All Tables
- Table 3:
Hardness Ratio
![$H_{\rm h}=S[2,30]/S[30,400]$](/articles/aa/full/2006/48/aa4501-05/img1.gif) and
and
![$H_{\rm s}=S[2,10]/S[40,700]$](/articles/aa/full/2006/48/aa4501-05/img2.gif) for 54 XRRs/XRFs.
for 54 XRRs/XRFs.
- Table 4:
Mean values and standard deviation of spectral parameters
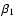 ,
,
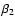 and
and
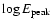 for the parent distribution of XRRs/XRFs and GRBs classes, according to the likelihood method. In the last row is the
for the parent distribution of XRRs/XRFs and GRBs classes, according to the likelihood method. In the last row is the
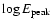 instrinsic mean value for the subsample of events used for the X-ray afterglow flux analysis in Sect. 4.3.
instrinsic mean value for the subsample of events used for the X-ray afterglow flux analysis in Sect. 4.3.
- Table 5:
Intrinsic Peak Energy, Isotropic Energy [1, 1000 keV] and redshift values or constraints for 14 XRRs/XRFs: the Type column indicates if the measure of the redshift is obtained from Host Galaxy spectroscopy (HG), or from Optical afterglow spectroscopy (OT). We report also the pseudo-redshift for 6 possibly high redshift GRBs(16).
- Table 6:
Afterglow properties of 54 XRRs/XRFS: X-ray ToO observations (AX), time in days of the start of ToO and satellite which performed the observation, optical afterglow detection (OT), time of the OT detection and observed magnitude, Radio afterglow detection (RT) and host galaxy detection.
- Table 7:
The X-ray
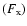 and optical
and optical
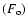 flux of the afterglow at 40 ks and their ratio
flux of the afterglow at 40 ks and their ratio
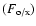 ;
;
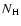 is the hydrogen column density,
is the hydrogen column density,
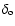 is the temporal index decay of the optical afterglow and
is the temporal index decay of the optical afterglow and
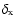 is the temporal decay index of the X-ray afterglow.
is the temporal decay index of the X-ray afterglow.
- Table 8:
Intrinsic mean value and variance of the logarithm of the X-ray [1.6-10 keV] and optical flux [R band], at 40 ks for XRRs/XRFs with early afterglow observations and GRBs. The X-ray flux is in units of
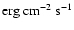 and the optical flux
in units of
and the optical flux
in units of
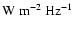 .
.
- Table 1:
Spectral parameters of 54 XRRs/XRFs. The models used are: BAND = Band function, PL = powerlaw as N(E) =
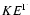 ,
PLE = powerlaw
,
PLE = powerlaw 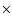 exponential cutoff as N(E) =
exponential cutoff as N(E) =
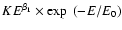 ,
PLA = absorbed powerlaw as N(E) =
,
PLA = absorbed powerlaw as N(E) =
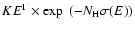 .
When not given directly, we have derived
.
When not given directly, we have derived
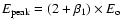 .
.
- Table 2:
General properties of 54 events XRRs/XRFs: Time UT of the burst trigger, instrument of the observation, fluences in
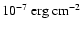 in the energy range 30-400 keV (S[30, 400]), 2-30 keV (S[2, 30]), 40-700 keV (S[40, 700]) and 2-10 keV (S[2, 10]).
in the energy range 30-400 keV (S[30, 400]), 2-30 keV (S[2, 30]), 40-700 keV (S[40, 700]) and 2-10 keV (S[2, 10]).