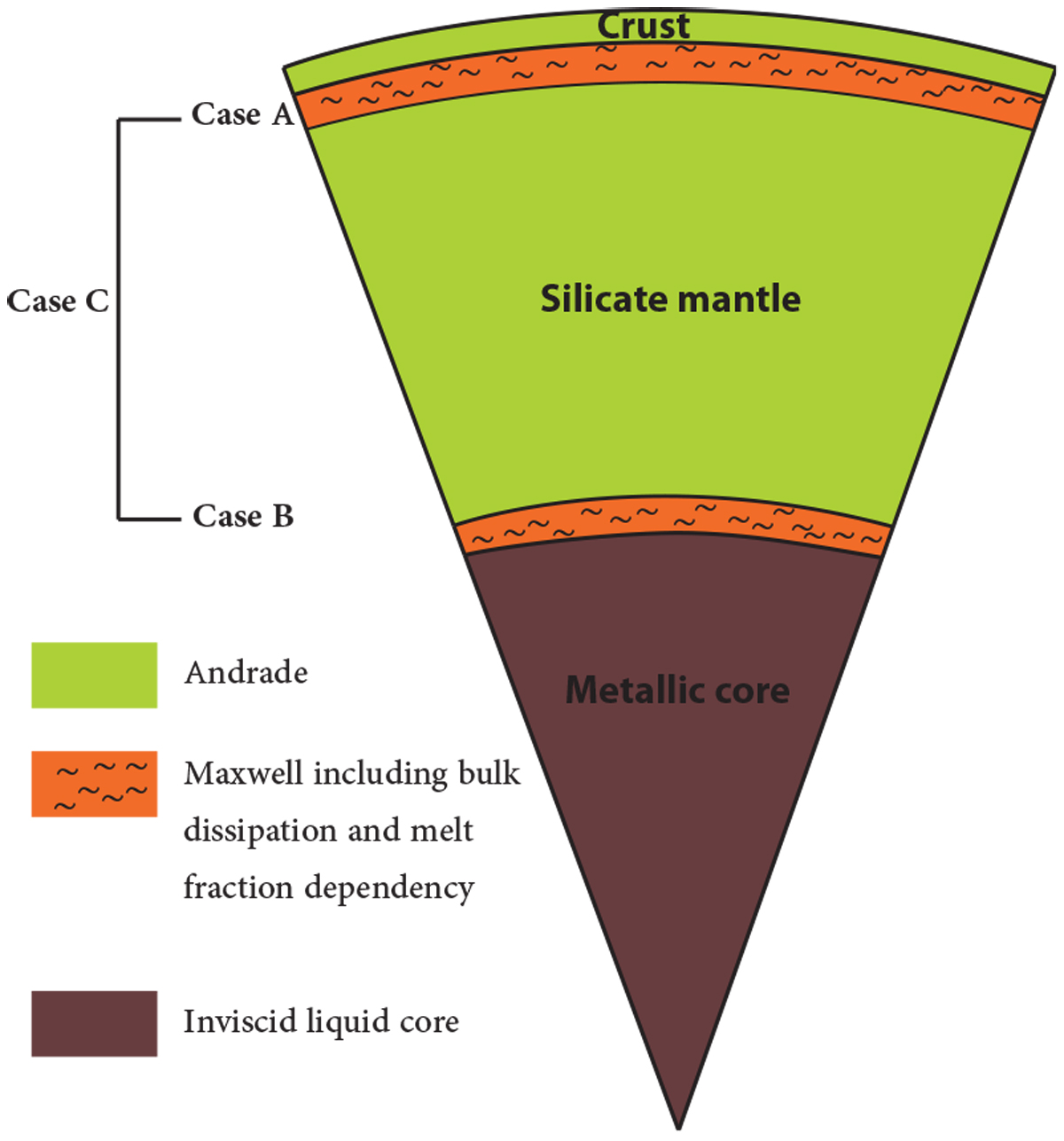
Model of Io’s internal structure used for the computations. The considered rheology can be divided into three groups: (1) the solid mantle and crust, described by an Andrade rheology neglecting bulk dissipation; (2) the partially molten layers, either beneath the crust (case A) or at the core mantle boundary (case B), or a combination of both (Case C), described by a Maxwell rheology including both shear and bulk dissipation and accounting for the effect of melt on the viscoelastic parameters (following the rheological law described in Sect. 3.2); (3) the inviscid liquid metallic core.