All Tables
- Table 1:
Radius and central thermodynamic properties of a planet of mass
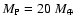 at 1 Gyr with a total heavy element mass fraction
at 1 Gyr with a total heavy element mass fraction
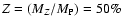 .
Results for different heavy element compositions (water = W, rock = R, iron = I) and EOS (aneos = a, sesame = s, SCVH = SC) and different heavy element distributions are given.
.
Results for different heavy element compositions (water = W, rock = R, iron = I) and EOS (aneos = a, sesame = s, SCVH = SC) and different heavy element distributions are given.
- Table 2:
Radius and central thermodynamic properties of a planet of mass
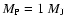 at 1 Gyr for two
heavy element mass fractions
at 1 Gyr for two
heavy element mass fractions
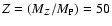 % and Z=20%. The labels are the same as in Table 1. As mentioned at the end of Sect. 4.2, for Z=50%, the solution with
% and Z=20%. The labels are the same as in Table 1. As mentioned at the end of Sect. 4.2, for Z=50%, the solution with
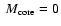 and
and
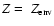 is similar to a solution with
is similar to a solution with
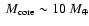 and the rest of the heavy material distributed in the
envelope.
and the rest of the heavy material distributed in the
envelope.
- Table 3:
Radius of a 22.6
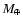 planet at 2 Gyr with different water core masses, EOS and levels of irradiation, characterised by a stellar incident flux,
planet at 2 Gyr with different water core masses, EOS and levels of irradiation, characterised by a stellar incident flux,
 .
Two cases are considered: no irradiation (
.
Two cases are considered: no irradiation (
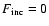 )
and
)
and
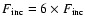 of GJ 436b. Comparison is done with the pure water (ice) case of Seager et al. (2007).
Results based on the assumption of a uniform core temperature of T=300 K are also given.
of GJ 436b. Comparison is done with the pure water (ice) case of Seager et al. (2007).
Results based on the assumption of a uniform core temperature of T=300 K are also given.
- Table 4:
Radii of planets (in
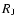 )
in the mass range 20
)
in the mass range 20
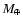 -1
-1 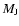 for different levels of heavy element enrichment Z (see text, Sect. 7.2, for the choice of the heavy material
distribution) and at different ages.
for different levels of heavy element enrichment Z (see text, Sect. 7.2, for the choice of the heavy material
distribution) and at different ages.
- Table 5:
Same as Table 4 for irradiated models by a Sun at 0.045 AU.