- ...
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- In reality, this assumption does not hold, in particular due to undersampling of the PSF and pixel noise in those images from which the kernel model has to be inferred. Since g enters P (Eq. (7)), and P has to be inverted explicitly (Eq. (11)) or implicitly (Eq. (13)), a modest error in the kernel modeling can have severe implications for the quality of the deconvolution results. But this is also true for any other deconvolution method.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...S
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The models for both f and g have unit flux, so the surface brightness of the convolved object h depends on
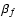 and
and 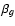 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.