All Tables
- Table 1:
Chemical composition of stellar models with total metallicity Z, initial helium Y0,
hydrogen abundance X0, iron abundance with respect to
hydrogen (in spectroscopic notation [Fe/H]) and total metallicity with respect to hydrogen [M/H].
- Table 2:
Combinations of age indicators. The weight wi
in Eq. (3) is given for each indicator.
- Table 3:
Indicator value, age
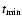 ,
minimum value
,
minimum value
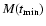 ,
and fit quality Q for all age indicators applied to NGC 6934.
,
and fit quality Q for all age indicators applied to NGC 6934.
- Table 4:
Comparison of bump properties for stellar models of
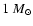 and Z=0.001. The references are:
Girardi et al. (2000, Padova), Cariulo et al. (2004, Pisa),
Pietrinferni et al. (2004, BASTI), and Kim et al. (2002, Y2).
and Z=0.001. The references are:
Girardi et al. (2000, Padova), Cariulo et al. (2004, Pisa),
Pietrinferni et al. (2004, BASTI), and Kim et al. (2002, Y2).
- Table 5:
Ages (in Gyr) for galactic globular clusters
from Case A (Col. 4), from Case S (Col. 5) and quoted from
Salaris & Weiss (2002, Col., "SW02''). The age range is that for which M(t) has
Q > 0.32 (
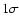 -range). If only one age is given, it is
-range). If only one age is given, it is
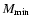 ,
with
,
with
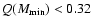 .
Columns 7 and 8 contain the result when using
the BASTI isochrones (Pietrinferni et al. 2004) for Case A, and for case BC
(see Table 2), which includes the bump brightness. Case S is not shown as it is not better than for our own isochrones.
.
Columns 7 and 8 contain the result when using
the BASTI isochrones (Pietrinferni et al. 2004) for Case A, and for case BC
(see Table 2), which includes the bump brightness. Case S is not shown as it is not better than for our own isochrones.
- Table 6:
Data of the critical points of all Globular
Cluster Colour-Magnitude Diagrams in our sample as determined by us
(see Sect. 3); part I: the turn-off region and colours of turn-off,
lower RGB, and bump.
- Table 7:
As Table 6, but displaying horizontal branch, RGB bump, and
tip brightness as well as the cluster distances inferred from
 and
and
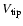 .
.
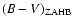 is the colour of the point on the ZAHB
closest to the TO colour.
is the colour of the point on the ZAHB
closest to the TO colour.
- Table 8:
Polynomial relations for points along our
isochrones used as age indicators. The relations are all of
the form
f(t)=a0+a1t+a2t2+a3t3, where t is in Gyr.
Part I: V-magnitudes.
- Table 9:
As Table 8. Part II: Colours.