A&A 454, 609-615 (2006)
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20054792
P. J. D. Mauas1 - C. Cacciari2 - L. Pasquini3
1 - Instituto de Astronomía y Física del Espacio, Buenos Aires, Argentina
2 -
INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna, via Ranzani 1, 40127 Bologna,
Italy
3 -
European Southern Observatory, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, 85749
Garching b. München, Germany
Received 30 December 2005 / Accepted 21 March 2006
Abstract
In this study we test the possibility that the asymmetry
in the profiles of the H![]() and Ca II K lines in red giant stars
is due to the presence of an active chromosphere rather than to mass loss.
To this end, we compare line profiles computed using relevant model
chromospheres to profiles of the H
and Ca II K lines in red giant stars
is due to the presence of an active chromosphere rather than to mass loss.
To this end, we compare line profiles computed using relevant model
chromospheres to profiles of the H![]() and Ca II K lines observed
in five red giant stars of the globular cluster NGC 2808.
The spectra were taken with FLAMES during the science verification, using the
UVES mode at high resolution (R=43 000) for the H
and Ca II K lines observed
in five red giant stars of the globular cluster NGC 2808.
The spectra were taken with FLAMES during the science verification, using the
UVES mode at high resolution (R=43 000) for the H![]() line, and GIRAFFE
in MEDUSA mode (R=20 000) for the Ca II K line.
We find that the observed profiles are better described if a negative
(outward) velocity field is included in the model chromospheres.
This leads to mass loss rates of a few 10-9
line, and GIRAFFE
in MEDUSA mode (R=20 000) for the Ca II K line.
We find that the observed profiles are better described if a negative
(outward) velocity field is included in the model chromospheres.
This leads to mass loss rates of a few 10-9 ![]() yr-1, so
very close to the requirements of the stellar evolution theory.
yr-1, so
very close to the requirements of the stellar evolution theory.
Key words: line: profiles - globular clusters: individual: NGC 2808 - stars: atmospheres - stars: mass loss - stars: Population II - techniques: spectroscopic
It has long been known that
the stellar evolution theory requires that some mass
(![]() 0.1-0.2
0.1-0.2 ![]() )
be lost by Population II stars during the evolutionary phases
preceding the horizontal branch (HB) phase, in order to account for
(1) the observed morphologies of the HB in globular clusters (GC), and
the maximum luminosity reached by stars on the asymptotic giant branch
(Castellani & Renzini 1968; Iben & Rood 1970; Rood 1973;
Martinez Roger & Paez 1987; Jorgensen & Thejll 1993; Ferraro et al. 1998;
Catelan 2000; Soker et al. 2001),
and (2) the pulsational properties of the RR Lyrae variables (Christy 1966;
Fusi Pecci et al. 1993; D'Cruz et al. 1996).
)
be lost by Population II stars during the evolutionary phases
preceding the horizontal branch (HB) phase, in order to account for
(1) the observed morphologies of the HB in globular clusters (GC), and
the maximum luminosity reached by stars on the asymptotic giant branch
(Castellani & Renzini 1968; Iben & Rood 1970; Rood 1973;
Martinez Roger & Paez 1987; Jorgensen & Thejll 1993; Ferraro et al. 1998;
Catelan 2000; Soker et al. 2001),
and (2) the pulsational properties of the RR Lyrae variables (Christy 1966;
Fusi Pecci et al. 1993; D'Cruz et al. 1996).
Theoretical estimates of mass loss rates at the tip of the red giant branch
(RGB) are a few times 10-8 ![]() yr-1 (Fusi Pecci &
Renzini 1975, 1976; Renzini 1977). More recently, Mullan & MacDonald (2003)
find that the evolution through the "bump'' in the luminosity function of
RGB stars might be associated with the onset of a cool
massive wind. In a study of RGB stars in the halo of the Milky Way,
de Boer (2004) estimates that on average
yr-1 (Fusi Pecci &
Renzini 1975, 1976; Renzini 1977). More recently, Mullan & MacDonald (2003)
find that the evolution through the "bump'' in the luminosity function of
RGB stars might be associated with the onset of a cool
massive wind. In a study of RGB stars in the halo of the Milky Way,
de Boer (2004) estimates that on average ![]() 0.3
0.3 ![]() per star
are lost by metal-poor red giants, and would contribute a sizeable fraction
of the observed H I gas falling in from the halo.
per star
are lost by metal-poor red giants, and would contribute a sizeable fraction
of the observed H I gas falling in from the halo.
As a result, a few tens of solar masses of intracluster matter are expected
to be produced in any given GC. This matter should accumulate in the
central regions, especially of the more massive clusters, in the absence of
sweeping mechanisms between Galactic plane crossings.
However, efforts to obtain evidence of intracluster matter
have been largely unsuccessful: diffuse gas in GCs was detected
only as an upper limit and well below 1 ![]() (Roberts 1988;
Smith et al. 1990; Faulkner & Smith 1991; Freire et al. 2001).
(Roberts 1988;
Smith et al. 1990; Faulkner & Smith 1991; Freire et al. 2001).
Table 1: Physical and atmospheric parameters for the RGB stars in NGC 2808 used for the present study. The temperatures, luminosities, and gravities listed in Cols. 3-5 are derived from the (V-K) colours (see Sect. 2). The expansion velocities and mass loss rates in Cols. 11 and 12 are discussed in Sect. 4.1.
Direct detection of mass loss from individual metal-poor RGB stars, either
in the field or in GCs, has been attempted with various observational
approaches.
Infrared excess, indicative of dusty circumstellar envelopes, has been
detected with ISOCAM in ![]() 15% of the globular cluster RGB (or AGB)
stars in the
15% of the globular cluster RGB (or AGB)
stars in the ![]() 0.7 mag brightest interval (
0.7 mag brightest interval (
![]() )
(see Origlia et al. 2002, and references therein).
Spectroscopic surveys of a few hundred GC red giants
(Cohen 1976, 1978, 1979, 1980, 1981;
Mallia & Pagel 1978;
Peterson 1981, 1982; Cacciari & Freeman 1983; Gratton et al. 1984)
revealed H
)
(see Origlia et al. 2002, and references therein).
Spectroscopic surveys of a few hundred GC red giants
(Cohen 1976, 1978, 1979, 1980, 1981;
Mallia & Pagel 1978;
Peterson 1981, 1982; Cacciari & Freeman 1983; Gratton et al. 1984)
revealed H![]() emission wings in a good fraction of the stars along
the uppermost 1.25 mag interval of the RGB.
This emission, generally asymmetric and possibly variable on a short-time
scale, was initially interpreted as evidence of an extended atmosphere,
until Dupree et al. (1984) demonstrated that it could arise naturally in
a static stellar chromosphere, in analogy with Reimers' (1975, 1977, 1981)
speculations on Population I red giants.
emission wings in a good fraction of the stars along
the uppermost 1.25 mag interval of the RGB.
This emission, generally asymmetric and possibly variable on a short-time
scale, was initially interpreted as evidence of an extended atmosphere,
until Dupree et al. (1984) demonstrated that it could arise naturally in
a static stellar chromosphere, in analogy with Reimers' (1975, 1977, 1981)
speculations on Population I red giants.
Profile asymmetry and coreshifts of chromospheric lines, such as
the Na I D and Ca II K lines, in addition to H![]() ,
were
then considered as possible indicators of mass motions.
Several red giants in GCs were found to exhibit small negative velocity
shifts in the cores of these lines (Peterson 1981; Bates et al. 1990,
1993;
Dupree et al. 1994; Lyons et al. 1996), as did metal-poor field giants that
might be taken as the field counterparts of GC giants (Smith et al. 1992;
Dupree & Smith 1995).
These coreshifts are all
,
were
then considered as possible indicators of mass motions.
Several red giants in GCs were found to exhibit small negative velocity
shifts in the cores of these lines (Peterson 1981; Bates et al. 1990,
1993;
Dupree et al. 1994; Lyons et al. 1996), as did metal-poor field giants that
might be taken as the field counterparts of GC giants (Smith et al. 1992;
Dupree & Smith 1995).
These coreshifts are all ![]() 15 km s-1, i.e. much smaller than the
escape velocity from the stellar photosphere (
15 km s-1, i.e. much smaller than the
escape velocity from the stellar photosphere (![]() 50-60 km s-1).
50-60 km s-1).
However, in those cases where the Mg II ![]() 2800 h and k
lines were also available for GC RGB or metal-poor field stars
(Dupree et al. 1990a, 1990b, 1994; Smith & Dupree 1998),
the asymmetries in the Mg II lines provided, under certain
assumptions, some evidence of
a stellar wind with a terminal velocity as high as
2800 h and k
lines were also available for GC RGB or metal-poor field stars
(Dupree et al. 1990a, 1990b, 1994; Smith & Dupree 1998),
the asymmetries in the Mg II lines provided, under certain
assumptions, some evidence of
a stellar wind with a terminal velocity as high as
![]() 50-150 km s-1, exceeding both the stellar photospheric
escape velocity and the escape velocity from many cluster cores
(
50-150 km s-1, exceeding both the stellar photospheric
escape velocity and the escape velocity from many cluster cores
(![]() 20-70 km s-1; Webbink 1981).
These velocity values, along with appropriate values of stellar
radius and chemical abundance, would be consistent with mass loss rates
of a few 10-11 to a few 10-9
20-70 km s-1; Webbink 1981).
These velocity values, along with appropriate values of stellar
radius and chemical abundance, would be consistent with mass loss rates
of a few 10-11 to a few 10-9 ![]() yr-1(Dupree et al. 1990b, 1994), leading to a total mass loss
of up to
yr-1(Dupree et al. 1990b, 1994), leading to a total mass loss
of up to ![]() 0.2
0.2 ![]() over a time of
over a time of
![]() yr
on the RGB, in general agreement with expectations
of the stellar evolution theory.
yr
on the RGB, in general agreement with expectations
of the stellar evolution theory.
Further observational evidence of mass outflows from individual
metal-poor red giants was provided by Dupree et al. (1992) and
Smith et al. (2004) using the He I ![]() 10830.3
absorption line on five field metal-poor red giants and six RGB stars
in the GC M13. This weak line forms higher in the atmosphere than H
10830.3
absorption line on five field metal-poor red giants and six RGB stars
in the GC M13. This weak line forms higher in the atmosphere than H![]() or the Ca II and Mg II emission cores and is, therefore,
a better probe of the outer regions of the atmosphere where the wind begins
to accelerate. The study by Smith et al. (2004) has revealed the
possible presence of mass outflows in fainter (and hotter) RGB stars
than previously monitored by chromospheric lines in the UV
and optical ranges.
or the Ca II and Mg II emission cores and is, therefore,
a better probe of the outer regions of the atmosphere where the wind begins
to accelerate. The study by Smith et al. (2004) has revealed the
possible presence of mass outflows in fainter (and hotter) RGB stars
than previously monitored by chromospheric lines in the UV
and optical ranges.
If we restrict our attention only to studies in the optical range,
the most recent study was done by Cacciari et al. (2004,
hereafter C04), who used FLAMES (Pasquini et al. 2002)
spectra centred on Ca II K,
Na I D, and H![]() lines of
lines of ![]() 100 RGB stars in NGC 2808.
Their purpose was to monitor the profiles of these lines along the RGB
in search of asymmetries and core shifts, taken to indicate mass motions
in the atmospheres.
Indeed, a good fraction of the brightest RGB stars was found to show
these features, with negative (outward) velocities of
100 RGB stars in NGC 2808.
Their purpose was to monitor the profiles of these lines along the RGB
in search of asymmetries and core shifts, taken to indicate mass motions
in the atmospheres.
Indeed, a good fraction of the brightest RGB stars was found to show
these features, with negative (outward) velocities of ![]() 10 km s-1.
However, these velocities are quite low and might be accounted for by the
presence of local hydrodynamic effects in the chromosphere
(Dupree et al. 1984; Smith & Dupree 1988; Dupree & Smith 1995).
One could fairly summarise the current status by stating that the
long-sought direct evidence of mass loss in Population II RGB stars is
still quite elusive.
10 km s-1.
However, these velocities are quite low and might be accounted for by the
presence of local hydrodynamic effects in the chromosphere
(Dupree et al. 1984; Smith & Dupree 1988; Dupree & Smith 1995).
One could fairly summarise the current status by stating that the
long-sought direct evidence of mass loss in Population II RGB stars is
still quite elusive.
The purpose of the present study is to compare the observed profiles of
the Ca II K and H![]() lines in a few RGB stars in the
GC NGC 2808 with theoretical profiles from suitable model chromospheres and
to verify whether a static chromosphere can account for the observed features or
a velocity field needs to be considered.
In the latter case, we estimate quantitatively if the adopted field is
consistent with the amount of mass loss expected from theory.
lines in a few RGB stars in the
GC NGC 2808 with theoretical profiles from suitable model chromospheres and
to verify whether a static chromosphere can account for the observed features or
a velocity field needs to be considered.
In the latter case, we estimate quantitatively if the adopted field is
consistent with the amount of mass loss expected from theory.
In Sects. 2 and 3 we describe the data and the models we have used, in Sect. 4 the results of our analysis are discussed, and Sect. 5 contains a summary of this work and our conclusions.
We list in Table 1 the five RGB stars of NGC 2808 selected
from the C04 sample for the present analysis. They were
selected among the brightest and coolest stars with clear evidence of
emission in the H![]() wings and at the bottom of the Ca II K
absorption core (K2 reversal).
The temperatures and luminosities listed in Table 1 are derived
from the (V-K) colours, and
the gravities assume a mass of 0.85
wings and at the bottom of the Ca II K
absorption core (K2 reversal).
The temperatures and luminosities listed in Table 1 are derived
from the (V-K) colours, and
the gravities assume a mass of 0.85 ![]() for these stars (see C04 and
Carretta et al. 2004, for more details).
Columns 6 and 8 show the shifts
with respect to photospheric lines of the H
for these stars (see C04 and
Carretta et al. 2004, for more details).
Columns 6 and 8 show the shifts
with respect to photospheric lines of the H![]() and Ca II K3
absorption line cores, respectively. Columns 7 and 9 show the asymmetry of
the H
and Ca II K3
absorption line cores, respectively. Columns 7 and 9 show the asymmetry of
the H![]() and K2 emission using the ratio B/R
of the respective blue and red wings.
As found in all previous studies, the emission wings show the characteristic
signature of downflow (i.e. B/R > 1) about as often as that of outflow
(B/R < 1), suggesting that the emission could be produced in
a locally non-static chromosphere.
The consistently negative shifts of the absorption cores should be
better indicators of a net outflow; however, the low velocity of
these features might also be compatible with normal chromospheric activity.
and K2 emission using the ratio B/R
of the respective blue and red wings.
As found in all previous studies, the emission wings show the characteristic
signature of downflow (i.e. B/R > 1) about as often as that of outflow
(B/R < 1), suggesting that the emission could be produced in
a locally non-static chromosphere.
The consistently negative shifts of the absorption cores should be
better indicators of a net outflow; however, the low velocity of
these features might also be compatible with normal chromospheric activity.
For the photospheric temperature distribution we used the
model computed by Kurucz (2005) for log(g) = 0.5
and
![]() K.
Although there are differences in these parameters for the
stars in our sample, this model is the closest one in all cases
(except perhaps for star 47606, for which the model with
K.
Although there are differences in these parameters for the
stars in our sample, this model is the closest one in all cases
(except perhaps for star 47606, for which the model with
![]() K is marginally closer).
K is marginally closer).
On this model, we superimposed a
chromospheric rise, with T increasing linearly with negative
log(m). In this way, our chromospheric models depend on
three free parameters: i) the column mass log(m) where the chromosphere
starts, i.e. where the temperature distribution departs
from Kurucz' model and where, therefore, the temperature has
its minimum value; ii) the slope of the chromospheric T vs.
log(m) distribution; and iii) the maximum temperature to which
the chromospheric rise extends, which relates directly to
the value of log(m) where the chromosphere ends. Upon this
chromosphere, we added a "transition region'' where the
temperature rises abruptly up to
![]() K, to
assure convergence of the calculations. The structure of this
"transition region'' has no influence on the computed
profiles. As a matter of fact, the computed profiles are
unaffected by the structure of the regions where the
temperature is higher than
K, to
assure convergence of the calculations. The structure of this
"transition region'' has no influence on the computed
profiles. As a matter of fact, the computed profiles are
unaffected by the structure of the regions where the
temperature is higher than
![]() K, as
we see below. Examples of the different models we computed are
shown in Fig. 1.
K, as
we see below. Examples of the different models we computed are
shown in Fig. 1.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.7cm,clip]{4792f1.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/29/aa4792-05/Timg29.gif) |
Figure 1:
Examples of our chromospheric models. The thick
line is Kurucz' model for
|
| Open with DEXTER | |
For every T vs. log(m) distribution, we solved the non-LTE radiative transfer and the statistical and hydrostatic equilibrium equations, using the program Pandora (Avrett & Loeser 1984). Assuming a gravity log(g) = 0.5, a turbulent velocity varying from 2 to 20 km s-1, and a metallicity [Fe/H] = -1.14 with all elements scaled solar, we self-consistently computed non-LTE populations for 10 levels of H (for details on the atomic models, see Falchi & Mauas 2002), 13 of He I (see Mauas et al. 2004), 9 of C I, 15 of Fe I, 8 of Si I (see Cincunegui & Mauas 2001), 8 of Ca I and Na I, 6 of Al I (see Mauas et al. 2002), and 7 of Mg I (see Mauas et al. 1988). In addition, we computed 6 levels of He II (see Mauas et al. 2004) and Mg II, and 5 of Ca II (see Falchi & Mauas 2002).
For every species under
consideration we included all the bound-free transitions and
the most important bound-bound transitions. Ly-![]() ,
the
Ca II H and K, and Mg II h and k lines were all
computed with a full partial-redistribution treatment.
A test was performed assuming helium abundance Y=0.23
and
,
the
Ca II H and K, and Mg II h and k lines were all
computed with a full partial-redistribution treatment.
A test was performed assuming helium abundance Y=0.23
and ![]() -element enhancement [Ca/Fe] = +0.3, which are
more appropriate for a GC stellar population, and no significant
difference was detected in the results discussed in
the following section.
We also performed several test runs varying the gravity
within the observed range, and found that the emitted profiles
were not affected.
-element enhancement [Ca/Fe] = +0.3, which are
more appropriate for a GC stellar population, and no significant
difference was detected in the results discussed in
the following section.
We also performed several test runs varying the gravity
within the observed range, and found that the emitted profiles
were not affected.
In our calculations we assumed a plane-parallel atmosphere, for simplicity. However, once the final model was obtained, we computed the emitted profiles assuming a spherically symmetric atmosphere, and we found no significant changes in the emitted profiles with respect to the plane-parallel approximation. The abundances adopted in the present study are taken from the detailed chemical analysis of the same stars performed by Carretta (2006).
The observed profiles for three of our stars (48889, 51454, and
51499) are very similar, differing mainly in the amount of
asymmetry in the K2 and H![]() emission wings.
The profiles for the other two stars (37872 and 47606) are
also similar and differ mainly in the asymmetry.
Furthermore, the asymmetries are not very large and
can be considered as a second order change in the
profiles. For these reasons, we computed two atmospheric models, one
(model A) to fit the profiles of the first three stars and the other
(model B) to fit the profiles of the remaining two stars.
emission wings.
The profiles for the other two stars (37872 and 47606) are
also similar and differ mainly in the asymmetry.
Furthermore, the asymmetries are not very large and
can be considered as a second order change in the
profiles. For these reasons, we computed two atmospheric models, one
(model A) to fit the profiles of the first three stars and the other
(model B) to fit the profiles of the remaining two stars.
Once the models that gave the best fit to the symmetric profiles were obtained, we applied a velocity field to each of them, computed the resulting profiles, and compared them with the observed asymmetries. We modified this velocity field until a satisfactory match between observed and computed profiles was found. The advantage of this approach is that the velocities are not "measured'' from the profiles, but modelled self-consistently along with the rest of the atmospheric parameters, and the region corresponding to each value of the velocity field is well-determined, unlike for other methods such as the bisector.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.7cm,clip]{4792f2.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/29/aa4792-05/Timg30.gif) |
Figure 2:
Our chromospheric models: model A (solid line), for
the least active stars, and model B (dashed line) for the
most active stars (37872 and 47606). These models do not include any
velocity field. The approximate depth of formation of the
H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
Our two models are shown in Fig. 2, together with the depth of
formation of the lines we used as diagnostics, and the
velocities obtained are plotted in Fig. 3. The computed H![]() and Ca II K line profiles are compared with
the observations in Figs. 4 to 8.
The observed profiles have been reported to the continuum emission implied
by Kurucz's model and shifted by a quantity
corresponding to the individual stellar radial velocity
(see Table 2 in C04), to report the profiles to their
wavelengths at rest. Also shown are the profiles computed
for the corresponding model without including the velocity
field, as a reference for clarity. These profiles have been
superimposed to those with velocity to highlight the asymmetries.
and Ca II K line profiles are compared with
the observations in Figs. 4 to 8.
The observed profiles have been reported to the continuum emission implied
by Kurucz's model and shifted by a quantity
corresponding to the individual stellar radial velocity
(see Table 2 in C04), to report the profiles to their
wavelengths at rest. Also shown are the profiles computed
for the corresponding model without including the velocity
field, as a reference for clarity. These profiles have been
superimposed to those with velocity to highlight the asymmetries.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8cm,clip]{4792f3.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/29/aa4792-05/Timg31.gif) |
Figure 3:
The velocity as a function of depth (solid line),
derived from the best match with the Ca K (innermost) and
H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.7cm,clip]{4792f4.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/29/aa4792-05/Timg32.gif) |
Figure 4:
H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,clip]{4792f5.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/29/aa4792-05/Timg33.gif) |
Figure 5: Same as in Fig. 4 for the star 48889. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,clip]{4792f6.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/29/aa4792-05/Timg34.gif) |
Figure 6: Same as in Fig. 4 for the star 51454. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.7cm,clip]{4792f7.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/29/aa4792-05/Timg35.gif) |
Figure 7: Same as in Fig. 4 for the star 47606. In this case we use model B. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.7cm,clip]{4792f8.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/29/aa4792-05/Timg36.gif) |
Figure 8: Same as in Fig. 4 for the star 37872. In this case we use model B. |
| Open with DEXTER | |
One can see in the figures that the agreement between computed
and observed profiles is quite good. In fact, the main difference
is that the H![]() computed profiles are broader and
slightly deeper in the line core.
We point out that in these calculations we are assuming a
homogeneous atmosphere and that the broader and
deeper core shown by the computed profiles can be due to
inhomogeneities in the atmosphere. For example, in
Fig. 9 we show the H
computed profiles are broader and
slightly deeper in the line core.
We point out that in these calculations we are assuming a
homogeneous atmosphere and that the broader and
deeper core shown by the computed profiles can be due to
inhomogeneities in the atmosphere. For example, in
Fig. 9 we show the H![]() profile
computed from model A and the profile obtained from an atmosphere
with no chromospheric rise (and no velocity field),
i.e. a purely photospheric profile.
Also shown is the profile obtained by combining 90% of the profile computed
from model A and 10% of the profile obtained from the model without
chromospheric rise, as a way to simulate an inhomogeneus atmosphere.
The resulting profile is narrower and more asymmetric in the centre,
and fits the observations much better. We stress that the
results discussed below are not affected by this disagreement,
since they are mainly based on the asymmetries of the wings.
profile
computed from model A and the profile obtained from an atmosphere
with no chromospheric rise (and no velocity field),
i.e. a purely photospheric profile.
Also shown is the profile obtained by combining 90% of the profile computed
from model A and 10% of the profile obtained from the model without
chromospheric rise, as a way to simulate an inhomogeneus atmosphere.
The resulting profile is narrower and more asymmetric in the centre,
and fits the observations much better. We stress that the
results discussed below are not affected by this disagreement,
since they are mainly based on the asymmetries of the wings.
Also, some of the Ca II photospheric profiles in Figs. 5-8
show a slight mismatch on the blue side of the line, and the model
is slightly higher than the observed profile.
This is most likely due to the presence of extra photospheric absorption
lines in the spectra that are not included in the model,
like the Fe I lines at 3930.3 Å and 3929 Å.
Some small residual tilt induced by the flat fielding process cannot be
excluded (see e.g. the discussion in Pasquini 1992), but this is not
relevant to the following discussion.
In modelling the Ca II K line, we have been careful to match the
chromospheric core intensity, asymmetry, and width
(Wilson-Bappu width, Wilson & Bappu 1957).
The models tend to produce a higher K3 central intensity with
respect to the observed profiles. This is also possibly due to the assumption
of a homogeneous chromosphere, since any contribution of a pure photospheric
line should be noticed mainly in the line centre.
We do not expect a significant contribution of interstellar Ca, since
we do not see evidence of it in our spectra, and it could contribute
to the Ca II core profile only if the velocity of the interstellar
medium were similar to that of the cluster (![]() 100 km s-1).
100 km s-1).
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8cm,clip]{4792f9.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/29/aa4792-05/Timg37.gif) |
Figure 9:
H |
| Open with DEXTER | |
In our models, the chromosphere starts (i.e. our model departs from Kurucz' purely photospheric one) at log(m) = 0.8 for the least active stars and at 0.95 for the most active ones. It is this fact that results in stronger emission wings for model B. In both models, the slope of the chromosphere (i.e. T vs. log(m), with T in K and m in g cm-2) is -21 000, and the "transition region'' starts where the temperature reaches 18 000 K.
Regarding the
![]() region, we found the best
agreement in the Ca II K1 minima with a slightly
rounder temperature distribution, which does not show the sharp
transition from Kurucz' model to ours, which can be seen in
Fig. 1.
In fact, the temperature for model B is slightly larger in
this region, to account for the more intense K1 minima
seen in stars 37872 and 47606.
region, we found the best
agreement in the Ca II K1 minima with a slightly
rounder temperature distribution, which does not show the sharp
transition from Kurucz' model to ours, which can be seen in
Fig. 1.
In fact, the temperature for model B is slightly larger in
this region, to account for the more intense K1 minima
seen in stars 37872 and 47606.
Regarding the slope of the chromospheric temperature vs. mass,
we found that this is the fundamental
parameter affecting the H![]() emission wings: a
shallower slope results in no emission wings, and
a steeper slope produces too large an emission. In other words,
the emission wings are a direct sign of how steep the
chromospheric temperature rise is.
emission wings: a
shallower slope results in no emission wings, and
a steeper slope produces too large an emission. In other words,
the emission wings are a direct sign of how steep the
chromospheric temperature rise is.
With respect to the upper end of the chromosphere, we point
out that the temperature distribution above
![]() K does not affect our observed profiles. Therefore, the
influence of this parameter is related to the mass load of
the chromosphere, and not to the real temperature.
K does not affect our observed profiles. Therefore, the
influence of this parameter is related to the mass load of
the chromosphere, and not to the real temperature.
We see in the figures that the presence
of emission in the H![]() wings can be reproduced
without considering any velocities.
However, the asymmetries of these wings and of other
features of the profiles can only be reproduced with the
inclusion of velocity fields. In all cases, the
profiles that include some velocity provide a better fit to the
data than those with zero velocity.
wings can be reproduced
without considering any velocities.
However, the asymmetries of these wings and of other
features of the profiles can only be reproduced with the
inclusion of velocity fields. In all cases, the
profiles that include some velocity provide a better fit to the
data than those with zero velocity.
The H![]() line core is the feature that forms higher up
in the atmosphere, so we can only infer the
velocity up to the height where it is formed, about
1 stellar radius above the photosphere. These are the
velocities
line core is the feature that forms higher up
in the atmosphere, so we can only infer the
velocity up to the height where it is formed, about
1 stellar radius above the photosphere. These are the
velocities
![]() listed in Table 1. In
Fig. 3 we show the full velocity field. For comparison, we
also show the corresponding escape velocity, at each height Z from the centre of the star, computed as
listed in Table 1. In
Fig. 3 we show the full velocity field. For comparison, we
also show the corresponding escape velocity, at each height Z from the centre of the star, computed as
![]() ,
where Z and the stellar mass M are in solar units. We
assumed a typical mass
,
where Z and the stellar mass M are in solar units. We
assumed a typical mass
![]() for all the stars.
for all the stars.
It can be seen that for one of the stars (48889) the
expansion velocity at the most external point
estimated from the H![]() profile is
larger than the escape velocity at about 2 stellar radii
(from the centre of the star), where the H
profile is
larger than the escape velocity at about 2 stellar radii
(from the centre of the star), where the H![]() core forms.
This velocity is reflected in the blue wing of the H
core forms.
This velocity is reflected in the blue wing of the H![]() profile, which has an absorption feature, whereas the red wing
has an emission peak. This is due to the displacement of the
line core, which is shallower in the profile with velocity.
profile, which has an absorption feature, whereas the red wing
has an emission peak. This is due to the displacement of the
line core, which is shallower in the profile with velocity.
This implies that, at least for this star, the material
above this level is escaping from the atmosphere.
For the other stars, the expansion velocity we estimate for
the outermost point for which we have an indication, i.e. where the H![]() core is formed, is smaller than the
escape velocity at that depth. However, there is mass outflow
at this height, and the velocity is increasing in all cases,
while, of course, the escape velocity is decreasing. Furthermore,
there are no signs of a reversal in the velocity field;
i.e. there is no material falling back in. Therefore,
the most probable situation is that the velocity continues to
increase, until eventually it reaches the escape
velocity. The particularity of star 48889 is only that it
reaches this high level of velocity deep enough to be seen
in the H
core is formed, is smaller than the
escape velocity at that depth. However, there is mass outflow
at this height, and the velocity is increasing in all cases,
while, of course, the escape velocity is decreasing. Furthermore,
there are no signs of a reversal in the velocity field;
i.e. there is no material falling back in. Therefore,
the most probable situation is that the velocity continues to
increase, until eventually it reaches the escape
velocity. The particularity of star 48889 is only that it
reaches this high level of velocity deep enough to be seen
in the H![]() profile.
profile.
We can estimate the mass loss rate for these stars using a
simple formulation based on mass outflow:
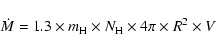
The rates expected from stellar evolution theory can be
estimated using Renzini (1977) parameterisation (his Eq. (6.10))
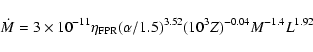
For completeness, we estimated the mass loss rates
according to Eq. (4) of Schroeder & Cuntz (2005)
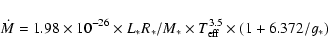
To estimate the energy requirements to sustain the
chromosphere, i.e. to constrain the possible heating
mechanisms at work, we
compute the radiative cooling rate ![]() (erg cm-3 s-1),
namely the net amount of energy radiated at a given depth by the
atmosphere, which is given by
(erg cm-3 s-1),
namely the net amount of energy radiated at a given depth by the
atmosphere, which is given by
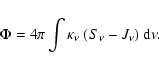
These rates can be compared with those for dwarf stars of
similar
![]() (Mauas et al. 1997). It can be seen that
the energy required is, as expected, much lower for giant
stars: in the
mid-chromosphere, where it is largest, it reaches up to
10-4 erg cm-3 s-1 for these giant stars, 5 orders of magnitude smaller than for the dwarfs.
However, since the particle density is also 5 orders
of magnitude smaller in giants, the energy per
particle is within the same order of magnitude.
(Mauas et al. 1997). It can be seen that
the energy required is, as expected, much lower for giant
stars: in the
mid-chromosphere, where it is largest, it reaches up to
10-4 erg cm-3 s-1 for these giant stars, 5 orders of magnitude smaller than for the dwarfs.
However, since the particle density is also 5 orders
of magnitude smaller in giants, the energy per
particle is within the same order of magnitude.
In the temperature minimum region, the cooling rate is negative. In this case there should be a missing cooling agent, a fact that has already been noted for dwarf stars. However, it should be pointed out that almost all cooling is due to CO, which is the only molecule included in the calculations. It seems reasonable to expect that, should other molecules be computed in detail, the results would show a similar behaviour as the CO calculations, bringing this region closer to radiative balance.
In the mid- and high-chromosphere the energy balance is determined essentially by the hydrogen cooling rate. In this region, the Mg II rate is also important, and it is an order of magnitude higher than the one for Ca II. Although it is not trivial to compare chromospheric non-radiative losses in different lines, such as Mg II and Ca II, observed with different instruments, Pasquini & Brocato (1992) analysed the metal-poor stars observed by Dupree et al. (1994) and found that chromopheric losses in the Mg II lines are a factor 2-3 higher than in the Ca II. This, at least qualitatively, agrees with the present analysis.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=8cm,clip]{4792f10.ps}
\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/29/aa4792-05/Timg57.gif) |
Figure 10:
Log |
| Open with DEXTER | |
We can summarise our conclusions as follows:
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. E.H. Avrett for interesting discussions and comments. C.C. acknowledges the support of the MIUR (Ministero dell'Istruzione, dell'Università e della Ricerca). PM acknowledges the Visiting Scientist programme at ESO-Garching.