A&A 491, L1-L4 (2008)
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:200810641
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Winds of M-type AGB stars driven by micron-sized grains
S. Höfner
Department of Physics & Astronomy,
Division of Astronomy & Space Physics,
Uppsala University,
Box 515, 751 20 Uppsala, Sweden
Received 18 July 2008 / Accepted 11 September 2008
Abstract
Context. In view of the recent problem regarding the dynamical modelling of winds of M-type AGB stars (insufficient radiation pressure on silicate grains), some of the basic assumptions of these models need to be re-evaluated critically.
Aims. Accepting the conclusion that non-grey effects will force silicate grains to be virtually Fe-free, the viability of driving winds with micron-sized Fe-free silicates, instead of small particles, is examined.
Methods. Using both simple estimates and detailed dynamical atmosphere and wind models, it is demonstrated that radiation pressure on Fe-free silicate grains is sufficient to drive outflows if the restriction to the small particle limit is relaxed, and prevailing thermodynamic conditions allow grains to grow to sizes in the micrometer range.
Results. The predicted wind properties, such as mass loss rates and outflow velocities, are in good agreement with observations of M-type AGB stars. Due to a self-regulating feedback between dust condensation and wind acceleration, grain growth naturally comes to a halt at particle diameters of about 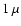 m.
m.
Conclusions. The most efficient grain sizes to drive winds are in a rather narrow interval around 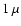 m. These values are set by the wavelength range corresponding to the flux maximum in typical AGB stars, and are very similar to interstellar grains.
m. These values are set by the wavelength range corresponding to the flux maximum in typical AGB stars, and are very similar to interstellar grains.
Key words: stars: AGB and post-AGB - stars: mass-loss - stars: atmospheres - stars: winds,
outflows - circumstellar matter - dust, extinction
1 Introduction
Mass loss through slow stellar winds is a decisive feature of AGB stars which influences both their evolution and their observable properties. The basic scenario for this process is that of a
pulsation-enhanced dust-driven wind: stellar pulsation triggers propagating atmospheric shock waves which intermittently lift gas above the stellar surface, creating dense, cool layers where solid
particles may form. The grains are accelerated away from the star by radiation pressure, dragging the gas along. The composition of the dust is determined by the relative elemental abundances in the
stellar atmosphere, with C-rich stars forming mostly amorphous carbon grains, and M-type objects producing silicate particles.
For the case of C-rich AGB stars, this scenario has successfully passed many tests, e.g., comparisons of detailed self-consistent dynamical models with observations as diverse as low-resolution IR spectra (e.g., Gautschy-Loidl et al. 2004) and line profile
variations of CO vibration-rotation lines (e.g., Nowotny et al. 2005).
However, similar models for M-type AGB stars (Woitke 2006; Höfner & Andersen 2007) recently demonstrated two things: (i) silicate particles will be basically Fe-free due to non-grey effects on the grain temperature which were not apparent in earlier grey models (e.g., Jeong et al. 2003); and (ii) small Fe-free silicate particles result in insufficient radiative pressure to drive a wind since they are rather transparent at wavelengths around 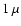 m, corresponding to the flux maximum in AGB stars.
m, corresponding to the flux maximum in AGB stars.
In this paper, the cross-section relevant for radiative pressure on
Fe-free silicates is examined for a wide range of particle sizes,
and the viability of micrometer-sized grains as wind drivers in
M-type AGB stars is demonstrated, both with simple estimates and
with detailed radiation-hydrodynamical models.
2 Silicates: Mg/Fe and grain size
To be considered for the short list of candidate AGB star wind drivers, any grain type must
- have a sufficiently high flux mean opacity per mass;
- form in sufficient quantities in the challenging environment of a pulsating atmosphere.
The first condition can be expressed as
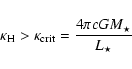 |
(1) |
where
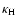 denotes the flux mean opacity (cross-section per mass), and
denotes the flux mean opacity (cross-section per mass), and 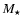 and
and 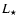 are the stellar mass and luminosity, respectively, with c and G representing the speed of light and the gravitation constant.
are the stellar mass and luminosity, respectively, with c and G representing the speed of light and the gravitation constant.
The second condition is somewhat more complicated to specify as a
quantitative criterion but it can be broken down into two separate
estimates, i.e., how close to the stellar surface a certain grain
type can form/survive, and how fast the grains (and, consequently,
the amount of dust) will grow in given thermodynamical and chemical
conditions. The condensation distance is mainly a question of grain
temperature, while the growth rate and the maximum possible
abundance of a dust type depend on the density and abundances of raw
material for grain formation. Typical element abundances, together
with observations of characteristic spectral features, lead to the
expectation that silicates in the form of olivine, i.e.
Mg2xFe2(1-x)SiO4 (
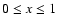 ), and/or pyroxene,
i.e. MgxFe(1-x)SiO3, are the dominant dust species in
M-type AGB stars.
), and/or pyroxene,
i.e. MgxFe(1-x)SiO3, are the dominant dust species in
M-type AGB stars.
A grain's temperature will be mostly determined by its interaction
with the radiation field. We can make a simple estimate for the
condensation radius 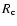 by defining it as the distance where the
radiative equilibrium temperature of a grain is equal to the
condensation temperature
by defining it as the distance where the
radiative equilibrium temperature of a grain is equal to the
condensation temperature 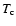 of the material. Assuming a Planckian
radiation field, geometrically diluted with distance from the star,
and a power law for the grain absorption coefficient,
of the material. Assuming a Planckian
radiation field, geometrically diluted with distance from the star,
and a power law for the grain absorption coefficient,
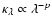 ,
in the relevant wavelength
range (around the flux maximum of the star) the condensation radius
can be expressed as
,
in the relevant wavelength
range (around the flux maximum of the star) the condensation radius
can be expressed as
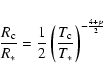 |
(2) |
(cf. Höfner 2007, and references therein for details). This implies that silicates forming in atmospheres of AGB stars (
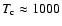 K,
K,
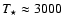 K) have to be virtually iron-free, as the inclusion of Fe leads to
K) have to be virtually iron-free, as the inclusion of Fe leads to
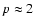 and, consequently, to
and, consequently, to
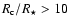 ,
whereas iron-free silicates (
,
whereas iron-free silicates (
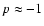 )
can form at typically
)
can form at typically
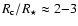 .
These numbers are in good agreement with detailed models (Woitke 2006; Höfner & Andersen 2007).
.
These numbers are in good agreement with detailed models (Woitke 2006; Höfner & Andersen 2007).
Having concluded that the silicates will be Fe-free, we are faced with the fact that such grains are nearly transparent at wavelengths around 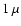 m, meaning that their absorption cross section
m, meaning that their absorption cross section
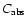 is very low. In the case of particles being small compared to
the relevant wavelengths, the grain cross section determining the radiative pressure,
is very low. In the case of particles being small compared to
the relevant wavelengths, the grain cross section determining the radiative pressure,
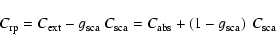 |
(3) |
(where
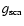 is the mean of the cosine of the angle of scattering; cf., e.g., Krügel 2003), is dominated by the extinction cross section
is the mean of the cosine of the angle of scattering; cf., e.g., Krügel 2003), is dominated by the extinction cross section
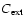 ,
which in turn is equivalent to the absorption cross-section
,
which in turn is equivalent to the absorption cross-section
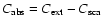 ,
as scattering is negligible (
,
as scattering is negligible (
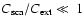 )
in this limit. This leads to the previously discussed problem of insufficient opacity for driving winds. As grains become larger and
approach sizes comparable to the wavelength of interest, however, scattering plays an increasingly important role, and starts to dominate
)
in this limit. This leads to the previously discussed problem of insufficient opacity for driving winds. As grains become larger and
approach sizes comparable to the wavelength of interest, however, scattering plays an increasingly important role, and starts to dominate
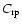 .
.
While cross-sections as such are useful for comparing individual grains of different sizes and materials, we need the total opacity (cross section per mass),
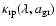 ,
of all grains of a certain radius
,
of all grains of a certain radius
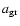 in a matter element (with a total mass density
in a matter element (with a total mass density 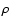 )
at wavelength
)
at wavelength 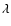 to estimate their contribution to the radiative pressure. Introducing the efficiency
to estimate their contribution to the radiative pressure. Introducing the efficiency
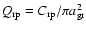 and denoting the number density of grains of radius
and denoting the number density of grains of radius
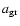 by
by
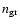 ,
we can write this opacity as
,
we can write this opacity as
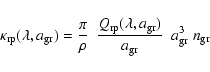 |
(4) |
where
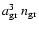 represents the fraction of a given volume which is occupied by the grains, apart from a factor
represents the fraction of a given volume which is occupied by the grains, apart from a factor 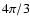 .
This quantity can be rewritten in terms of the space
occupied by a monomer (basic building block) in the condensed material times the number of monomers found in a certain volume,
.
This quantity can be rewritten in terms of the space
occupied by a monomer (basic building block) in the condensed material times the number of monomers found in a certain volume,
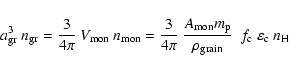 |
(5) |
where we have expressed the monomer volume
 in terms of the atomic weight of the monomer
in terms of the atomic weight of the monomer
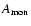 and the density of the grain material
and the density of the grain material
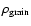 ,
and the number of monomers in a volume
,
and the number of monomers in a volume
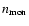 by the abundance of the key element of the condensate
by the abundance of the key element of the condensate
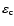 ,
the degree of condensation of this key element
,
the degree of condensation of this key element 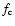 ,
and the total number density of H atoms
,
and the total number density of H atoms 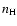 (
(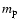 = proton mass). Using
= proton mass). Using
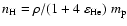 ,
we obtain
,
we obtain
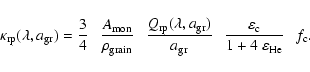 |
(6) |
Figure 1 shows the opacity
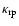 of Fe-free olivine grains (forsterite, Mg2SiO4) as a function of wavelength and grain radius
of Fe-free olivine grains (forsterite, Mg2SiO4) as a function of wavelength and grain radius
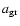 relative to the critical
opacity
relative to the critical
opacity
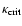 (Eq. (1)), assuming that 30 percent of the Si are condensed into dust (
(Eq. (1)), assuming that 30 percent of the Si are condensed into dust (
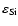 = 3.55
= 3.55 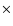 10-5,
10-5,
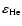 = 0.1,
= 0.1,
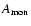 = 140,
= 140,
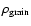 = 3.27 g/cm3). The quantity
= 3.27 g/cm3). The quantity
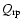 has been calculated using Mie theory for spherical particles (program BHMIE from Bohren & Huffman 1983, modified by Draine, www.astro.princeton.edu/~draine/scattering.html) and refractive index data by Jäger et al. (2003). The critical opacity is taken for a stellar mass of
has been calculated using Mie theory for spherical particles (program BHMIE from Bohren & Huffman 1983, modified by Draine, www.astro.princeton.edu/~draine/scattering.html) and refractive index data by Jäger et al. (2003). The critical opacity is taken for a stellar mass of
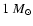 and a luminosity of
and a luminosity of
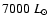 .
For wavelengths around
.
For wavelengths around 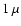 m, starting from very low values for small grains, the opacity reaches a pronounced maximum for particles of
m, starting from very low values for small grains, the opacity reaches a pronounced maximum for particles of
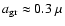 m, and then decreases again. Looking at the actual values of the opacity, there are several regions where it clearly exceeds the critical opacity: a diagonal band where
m, and then decreases again. Looking at the actual values of the opacity, there are several regions where it clearly exceeds the critical opacity: a diagonal band where
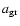 is about equal to the wavelength, and two vertical zones, corresponding to two maxima of
is about equal to the wavelength, and two vertical zones, corresponding to two maxima of
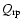 near
near 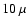 m which produce the characteristic silicate feature in spectra of M-type AGB stars.
m which produce the characteristic silicate feature in spectra of M-type AGB stars.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8cm]{0641f1}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2008/44/aa10641-08/Timg61.gif) |
Figure 1:
Opacity
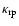 of forsterite grains in units of the critical opacity
of forsterite grains in units of the critical opacity
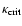 (
(
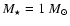 , ,
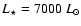 ), assuming that 30 percent of Si is condensed into grains; The black contour shows the region where the flux-weighted opacity exceeds the critical opacity, assuming a Planckian flux distribution with ), assuming that 30 percent of Si is condensed into grains; The black contour shows the region where the flux-weighted opacity exceeds the critical opacity, assuming a Planckian flux distribution with
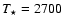 K. K. |
| Open with DEXTER |
In order to decide which grains will contribute to driving a wind,
however, the opacity needs to be weighted with the relative flux as
a function of wavelength. For simplicity, we assume that the stellar
flux can be approximated by a Planck function, and we define the
monochromatic flux-weighted opacity as
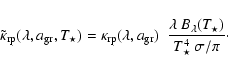 |
(7) |
The black contour in Fig. 1 shows the region where this opacity exceeds the critical opacity for
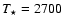 K. This last criterion limits the effective sizes for grains to a rather
narrow interval around
K. This last criterion limits the effective sizes for grains to a rather
narrow interval around
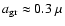 m. Only grains in this size range can drive the wind, and a considerable fraction of the available material has to be contained in these grains to
push the total opacity above the critical value.
m. Only grains in this size range can drive the wind, and a considerable fraction of the available material has to be contained in these grains to
push the total opacity above the critical value.
So far, we have deduced that silicate grains in M-type AGB stars have to be virtually Fe-free to bring the condensation distance down well below
 ,
and they have to have particle radii in
the range of about
,
and they have to have particle radii in
the range of about
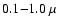 m to achieve a large radiative cross-section. The remaining question is, whether sufficient amounts of material are able to condense into grains in the variable
conditions of the stellar atmosphere. While it is possible to make simple estimates for grain growth time scales based on densities, abundances, and grain properties (cf. Gustafsson & Höfner
2004), this question will be answered with detailed wind models presented in the next section.
m to achieve a large radiative cross-section. The remaining question is, whether sufficient amounts of material are able to condense into grains in the variable
conditions of the stellar atmosphere. While it is possible to make simple estimates for grain growth time scales based on densities, abundances, and grain properties (cf. Gustafsson & Höfner
2004), this question will be answered with detailed wind models presented in the next section.
3 Detailed dynamical models
In order to test the hypothesis of micron-sized Fe-free silicate grains as wind drivers in a reasonably realistic setting, the dynamical atmosphere and wind models of Höfner et al. (2003) are adapted by including routines which compute frequency-dependent dust
opacities for arbitrary grain sizes (cf. Sect. 2). In contrast to earlier versions, the models contain a time-dependent description of grain growth for silicate grains and they are based
on radiative transfer in 319 wavelength points (instead of 64), to ensure a better coverage of the complex radiation field, taking both molecular and grain opacities into account. In the present context, we consider the formation of pure forsterite particles according to
the net reaction
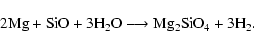 |
(8) |
The grain growth rate is calculated following Gail & Sedlmayr
(1999), assuming that the step determining the total rate is the
addition of a SiO molecule to the grain surface. The vapor pressure
of SiO over olivine is based on data for free energies from Sharp &
Huebner (1990).
![\begin{figure}
\par\hspace*{-2mm}\includegraphics[width=7.2cm]{0641f2ab} %
\par\vspace*{5mm}
\includegraphics[width=7cm]{0641f2c}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2008/44/aa10641-08/Timg66.gif) |
Figure 2:
Snapshot of the spatial structure of model B with
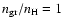 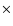 10-15: top: velocity, middle: grain radius, bottom: grain temperature (solid) and gas temperature (dashed).
10-15: top: velocity, middle: grain radius, bottom: grain temperature (solid) and gas temperature (dashed). |
| Open with DEXTER |
While treating the growth of grains with a detailed time-dependent
description, the nucleation of new grains from the gas phase is not
considered, assuming the presence of seed nuclei (a given number per
H atom,
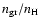 )
at the point where grain growth
becomes possible. At present, this is necessary due to the lack of
nucleation rates for such grains. The value of
)
at the point where grain growth
becomes possible. At present, this is necessary due to the lack of
nucleation rates for such grains. The value of
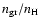 is varied within (but not fully covering) a range which, in
principle, allows particles to grow to sizes up to and beyond the
micrometer range. At the upper end of the viable
is varied within (but not fully covering) a range which, in
principle, allows particles to grow to sizes up to and beyond the
micrometer range. At the upper end of the viable
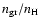 range (many particles), grain growth will be limited by the
availability of material, resulting in small grains and,
consequently, a too low radiative cross-section to drive a wind. At
the lower end (few particles), grains may grow quickly beyond the
efficient size range to drive a wind (see contour in
Fig. 1), leading to a rather low total opacity, even for
high degrees of condensation. Since the relevant interval of grain
radii is about one order of magnitude, the corresponding range in
range (many particles), grain growth will be limited by the
availability of material, resulting in small grains and,
consequently, a too low radiative cross-section to drive a wind. At
the lower end (few particles), grains may grow quickly beyond the
efficient size range to drive a wind (see contour in
Fig. 1), leading to a rather low total opacity, even for
high degrees of condensation. Since the relevant interval of grain
radii is about one order of magnitude, the corresponding range in
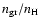 should span about 3 orders of magnitude for a
given
should span about 3 orders of magnitude for a
given 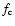 (cf. Eq. (5)).
(cf. Eq. (5)).
It should be noted that the actual value of
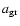 is a result
of the models, not a parameter. For a given
is a result
of the models, not a parameter. For a given
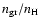 ,
the final grain radius is determined by the growth rates under the
prevailing dynamical and thermodynamical conditions in the
atmosphere and wind.
,
the final grain radius is determined by the growth rates under the
prevailing dynamical and thermodynamical conditions in the
atmosphere and wind.
The parameters and resulting wind properties of the detailed models
are listed in Table 1 (
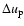 = velocity
amplitude of piston). The letters A and B denote different
combinations of stellar parameters, i.e., mass
= velocity
amplitude of piston). The letters A and B denote different
combinations of stellar parameters, i.e., mass
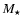 ,
luminosity
,
luminosity
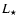 ,
effective temperature
,
effective temperature
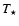 (initial model) and pulsation period P (solar abundances,
Grevesse et al. 1996)
(initial model) and pulsation period P (solar abundances,
Grevesse et al. 1996)
| Model |
![${M_{\star}} [{M_{\odot}}]$](/articles/aa/full/2008/44/aa10641-08/img70.gif) |
![${L_{\star}} [{L_{\odot}}]$](/articles/aa/full/2008/44/aa10641-08/img71.gif) |
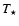 [K]
[K] |
P [d] |
| A |
1.0 |
5000 |
2800 |
310 |
| B |
1.0 |
7000 |
2700 |
390 |
Table 1:
Model parameters and resulting wind properties.
The resulting mass loss rates 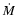 and wind velocities
and wind velocities
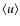 are in good agreement with observed values for M-type AGB stars (cf. Olofsson 2004, and references therein), and the predicted grain sizes
are in good agreement with observed values for M-type AGB stars (cf. Olofsson 2004, and references therein), and the predicted grain sizes
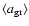 are in
accordance with the simple estimates in Sect. 2. The
fact that the mean degrees of condensation of Si
are in
accordance with the simple estimates in Sect. 2. The
fact that the mean degrees of condensation of Si
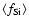 are well below 0.5 (limit for forsterite due to Mg abundance) is a consequence of grain growth practically coming to a halt when sizes efficient for driving the wind are reached, due to
the acceleration of the wind and the resulting fast decrease in gas
densities. This is also illustrated by Fig. 2, showing
a snapshot of the radial structure of a selected model.
are well below 0.5 (limit for forsterite due to Mg abundance) is a consequence of grain growth practically coming to a halt when sizes efficient for driving the wind are reached, due to
the acceleration of the wind and the resulting fast decrease in gas
densities. This is also illustrated by Fig. 2, showing
a snapshot of the radial structure of a selected model.
Both simple estimates and results of detailed radiation-hydrodynamical models presented in this article demonstrate that winds of M-type AGB stars can be driven by radiation pressure on micron-sized Fe-free silicate grains. Particles in this size range have a considerable radiative
scattering cross-section which compensates for their low absorption cross-section, leading to efficient radiative acceleration. Resulting combinations of mass loss rates and wind velocities are in good agreement with observations, and a less than 30 percent fraction of Si condensed into forsterite is sufficient to drive winds for typical stellar parameters.
The results presented here are for solar abundances and olivine grains, but similar arguments should hold for pyroxene particles. Different chemical compositions of both the gas phase and the
condensates will be discussed in a forthcoming paper. As C/O approaches 1 (S-type AGB stars), silicate formation will eventually be limited by the lack of oxygen not bound in CO, rather than by the abundances of Si and Mg. The fact that S stars show similar wind properties as M- and C-type AGB stars (Ramstedt et al. 2006) may indicate that some oxygen is made available for grain formation by partial breaking up of CO due to shocks. The scenario suggested by Höfner & Andersen (2007)
could be modified such that silicate grains contribute to or take over the wind-driving for stars with somewhat more oxygen than carbon.
The probably most attractive conclusion based on the current results
is that silicate grains from AGB stars found in the
interstellar
medium should be expected to have diameters of the order of 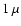 m - provided they are driving the stellar outflow - due to a self-regulating feedback between grain growth and wind acceleration.
Particles produced in this way will fall into a rather narrow size range which coincides with observations of grains in the interstellar medium.
m - provided they are driving the stellar outflow - due to a self-regulating feedback between grain growth and wind acceleration.
Particles produced in this way will fall into a rather narrow size range which coincides with observations of grains in the interstellar medium.
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the Swedish Research Council (Vetenskapsrådet).
- Andersen, A. C.,
Höfner, S., & Gautschy-Loidl, R. 2003, A&A, 400,
981 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences]
- Bohren, C. F., &
Huffman, D. 1983, Absorption and scattering of light by small
particles (New York: John Wiley)
(In the text)
- Gail, H.-P., &
Sedlmayr, E. 1999, A&A, 347, 594 [NASA ADS]
(In the text)
- Gautschy-Loidl, R.,
Höfner, S., Jørgensen, U. G., & Hron, J. 2004,
A&A, 422, 289 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences]
(In the text)
- Gustafsson, B., &
Höfner, S. 2004, in Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars, ed. H. J.
Habing, & H. Olofsson (Springer)
(In the text)
- Grevesse, N., Noels,
A., & Sauval, J. 1996, ASP Conf. Ser., 99, 117 [NASA ADS]
(In the text)
- Höfner, S. 2007,
ASP Conf. Ser., 378, 145 [NASA ADS]
(In the text)
- Höfner, S.,
& Andersen, A. C. 2007, A&A, 465, L39 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences]
(In the text)
- Höfner, S.,
Gautschy-Loidl, R., Aringer, B., & Jørgensen, U. G. 2003,
A&A, 399, 589 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences]
(In the text)
- Jäger, C.,
Dorschner, J., Mutschke, H., Posch, Th., & Henning, Th. 2003,
A&A, 408, 193 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences]
(In the text)
- Jeong, K. S., Winters,
J. M., Le Bertre, T., & Sedlmayr, E. 2003, A&A, 407,
191 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences]
(In the text)
- Krügel, E. 2003,
The Physics of Interstellar Dust, IoP
(In the text)
- Nowotny, W., Aringer,
B., Höfner, S., Gautschy-Loidl, R., & Windsteig, W. 2005,
A&A, 437, 273 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences]
(In the text)
- Olofsson, H. 2004, in
Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars, ed. H. Habing, & H. Olofsson
(New York: Springer)
(In the text)
- Ramstedt, S.,
Schöier, F. L., Olofsson, H., & Lundgren, A. A. 2006,
A&A, 454, L103 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences]
(In the text)
- Sharp, C. M., &
Huebner, W. F. 1990, ApJS, 72, 417 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef]
(In the text)
- Woitke, P. 2006,
A&A, 460, L9 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences]
(In the text)
Copyright ESO 2008
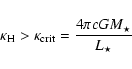
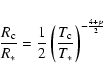
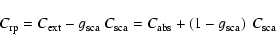
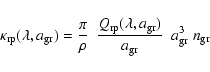
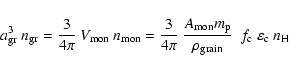
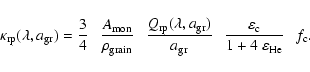
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8cm]{0641f1}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2008/44/aa10641-08/Timg61.gif)
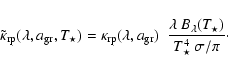
![\begin{figure}
\par\hspace*{-2mm}\includegraphics[width=7.2cm]{0641f2ab} %
\par\vspace*{5mm}
\includegraphics[width=7cm]{0641f2c}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2008/44/aa10641-08/Timg66.gif)