All Tables
- Table 1:
The sources and numbers of light curves NLC used to define the classes, their average total time span
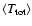 and their average number of measurements
and their average number of measurements
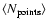 .
.
- Table 2:
Stellar variability classes considered in this study, their code, the
number of light curves we used (NLC) and their source. Also listed (when relevant for
the class) are the ranges for the parameters
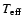 and
and 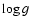 if they
could be determined from the literature. The last two columns list the range for the dominant frequencies (f1) and their amplitudes (A11) present in the light curves, resulting from our analysis (Sect. 2.1).
if they
could be determined from the literature. The last two columns list the range for the dominant frequencies (f1) and their amplitudes (A11) present in the light curves, resulting from our analysis (Sect. 2.1).
- Table 3:
The Confusion Matrix for the Gaussian Mixture method, using 25variability classes and 12 classification attributes. The last but one line
lists the total number of light curves (TOT) to define every class. The last
line lists the correct classification rate (CC) for every class separately. The
average correct classification rate is about
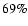 .
.
- Table 4:
The confusion matrix for the Gaussian mixture method using 14variability classes and 28 classification attributes. The last but one line
lists the total number of light curves (TOT) to define every class. The last
line lists the correct classification rate (CC) for every class separately. The
average correct classification rate is about
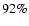 .
.
- Table 5:
The confusion matrix for the Bayesian model averaging of
artificial neural networks. The last but one line lists the total
number of light curves (TOT) to define every class. The last line
lists the correct classification rate (CC) for every class separately
as measured by 10 fold cross validation.
- Table 6:
The confusion matrix for the Bayesian model averaging of artificial
neural networks and the two class problem. The last but one line lists the
total number of light curves (TOT) to define every class. The last line lists
the correct classification rate (CC) for every class separately as measured by
10-fold cross validation. Separation between: A: eclipsing binaries (ECL) and
all other types; B: Cepheids (CEP) and all other types; C: long period variables
(LPV) and all other types except ECL and CEP; D: RR Lyrae stars (RR) from all
other types except ECL, CEP and LPV.
- Table 7:
The confusion matrix for the Bayesian model averaging of artificial
neural networks. The last but one line lists the total number of light curves
(TOT) to define every class. The last line lists the correct classification rate
(CC) for every class separately as measured by 10-fold cross validation.
Separation between: A: Cepheids; B: long period variables; C: RR Lyrae stars.
- Table 8:
The confusion matrix for the Bayesian model averaging of artificial
neural networks for the variables not assigned to any group. The last but one
line lists the total number of light curves (TOT) to define every class. The
last line lists the correct classification rate (CC) for every class separately
as measured by 10-fold cross validation.
- Table 9:
The complete confusion matrix for the Bayesian model averaging of
artificial neural networks. The last but one line lists the total number of light
curves (TOT) to define every class. The last line lists the correct
classification rate (CC) for every class separately as measured by 10-fold cross
validation.