A&A 492, 857-862 (2008)
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:200809928
1 - Royal Observatory of Belgium, 3 Av. Circulaire, 1180 Bruxelles, Belgium
2 -
Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Chilton, Didcot, Oxfordshire, OX11 0QX, UK
Received 8 April 2008 / Accepted 26 August 2008
Abstract
Aims. Studying the statistical properties of solar ultraviolet emission lines could provide information about the nature of small scale coronal heating. We expand on previous work to investigate these properties. We study whether the predicted statistical distribution of ion emission line intensities produced by a specified heating function is affected by the isoelectronic sequence to which the ion belongs, as well as the characteristic temperature at which it was formed (as found previously). Particular emphasis is placed on the strong resonance lines belonging to the lithium isoelectronic sequence. Predictions for emission lines observed by existing space-based UV spectrometers are given. The effects on the statistics of a line when observed with a wide-band imaging instrument rather than a spectrometer are also investigated.
Methods. We use a hydrodynamic model to simulate the UV emission of a loop system heated by nanoflares on small, spatially unresolved scales. We select lines emitted at similar temperatures but belonging to different isoelectronic groups: Fe IX and Ne VIII, Fe XII and Mg X, Fe XVIII, Fe XIX and Fe XXIV.
Results. Our simulations confirm previous results that almost all lines have an intensity distribution that follows a power-law, in a similar way to the heating function. However, only the high temperature lines best preserve the heating function's power law index (Fe XIX being the best ion in the case presented here). The Li isoelectronic lines have different statistical properties with respect to the lines from other sequences, due to the extended high temperature tail of their contribution functions. However, this is not the case for Fe XXIV which may be used as a diagnostic of the coronal heating function. We also show that the power-law index of the heating function is effectively preserved when a line is observed by a wide-band imaging instrument rather than a spectromenter.
Key words: Sun: UV radiation - Sun: corona - plasmas - methods: statistical
VUV and X-ray small-scale brightenings are often detected in images or spectra of the solar atmosphere (e.g. Aletti et al. 2000; Christe et al. 2008; Berghmans et al. 1998; Aschwanden & Parnell 2002). These observations and theoretical considerations indicate that these brightenings may be one manifestation of small-scale impulsive heating acting on the unresolved fine scale of the corona. Modelling unresolved small-scale brightenings can help, for example, to explain the long lifetimes of active region loops. Understanding the properties of this heating and its contribution to global coronal heating are among the most challenging questions in solar physics. An important starting point is identifying key observables that can diagnose proposed heating functions.
The study of the frequency distribution of the intensity of coronal VUV emission lines is one method for investigating this problem. The distributions derived from observations with a variety of instruments and data sets show power laws with indices mainly between -1.5 and -2 (e.g. Aschwanden 2005). Converting the frequency distribution into a distribution of thermal energy for the heating events yields a similar power-law, and this is assumed to represent the power-law index of the (unknown) coronal heating function. However, behind this method there is the assumption that the energy conversion mechanisms do not modify the original heating energy distribution, so that the measured events distribution is equivalent to the heating distribution.
Parenti et al. (2006) investigated this aspect using a forward modelling approach: a statistical model of coronal heating was posited and properties of the predicted emission line intensities and thermal energies were deduced. Their main result indicated that only high temperature lines, formed when the main cooling mechanism in the loop was conduction, are reliable.
These authors showed that the statistical properties of the heating function are conserved by the line intensity statistical distribution, only during such a period. The lines analyzed by these authors did not belong to the lithium isoelectronic sequence.
As with many other ions formed in the solar atmosphere, the Li isoelectronic ions are formed principally over a narrow temperature interval (![]() 0.3 dex in
0.3 dex in ![]() ), although, unlike most other ions, they also have a tail in their temperature distributions that extends to high temperatures (e.g. Fig. 3), which leads to the ions sampling a wider
temperature range than most other ions.
), although, unlike most other ions, they also have a tail in their temperature distributions that extends to high temperatures (e.g. Fig. 3), which leads to the ions sampling a wider
temperature range than most other ions.
In the present work, the results of Parenti et al. (2006) will be extended to investigate the following questions:
Due to the large number of current and planned VUV instruments, the present work concentrates on VUV lines and we do not investigate the consequences of the small-scale brightening model on X-ray emission. However, to our knowledge, soft X-ray microflare studies of this kind have not been completed previously, although results from the Hinode Soft X-ray Telescope (SXT) may be forthcoming.
The paper is organised as follows. Section 2 introduces the hydrodynamical model used in the simulations. Section 3 describes how the synthetic spectra are built. Section 4 provides the results, and conclusions are drawn in Sect. 5.
The hydrodynamical model used was described in detail by
Parenti et al. (2006), and we provide only a brief description.
A coronal loop was modelled by a bundle of unresolved, identical
threads following the approach of Cargill (1994). Two thousand threads were
used each with a half length, L, of
![]() ,
and a
cross-sectional area, A, of
,
and a
cross-sectional area, A, of
![]() .
At each
time t, a thread was described by a single temperature, T, and single density, N. The model simulates the heating-cooling cycle of each thread independently. After the thread was heated impulsively, the cooling proceeded first by thermal conduction (at high temperatures) and then by radiation (at low temperatures). During the period dominated by conduction, the strand was filled with plasma by evaporation from the chromosphere, while it drains during the radiation phase.
The time evolution of the density and temperature in each thread was used to calculate the time-dependent synthetic spectra in the entire loop. The assumed energy loss was
.
At each
time t, a thread was described by a single temperature, T, and single density, N. The model simulates the heating-cooling cycle of each thread independently. After the thread was heated impulsively, the cooling proceeded first by thermal conduction (at high temperatures) and then by radiation (at low temperatures). During the period dominated by conduction, the strand was filled with plasma by evaporation from the chromosphere, while it drains during the radiation phase.
The time evolution of the density and temperature in each thread was used to calculate the time-dependent synthetic spectra in the entire loop. The assumed energy loss was
![]() .
.
The heating function employed by Parenti et al. (2006) was derived from a
model of coronal turbulence developed by Buchlin et al. (2003). For the present work,
a synthetic heating function was used,
which simulated a sequence of small energy-impulsive events (![]()
![]() ), each involving only one thread at a time.
The heating function had a log-normal distribution with index
), each involving only one thread at a time.
The heating function had a log-normal distribution with index
![]() ,
over the energy range
,
over the energy range ![]()
![]() (Fig. 1). Our use of this synthetic heating function is justifiable because power-law distributions of observed energy events have been reported, and
theoretical models have also been shown to generate a power-law
distribution of energies (Parenti et al. 2006). A synthetic function can
also be easily modified, to allow a full investigation of model parameters.
(Fig. 1). Our use of this synthetic heating function is justifiable because power-law distributions of observed energy events have been reported, and
theoretical models have also been shown to generate a power-law
distribution of energies (Parenti et al. 2006). A synthetic function can
also be easily modified, to allow a full investigation of model parameters.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{9928fig1.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2008/48/aa09928-08/Timg12.gif) |
Figure 1: Probability Distribution Function of the heating function used for our simulations. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
To study the behaviour of the optically thin FUV-UV line intensities, it is helpful to consider the column Differential Emission Measure (DEM) distribution, which represents the amount of material at a given temperature along the line of sight h:
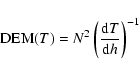 |
(1) |
In our model, we assumed that the line of sight was perpendicular to the loop axes, so that the line of sight was given by the diameter of the strand multiplied by the number of strands emitting at the given temperature. Under these conditions, the shape of the DEM can be represented by the distribution of N2 versus T. (For details on the dependence of
![]() on the model parameters see Parenti et al. 2006, and references therein.)
on the model parameters see Parenti et al. 2006, and references therein.)
Figure 2 shows the logarithm of N2 as a function of the logarithm of temperature, integrated over the entire loop system (2000 strands) and simulation time (
![]() ).
This plot helps to interpret our results.
).
This plot helps to interpret our results.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{9928fig2.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2008/48/aa09928-08/Timg19.gif) |
Figure 2:
Variation in
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
As mentioned earlier, in this model the cooling of a strand proceeded in two separate phases: the conduction phase, where the strand is still at a high temperature; and the radiation phase, for lower temperatures. For this reason, we are able to follow the cooling process in Fig. 2. The plasma evaporation from the chromosphere acting during the period dominated by thermal conduction fills the high temperature part (on the right side from the peak) of the N2-T distribution. The lower temperature part of the distribution is filled during the radiation phase. The peak corresponds to the temperature location at which part of the strands are cooling by conduction and part by radiation.
One of the main results of Parenti et al. (2006) was that the intensity distribution of a spectral line is representative of the heating function distribution, if the formation temperature of the line is within the high temperature region of the DEM distribution. This is due to the proximity with the moment of heat injection, which produces radiative emission that inherits the properties of the heating function.
For the case presented here, the DEM peaks at about
![]() .
This implies that lines emitted at lower temperatures are formed while the cooling in the strand is dominated by
radiation. For
.
This implies that lines emitted at lower temperatures are formed while the cooling in the strand is dominated by
radiation. For
![]() ,
the cooling is dominated by
conduction. An intermediate condition is found between these two
temperatures, in which the line emission loses all information about the
heating function.
,
the cooling is dominated by
conduction. An intermediate condition is found between these two
temperatures, in which the line emission loses all information about the
heating function.
Table 1 lists the lines modelled in the present work, and their formation temperatures. These lines are observable with the instruments SOHO/SUMER, EIT and Hinode/EIS. Where possible, we chose two lines with similar formation temperatures but belonging to ions of different isoelectronic sequences. Lines belonging to the Li isoelectronic sequence are highlighted. The SUMER instrument on board SOHO is an ultraviolet spectrometer observing in the wavelength range 500-1600 Å which was described by Wilhelm et al. (1995). This is one of the most useful bands in the VUV because it contains lines emitted from the chromosphere to the corona. Another SOHO instrument is EIT, which acquires solar images in four wavelength bands by using multilayer optical coatings (Delaboudiniere et al. 1995). EIS is an ultraviolet spectrometer on board the Hinode satellite operating in the wavelength ranges 170-211 Å and 246-292 Å and was described in Culhane et al. (2007).
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{9928fig3a.eps}\\
\hspace{-1mm}\includegraphics[width=8.9cm,clip]{9928fig3b.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2008/48/aa09928-08/Timg22.gif) |
Figure 3: Contribution functions for the spectroscopic lines (top) and the temperature response function for the EIT 171 and 195 filters (bottom). |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Table 1: List of lines synthesised in this work, and with the logarithm of the temperature of their maximum emission. These lines can be observed by SOHO/SUMER (Ne VIII, Mg X, Fe XVIII, Fe XIX), SOHO/EIT (Fe IX, Fe XII) and Hinode/EIS (Fe IX, Fe XII, Fe XXIV).
![\begin{figure}
\par\mbox{\includegraphics[width=8cm,clip]{9928fig4a.eps} \includ...
...928fig4c.eps} \includegraphics[width=8.1cm,clip]{9928fig4d.eps} }
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2008/48/aa09928-08/Timg24.gif) |
Figure 4: Top: PDFs for the Fe IX (on the right) and Ne VIII (on the left) lines. Bottom: PDFs for the Fe XII (on the right) and Mg X (on the left) lines. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
For the theoretical calculation of the line intensities, we used the CHIANTI (v. 5.2, Dere et al. 1997; Landi et al. 2006) atomic database and software, adopting the Mazzotta et al. (1998) ion fractions and photospheric element abundances (Grevesse & Sauval 1998). We simulated the measured data numbers (DN) from the spectrometers by assuming observations with a 1 arcsec slit and 1 s cadence and using the standard calibration software available in the SolarSoft IDL package. In the case of EIT, we simulated the total emission in the channel by integrating the emission from all lines in the waveband, as predicted by the CHIANTI atomic database, taking into account the effective area of the instrument. The Fe IX 171 channel of EIT in particular, is affected by significant contributions from the slightly hotter Fe X 174.53 Å line, which therefore alters its response to the heating function. The 195 channel has a hot component due to Fe XXIV 192.03 Å.
Figure 3 shows the contribution functions G(T) for all lines (top) and the EIT response function for the channels (bottom) used in this work. The G(T) functions of the lithium isoelectronic lines in the top plot can be identified by their asymmetry towards high temperatures. We anticipate in our results that this a high temperature tail will increase the number of events with low intensity.
We investigate the intensity distribution of ``warm'' coronal lines, i.e., those lines that form at the average temperature of the corona (1-2 MK).
Figure 4 shows the PDFs for Fe IX and Ne VIII (
![]() ;
top panels), Fe XII, and Mg X (
;
top panels), Fe XII, and Mg X (
![]() ;
bottom panels).
The left panels in the Figure show the PDFs from the Li-like lines.
The power-law behaviour of the heating function was transmitted to the
predicted PDFs of each wavelength, although, in each case the index
;
bottom panels).
The left panels in the Figure show the PDFs from the Li-like lines.
The power-law behaviour of the heating function was transmitted to the
predicted PDFs of each wavelength, although, in each case the index
![]() was far smaller than the -1.7 value of the heating function.
This behaviour is consistent with the findings of Parenti et al. (2006).
The minimum value of
was far smaller than the -1.7 value of the heating function.
This behaviour is consistent with the findings of Parenti et al. (2006).
The minimum value of ![]() was reached for the two Li-like lines,
because of the increase in the number of strands emitting a weak intensity; this was caused by the extension of their contribution function to higher temperatures.
was reached for the two Li-like lines,
because of the increase in the number of strands emitting a weak intensity; this was caused by the extension of their contribution function to higher temperatures.
To confirm that high temperature tails produced the lower
![]() values for Li-like ions, the contribution functions were truncated at high temperature and the calculations repeated. The PDFs were found to then have
values for Li-like ions, the contribution functions were truncated at high temperature and the calculations repeated. The PDFs were found to then have ![]() values that were consistent with the Fe IX and Fe XII lines, confirming our hypothesis.
This comparison demonstrated that the Li-like ions had a
different response to the heating function than other ions formed at
the same temperature, due to the high temperature tails of
the contribution functions.
values that were consistent with the Fe IX and Fe XII lines, confirming our hypothesis.
This comparison demonstrated that the Li-like ions had a
different response to the heating function than other ions formed at
the same temperature, due to the high temperature tails of
the contribution functions.
We then investigated weather the difference in the bandwidth of the instrument could have an effect on the shape of the PDF. We simulated the EIT intensities in the 171 and 195 channels, which were compared with the results presented in the previous section (Fig. 5) for the 171 and 195 emission lines observed by Hinode/EIS.
Comparing Figs. 4 and 5, the PDFs for the EIS lines have indices higher than those derived for the two EIT channels. We have therefore demonstrated that observing emission lines with a wide band imager can affect the PDF of the emission line. We note that the EIS Fe IX line is situated at the border of the instrument waveband for which the response is low. The predicted DN values are therefore very small and the line is not useful in practice for the study of small-scale brightenings.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.3cm,clip]{9928fig5a.eps}\\
\includegraphics[width=8.3cm,clip]{9928fig5b.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2008/48/aa09928-08/Timg28.gif) |
Figure 5: PDF for the counts in the EIT 171 (top) and 195 (bottom) channels. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
To compare with the spectrometer lines,
the intensities from the EIT channels were calculated by assuming a 1 s
exposure time, which is generally far lower than true EIT exposure times. For a more realistic case, we also calculated the PDFs assuming 60 s exposure times (similar exposure times are
reached during the high cadence EIT ``Shutterless''
program![]() ), and
verified that the PDFs retained the same power-law indices as for the
1 s case.
), and
verified that the PDFs retained the same power-law indices as for the
1 s case.
By hot lines, we indicate those lines that form at temperatures higher than the average coronal temperature.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8.3cm,clip]{9928fig6a.eps}\\
\hspace{2mm}\includegraphics[width=8.5cm,clip]{9928fig6b.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2008/48/aa09928-08/Timg29.gif) |
Figure 6: PDFs of Fe XVIII (top) and Fe XIX (bottom). |
| Open with DEXTER | |
The forbidden lines Fe XVIII 974.86 Å and Fe XIX 1118.06 Å are important because they appear at long UV wavelengths
close to cooler lines from the transition region and chromosphere.
A spectrometer observing these lines will therefore observe simultaneously lines
from distinct regions of the solar atmosphere, a feature valuable for
understanding the multithermal nature of coronal structures.
At
![]() Fe XVIII forms, close to the DEM peak (see
Figs. 2 and 3), where the loop threads can cool
by both conduction and radiation. Fe XIX forms during the cooling phase dominated by thermal conduction only (
Fe XVIII forms, close to the DEM peak (see
Figs. 2 and 3), where the loop threads can cool
by both conduction and radiation. Fe XIX forms during the cooling phase dominated by thermal conduction only (
![]() ). Figure 6 shows the PDFs for these lines (Fe XVIII at the top and Fe XIX at the bottom). The PDF for Fe XVIII does not have a power-law distribution, while Fe XIX reproduces well the statistical behaviour of the heating function. The Fe XIX line was also modelled by Parenti et al. (2006), who
found similar results. This finding is then a positive test for our
heating function, which, in contrast to Parenti et al. (2006), has been completely synthesised.
Unfortunately there are no strong observed EUV Li-like lines that form
at the same temperatures as Fe XVIII and Fe XIX. For this reason, we cannot directly compare with the results shown in Fig. 6.
). Figure 6 shows the PDFs for these lines (Fe XVIII at the top and Fe XIX at the bottom). The PDF for Fe XVIII does not have a power-law distribution, while Fe XIX reproduces well the statistical behaviour of the heating function. The Fe XIX line was also modelled by Parenti et al. (2006), who
found similar results. This finding is then a positive test for our
heating function, which, in contrast to Parenti et al. (2006), has been completely synthesised.
Unfortunately there are no strong observed EUV Li-like lines that form
at the same temperatures as Fe XVIII and Fe XIX. For this reason, we cannot directly compare with the results shown in Fig. 6.
As a final test, we compiled the intensity distribution for the most prominent line of the Li-like
Fe XXIV ion, which exibits a key flare doublet in the EIS
wavelength bands at 192.03 Å and 255.11 Å and whose emission peaks at
![]() (Young et al. 2007b). If nanoflares are
responsible for the heating in ARs, we would expect faint, non flaring,
emission at these temperatures (e.g. Patsourakos & Klimchuk 2006). In the
simulation used here, the loop system has low DEM values at these high temperatures (Fig.
2), but emission is still found at the Fe XXIV
line, which will be completely formed during the conduction phase. For the final reason, we would expect that the high temperature wing of the line would not affect the slope of the PDF.
Figure 7 shows the resulting PDF. As expected from the previous results, the distribution follows a power-law and the index
(Young et al. 2007b). If nanoflares are
responsible for the heating in ARs, we would expect faint, non flaring,
emission at these temperatures (e.g. Patsourakos & Klimchuk 2006). In the
simulation used here, the loop system has low DEM values at these high temperatures (Fig.
2), but emission is still found at the Fe XXIV
line, which will be completely formed during the conduction phase. For the final reason, we would expect that the high temperature wing of the line would not affect the slope of the PDF.
Figure 7 shows the resulting PDF. As expected from the previous results, the distribution follows a power-law and the index ![]() is close to that of the heating function
but in fact a little higher, in contrast to results for the other ions that have
been studied. We believe that this is because the line forms at the very end of
the heating function energy range, for which the statistics are probably too small
to be representative (see also the drop of the
is close to that of the heating function
but in fact a little higher, in contrast to results for the other ions that have
been studied. We believe that this is because the line forms at the very end of
the heating function energy range, for which the statistics are probably too small
to be representative (see also the drop of the
![]() at high temperatures in Fig. 2). This may be a limit to our diagnostic method.
at high temperatures in Fig. 2). This may be a limit to our diagnostic method.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=9cm,clip]{9928fig7.eps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2008/48/aa09928-08/Timg33.gif) |
Figure 7: The PDF of Fe XXIV. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
In this work, we have modelled the statistical behaviour of emission line intensities from a coronal loop, whose heating function is distributed as a log-normal distribution in energy. We investigated the plasma response for a wide range of temperatures, by simulating measurements from SOHO/SUMER, Hinode/EIS, and SOHO/EIT lines, and comparing with the earlier work of Parenti et al. (2006). Our results may be summarised as follows:
The results presented here were obtained using a simple, hydrodynamical model, halthough it has been shown that the model could reproduce the general properties of the plasma well. In the future, we will search for further confirmation of our findings by using an evolved version of our model.
Acknowledgements
S.P. would like to thank David Berghmans for the fruitful discussion. S.P. acknowledge the support from the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office through the ESA-PRODEX programme. This work was partially supported by the International Space Science Institute in the framework of an international working team (No. 108). CHIANTI is a collaborative project involving the NRL (USA), RAL (UK), MSSL (UK), the Universities of Florence (Italy) and Cambridge (UK), and George Mason University (USA).