- ...
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Member of the Carrera del Investigador
Científico y Tecnológico, CONICET, Argentina.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... 0.228)
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- In
particular, the surface abundance of oxygen depends on the free
parameter f of overshooting (which is a measure of the extent of the
overshoot region) and the number of thermal pulses considered during
the AGB phase (see Herwig 2000).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
mass
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- We change the stellar mass in the following way. In our
evolutionary code, the independent variable is
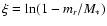 ,
where M* is the stellar mass and mr the mass
contained in a sphere of radius r. When the stellar mass is changed
(say to M'*), the
,
where M* is the stellar mass and mr the mass
contained in a sphere of radius r. When the stellar mass is changed
(say to M'*), the 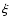 values at each grid point are the same as
before; so, the new mass at a given
values at each grid point are the same as
before; so, the new mass at a given 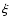 is
is
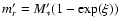 .
The chemical composition at each
.
The chemical composition at each 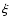 is the same as before,
but the mass contained at
is the same as before,
but the mass contained at 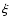 is different. For instance, if
M'* <
M*, then
m'r < mr at a given
is different. For instance, if
M'* <
M*, then
m'r < mr at a given 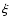 .
Note that this procedure is
different from, for instance, simply extracting mass from the outer
layers.
.
Note that this procedure is
different from, for instance, simply extracting mass from the outer
layers.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
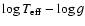 plane
plane![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- This procedure has been employed, for instance, by
O'Brien (2000) on a 0.573-
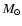 post-AGB evolutionary model.
post-AGB evolutionary model.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...1974)
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Specifically, a mode is classified as g if the
number of nodes in the G-region exceeds the number of nodes
in the P-region (
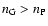 ), and is classified as
p if
), and is classified as
p if
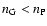 .
We then assign the radial order
according to
.
We then assign the radial order
according to
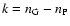 for g-modes, or
for g-modes, or
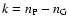 for p-modes.
for p-modes.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.