A&A 448, L29-L32 (2006)
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:200600004
X-rays from HH 210 in the Orion nebula
N. Grosso1 - E. D. Feigelson2
- K. V. Getman2 - J. H. Kastner3 - J. Bally4 - M. J. McCaughrean5,6
1 - Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Grenoble,
Université Joseph-Fourier,
38041 Grenoble Cedex 9, France
2 - Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics,
Pennsylvania State University,
University Park, PA 16802, USA
3 - Center for Imaging Science, Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester,
New York 14623-5604, USA
4 - Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy,
University of Colorado at Boulder, CB 389,
Boulder, CO 80309, USA
5 - School of Physics, University of Exeter, Stocker Road,
Exeter EX4 4QL, Devon, UK
6 - Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam,
An der Sternwarte 16,
14482 Potsdam, Germany
Received 23 November 2005 / Accepted 19 January 2006
Abstract
We report the detection during the Chandra Orion Ultradeep
Project (COUP) of two soft, constant, and faint X-ray sources associated
with the Herbig-Haro object HH 210. HH 210 is located at the tip of
the NNE finger of the emission line system bursting out of the
BN-KL complex, northwest of the Trapezium cluster in the OMC-1
molecular cloud. Using a recent H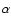 image obtained with the ACS imager on board HST, and taking into account the known
proper motions of HH 210 emission knots, we show that the position of
the brightest X-ray source, COUP 703, coincides with the
emission knot 154-040a of HH 210, which is the emission knot of
HH 210 having the highest tangential velocity
(425 km s-1). The second X-ray source, COUP 704, is
located on the complicated emission tail of HH 210 close to an
emission line filament and has no obvious optical/infrared
counterpart. Spectral fitting indicates for both sources a plasma
temperature of
image obtained with the ACS imager on board HST, and taking into account the known
proper motions of HH 210 emission knots, we show that the position of
the brightest X-ray source, COUP 703, coincides with the
emission knot 154-040a of HH 210, which is the emission knot of
HH 210 having the highest tangential velocity
(425 km s-1). The second X-ray source, COUP 704, is
located on the complicated emission tail of HH 210 close to an
emission line filament and has no obvious optical/infrared
counterpart. Spectral fitting indicates for both sources a plasma
temperature of 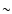 0.8 MK and absorption-corrected X-ray
luminosities of about 1030 erg s-1 (0.5-2.0 keV). These
X-ray sources are well explained by a model invoking a fast-moving,
radiative bow shock in a neutral medium with a density of
0.8 MK and absorption-corrected X-ray
luminosities of about 1030 erg s-1 (0.5-2.0 keV). These
X-ray sources are well explained by a model invoking a fast-moving,
radiative bow shock in a neutral medium with a density of
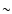 12 000 cm-3. The X-ray detection of COUP 704 therefore
reveals, in the complicated HH 210 region, an energetic shock not yet
identified at other wavelengths.
12 000 cm-3. The X-ray detection of COUP 704 therefore
reveals, in the complicated HH 210 region, an energetic shock not yet
identified at other wavelengths.
Key words: ISM: Herbig-Haro objects - ISM: individual objects: HH 210 - X-rays: ISM
Outflow activity is ubiquitous in young stellar objects (YSO), and
intimately connected to the accretion process building up the mass of
stars. The interaction of outflow from YSO and the interstellar medium
produces bow shocks associated with optically luminous small nebulae,
called Herbig-Haro (HH) objects (Herbig 1950; Haro 1952;
see review by Reipurth & Bally 2001). Optical emission from HH objects
includes Hydrogen Balmer lines, [O I], [S II],
[N II], [O III], tracing plasma with temperatures of
several 103 to 105 K. During these last years a handful of HH
objects have been detected in X-rays, tracing plasma with temperatures
of a few 106 K, as expected from the high velocities of these
shocks (e.g., Raga et al. 2002). The emission knot H of HH 2
was the first detected in X-rays; it also exhibits strong H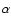 and free-free radio continuum emission
(Pravdo et al. 2001). HH 80 and HH 81 are excited by a
massive protostar, and are among the most luminous HH objects in the
optical; emission knots A and G/H of HH 80, and emission knot A of
HH 81 are now the most luminous known in X-rays (Pravdo et al. 2004).
and free-free radio continuum emission
(Pravdo et al. 2001). HH 80 and HH 81 are excited by a
massive protostar, and are among the most luminous HH objects in the
optical; emission knots A and G/H of HH 80, and emission knot A of
HH 81 are now the most luminous known in X-rays (Pravdo et al. 2004).
The soft X-ray emission from L1551 IRS5, associated with
HH 154 by Favata et al. (2002), is now considered as arising
from a shock at the base of the jet of this protostar binary
(Bonito et al. 2004; Bally et al. 2003). Recently, soft X-ray excesses were found in
the X-ray spectra of the "Beehive'' proplyd (Kastner et al. 2005)
and DG Tau (Güdel et al. 2005), two YSOs with jets.
Remarkably, in both sources, this soft and constant X-ray emission
suffers less extinction than the harder and variable X-ray component
likely emitted by the stellar corona, suggesting that it comes from
shocks along the base of these jets.
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.4cm,clip]{Hk231_f1.eps} \end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/11/aahk231/Timg17.gif) |
Figure 1:
HST/WFPC2 image of HH 210 for epoch 2000.70 in
[S II] (adapted from Fig. 2 of Doi et al. 2002). Each pixel is
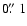 on a side, the color stretch is linear. HH 210 shows a
typical bow shock structure containing numerous emission knots and
filaments. The two crosses mark epoch 2003.04 positions of COUP 703
and COUP 704 (Getman et al. 2005b); cross sizes indicate the total positional
uncertainties of these X-ray sources (
on a side, the color stretch is linear. HH 210 shows a
typical bow shock structure containing numerous emission knots and
filaments. The two crosses mark epoch 2003.04 positions of COUP 703
and COUP 704 (Getman et al. 2005b); cross sizes indicate the total positional
uncertainties of these X-ray sources (
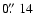 ). The white
arrows indicate velocity and epoch 2003.04 position for emission knots
with proper-motion measured in [S II] by Doi et al. (2002). The
white ). The white
arrows indicate velocity and epoch 2003.04 position for emission knots
with proper-motion measured in [S II] by Doi et al. (2002). The
white
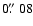 -radius circles indicate the optical resolution of
HST. -radius circles indicate the optical resolution of
HST.
|
| Open with DEXTER |
In January 2003, the Chandra Orion Ultradeep Project (COUP) was
carried out with ACIS-I (Garmire et al. 2003) on board the Chandra X-ray
Observatory (Weisskopf et al. 2002). COUP consisted of a nearly continuous
exposure over 13.2 days centered on the Trapezium cluster in the
Orion Nebula, yielding a total on-source exposure time of 838 ks,
i.e. 9.7 days (Getman et al. 2005b). Among the 1616 COUP X-ray sources,
there are only about fifty X-ray sources with the median energy of
their X-ray photons lower than 1 keV, i.e. having a very soft X-ray
spectrum. The bulk of this soft X-ray source sample is associated with
optical/infrared stars; two sources may be spurious; and two other
sources without counterparts may be newly discovered very low mass
members of the Orion nebula cluster. Of the very soft
sources, only COUP 703 and COUP 704 are possibly associated with an
HH object, HH 210 (Kastner et al. 2005; Getman et al. 2005a). More generally there
is in COUP no other X-ray source associated with HH objects
(Getman et al. 2005a).
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,clip]{Hk231_f2.eps} \end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/11/aahk231/Timg20.gif) |
Figure 2:
COUP view of HH 210. Red, green, and blue represent photons
in the 0.5-1.7 keV, 1.7-2.8 keV, and 2.8-8.0 keV energy bands,
respectively (Lupton et al. 2004). Green crosses and countours mark the
centre of COUP sources and source extraction polygons (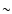 87%
encircled energy using PSF at 1.5 keV). Cross sizes indicate the
total positional uncertainties of these X-ray sources
( 87%
encircled energy using PSF at 1.5 keV). Cross sizes indicate the
total positional uncertainties of these X-ray sources
(
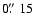 ). White contours show H ). White contours show H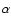 +[N II] knots
observed with HST/ACS ( +[N II] knots
observed with HST/ACS (
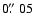 -pixels on a side; epoch
2004.05, Bally et al. 2005), which were moved individually to epoch 2003.04
using proper-motions of Doi et al. (2002). COUP 703 coincides with
154-040a HH 210, the emission knot having the highest tangential
velocity (425 km s-1; see Fig. 1). -pixels on a side; epoch
2004.05, Bally et al. 2005), which were moved individually to epoch 2003.04
using proper-motions of Doi et al. (2002). COUP 703 coincides with
154-040a HH 210, the emission knot having the highest tangential
velocity (425 km s-1; see Fig. 1).
|
| Open with DEXTER |
HH 210 is located 2.7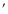 -north of
-north of 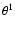 Ori C in the OMC-1
molecular cloud, and is one of the brightest HH objects in this area
revealed by emission of [O I] (Taylor et al. 1986; Axon & Taylor 1984). It
belongs to the powerful CO outflow from the BN-KL region, which
produces a spectacular set of H2 bow shocks and trailed wakes; it
is located at the tip of the NNE finger which is one of the
brightest emission systems in [Fe II] and lacks a trailed H2wake (Allen & Burton 1993). HH 210 has a pronounced bow shape containing
numerous knots and complicated filaments in [S II] (see
Fig. 1).
Ori C in the OMC-1
molecular cloud, and is one of the brightest HH objects in this area
revealed by emission of [O I] (Taylor et al. 1986; Axon & Taylor 1984). It
belongs to the powerful CO outflow from the BN-KL region, which
produces a spectacular set of H2 bow shocks and trailed wakes; it
is located at the tip of the NNE finger which is one of the
brightest emission systems in [Fe II] and lacks a trailed H2wake (Allen & Burton 1993). HH 210 has a pronounced bow shape containing
numerous knots and complicated filaments in [S II] (see
Fig. 1).
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=10.7cm,clip]{Hk231_f3a.eps}\hspace*{3mm} \includegraphics[width=4.8cm,clip]{Hk231_f3b.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/11/aahk231/Timg23.gif) |
Figure 3:
X-ray spectra of COUP 703 ( left) and COUP 704 ( middle),
and confidence regions of the plasma parameters ( right). Each
spectral bin contains at least 5 events. We used for the spectral fitting
a collisionally-ionized plasma model ( APEC),
assuming a plasma with solar elemental abundances (Anders & Grevesse 1989),
with X-ray absorption model ( WABS; Morrison & McCammon 1983).
Fit parameters are given in Table 1. In the right panel,
the grey region indicates for COUP 703 the confidence region at the
68% level of the plasma temperature and the absorption. The plus sign
and diamond mark the best parameter values for COUP 703 and COUP 704
(high 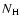 /low kT solution), respectively. The arrow
indicates the high temperature value for the null absorption solution
of COUP 704. /low kT solution), respectively. The arrow
indicates the high temperature value for the null absorption solution
of COUP 704.
|
| Open with DEXTER |
We present in Sect. 2 the astrometry and spectral analysis
of the X-ray sources associated with HH 210; we discuss in
Sect. 3 the origin of these X-ray emissions.
2 Astrometry and spectral analysis of the X-ray sources
associated with HH 210
Table 1:
Spectral parameters of X-ray sources associated with HH 210
using a WABS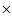 APEC plasma model with solar elemental
abundances. We used Chi statistics with
standard weighting. Confidence ranges at the 68% level
(
APEC plasma model with solar elemental
abundances. We used Chi statistics with
standard weighting. Confidence ranges at the 68% level
(
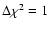 ;
corresponding to
;
corresponding to 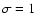 for Gaussian
statistics) are given in parentheses. Q in Col. (8) is the
probability that the best-fit model matches the data, given the value
of
for Gaussian
statistics) are given in parentheses. Q in Col. (8) is the
probability that the best-fit model matches the data, given the value
of 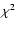 and
and 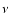 ,
the degree of freedom in Col. (7). The emission
measure in Col. (6) and the logarithm of the X-ray luminosities in the
0.5-2 keV energy range observed/corrected for absorption in
Col. (9) were computed assuming a distance of 450 pc.
,
the degree of freedom in Col. (7). The emission
measure in Col. (6) and the logarithm of the X-ray luminosities in the
0.5-2 keV energy range observed/corrected for absorption in
Col. (9) were computed assuming a distance of 450 pc.
We used the COUP source catalog and data products of
Getman et al. (2005b). A detailed discussion of the COUP data,
encompassing source detection, photon extraction, spectral analysis,
and variability analysis can be found in Getman et al. (2005b). We use
HST archival images to compare the position of COUP sources with
emission knots of HH 210.
The best view of the HH 210 emission system is obtained in the optical
using [S II] doublet (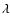 6717+
6717+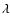 6731 lines) or
[O I] (
6731 lines) or
[O I] (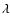 6300 line), where both bow shocks and a
complicated emission tail are visible, whereas in H
6300 line), where both bow shocks and a
complicated emission tail are visible, whereas in H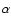 only the
heads of the bow shocks are visible. Figure 1 shows the
HH 210 emission system at epoch 2000.70 obtained with the WFPC2
on board HST with F673N filter, selecting [S II]
(program GO8121NW; Doi et al. 2002). The HH 210 emission system in
the [O I] line is very similar. We extracted star positions in the
full field-of-view of HST/WFPC2 using Source Extractor
(version 2.3.2; Bertin & Arnouts 1996)
only the
heads of the bow shocks are visible. Figure 1 shows the
HH 210 emission system at epoch 2000.70 obtained with the WFPC2
on board HST with F673N filter, selecting [S II]
(program GO8121NW; Doi et al. 2002). The HH 210 emission system in
the [O I] line is very similar. We extracted star positions in the
full field-of-view of HST/WFPC2 using Source Extractor
(version 2.3.2; Bertin & Arnouts 1996)![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif) , and cross-correlated these with COUP
positions. The estimated residual registration error between fifteen
stars in the WPFC2 image and the corresponding COUP sources is
, and cross-correlated these with COUP
positions. The estimated residual registration error between fifteen
stars in the WPFC2 image and the corresponding COUP sources is
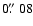 .
Finally, the total positional accuracy of X-ray sources,
which have a positional uncertainty in COUP of
.
Finally, the total positional accuracy of X-ray sources,
which have a positional uncertainty in COUP of
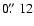 ,
is
,
is
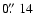 in Fig. 1. From this WFPC2 image and a
previous one obtained five years before, Doi et al. (2002) measured the
proper-motion of several [S II] knots of HH 210, ranging from
153 km s-1 for 155-040 HH 210 to 425 km s-1 for
154-040a HH 210. Using these proper motions we plotted in
Fig. 1 white arrows pointing at the estimated position of
HH 210 knots for COUP epoch 2003.04. We conclude that the position of
COUP 703 is consistent with the position of the [S II] knot
154-040a HH 210, whereas COUP 704 is located on the complicated
emission tail of HH 210 close to an emission filament.
in Fig. 1. From this WFPC2 image and a
previous one obtained five years before, Doi et al. (2002) measured the
proper-motion of several [S II] knots of HH 210, ranging from
153 km s-1 for 155-040 HH 210 to 425 km s-1 for
154-040a HH 210. Using these proper motions we plotted in
Fig. 1 white arrows pointing at the estimated position of
HH 210 knots for COUP epoch 2003.04. We conclude that the position of
COUP 703 is consistent with the position of the [S II] knot
154-040a HH 210, whereas COUP 704 is located on the complicated
emission tail of HH 210 close to an emission filament.
The image of HH 210 obtained with ACS on board HST at
epoch 2004.05 by Bally et al. (2005) is the closest in time to COUP. This
ACS observation was made in F658N filter selecting H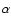 (
(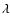 6563 line) and [N II] (
6563 line) and [N II] (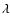 6584 line), and hence
detected mainly the heads of the bow shocks (Bally et al. 2005). To
register this ACS image with COUP, we extracted position of ACS stars, and cross-correlated these with COUP positions. The
estimated residual registration error between about ninety ACS
stars and their corresponding COUP sources is
6584 line), and hence
detected mainly the heads of the bow shocks (Bally et al. 2005). To
register this ACS image with COUP, we extracted position of ACS stars, and cross-correlated these with COUP positions. The
estimated residual registration error between about ninety ACS
stars and their corresponding COUP sources is
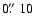 .
Finally,
the total positional accuracy between X-ray sources, which have a
positional uncertainty in COUP of
.
Finally,
the total positional accuracy between X-ray sources, which have a
positional uncertainty in COUP of
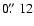 ,
and ACS sources is
,
and ACS sources is
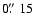 .
Figure 2 shows the COUP image of HH 210
using X-ray colors. The contour map indicates the brightest emission
knots observed in H
.
Figure 2 shows the COUP image of HH 210
using X-ray colors. The contour map indicates the brightest emission
knots observed in H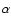 with HST/ACS, which were moved
individually to match epoch 2003.04 using proper-motions of
Doi et al. (2002). The most southern H
with HST/ACS, which were moved
individually to match epoch 2003.04 using proper-motions of
Doi et al. (2002). The most southern H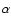 knot has no known
proper-motion; therefore we conservatively assumed for this knot the largest
proper-motion of HH 210 knots. We conclude that COUP 703 coincides with
the emission knot with the highest tangential velocity
(425 km s-1), 154-040a HH 210. In contrast, COUP 704 is not
associated with any bright H
knot has no known
proper-motion; therefore we conservatively assumed for this knot the largest
proper-motion of HH 210 knots. We conclude that COUP 703 coincides with
the emission knot with the highest tangential velocity
(425 km s-1), 154-040a HH 210. In contrast, COUP 704 is not
associated with any bright H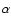 emission knot, or point source in
the VLT J-, H-,
emission knot, or point source in
the VLT J-, H-, 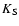 -band survey (McCaughrean et
al., in preparation) and the IRTF L-band survey
(McCaughrean et al. 1996). We note that it
is located near a filament of [S II] emission (see Fig. 1).
-band survey (McCaughrean et
al., in preparation) and the IRTF L-band survey
(McCaughrean et al. 1996). We note that it
is located near a filament of [S II] emission (see Fig. 1).
We compared the spatial distribution of events in COUP 703 and 704 with
those in the X-ray counterpart of a nearby star, after adding to this
reference source uniformly distributed background events to match the
background level measured in the extraction regions of COUP 703
and 704. Kolmogorov-Smirnov test shows that COUP 703 and 704 are
compatible with unresolved sources. Therefore the angular resolution
of Chandra at
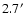 off-axis, i.e.
off-axis, i.e.  1
1
 ,
is an upper limit
for the size of these objects.
,
is an upper limit
for the size of these objects.
The observed X-ray spectra are shown in Fig. 3.
In XSPEC (version 11.3), we used
for the spectral fitting between 0.5 and 8 keV
(corresponding to channels PI = 35-548) a photoelectric absorption
(WABS) combined with a collisionally-ionized plasma model
(APEC), which provides plasma temperatures down to 0.1 MK.
Table 1 gives our best fit parameters. For the source with the
highest net counts, COUP 703, we found a column density of absorbing
material of
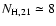 cm-2 (5-11 cm-2),
equivalent to
cm-2 (5-11 cm-2),
equivalent to
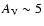 mag (3-7 mag) (Vuong et al. 2003), and
a plasma temperature of
mag (3-7 mag) (Vuong et al. 2003), and
a plasma temperature of
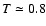 MK (0.5-1.6 MK). For
COUP 704, the absolute
MK (0.5-1.6 MK). For
COUP 704, the absolute 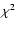 minimum corresponds to null absorption and
high plasma temperature, with a low intrinsic X-ray luminosity (see
the right panel of Fig. 3). This combination of high plasma temperature and
low X-ray luminosity would imply a small radius (
minimum corresponds to null absorption and
high plasma temperature, with a low intrinsic X-ray luminosity (see
the right panel of Fig. 3). This combination of high plasma temperature and
low X-ray luminosity would imply a small radius (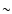 1014 cm)
of the object driving the shock (see Sect. 3). However,
another solution with a similar goodness-of-fit exists with higher
absorption and lower plasma temperature, similar to the best-fit
plasma parameters found for COUP 703. The latter parameters therefore
likely represent a better approximation of the actual physical
conditions in the plasma giving rise to COUP 704. The
absorption-corrected X-ray luminosities of COUP 703 and 704 implied
by the spectral fitting are about 1030 erg s-1 (0.5-2.0 keV).
1014 cm)
of the object driving the shock (see Sect. 3). However,
another solution with a similar goodness-of-fit exists with higher
absorption and lower plasma temperature, similar to the best-fit
plasma parameters found for COUP 703. The latter parameters therefore
likely represent a better approximation of the actual physical
conditions in the plasma giving rise to COUP 704. The
absorption-corrected X-ray luminosities of COUP 703 and 704 implied
by the spectral fitting are about 1030 erg s-1 (0.5-2.0 keV).
3 Discussion
HH 210 displays the largest proper motion among the outflow fingers
extending away from BN-KL, moreover the line emission is blue-shifted,
suggesting a deprojected velocity of about 500 km s-1(Taylor et al. 1986; Axon & Taylor 1984; Hu 1996). 154-040a HH 210 is also the brightest
feature in [O III] and has a small bow shock attached to it
(O'dell et al. 1997; Doi et al. 2002). The tip of the bow shock is seen as a knot in
[N II], H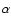 ,
[O III]; hence the tip is the fastest
moving portion of the shock. However, the fact that the [O III]
emission requires only a shock with a speed of about 90 km s-1and that the [O III] emission is seen only at the tip of the
bow, indicates that this HH object is moving in the wake of other
shocks moving ahead of it (Doi et al. 2002).
,
[O III]; hence the tip is the fastest
moving portion of the shock. However, the fact that the [O III]
emission requires only a shock with a speed of about 90 km s-1and that the [O III] emission is seen only at the tip of the
bow, indicates that this HH object is moving in the wake of other
shocks moving ahead of it (Doi et al. 2002).
The observed X-ray emission can be explained with fast moving bow
shocks. The postshock temperature in the adiabatic (non-radiative)
portion of a shock is given by
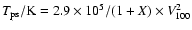 (Ostriker & McKee 1988), where V100 is
the velocity of the shock front with respect to the downstream
material (the shock velocity) in units of 100 km s-1 and X is
the ionization fraction of the preshock gas (X=0 for a neutral
medium and 1 for a fully ionized one). Thus, COUP 703 and
COUP 704 plasma temperatures of
(Ostriker & McKee 1988), where V100 is
the velocity of the shock front with respect to the downstream
material (the shock velocity) in units of 100 km s-1 and X is
the ionization fraction of the preshock gas (X=0 for a neutral
medium and 1 for a fully ionized one). Thus, COUP 703 and
COUP 704 plasma temperatures of 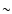 0.8 MK require a shock speed of
0.8 MK require a shock speed of
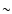 170 km s-1 for a shock moving into a mostly neutral
medium, or
170 km s-1 for a shock moving into a mostly neutral
medium, or 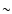 240 km s-1 for a shock moving into a fully
ionized medium. The lower speed is comparable with the bow shock
velocity of 133 km s-1 estimated by O'dell et al. (1997) from the
deprojected velocity and the opening angle of the bow wing.
240 km s-1 for a shock moving into a fully
ionized medium. The lower speed is comparable with the bow shock
velocity of 133 km s-1 estimated by O'dell et al. (1997) from the
deprojected velocity and the opening angle of the bow wing.
The expected X-ray luminosity of a shock-heated source depends on the
emissivity per unit volume, which depends on the plasma temperature
and density, the volume of the emitting region, and the type of shock,
radiative or non-radiative (Raga et al. 2002). Neglecting the line
emission, Raga et al. (2002) find for a radiative shock
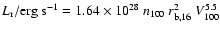 ;
and for a non-radiative shock
;
and for a non-radiative shock
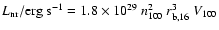 ,
where n100 is the preshock density in units of 100 cm-3 and
,
where n100 is the preshock density in units of 100 cm-3 and
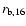 is the radius of the object driving the shock in units
of 1016 cm. The X-ray luminosity of a bow shock is the minimum
of these two values. The multiplicative factor to take into account
line emission is 2.5 and 3.0 at 0.1 MK and 1 MK, respectively
(Raga et al. 2002). The HST/ACS observation of 154-040a HH 210
shows a radius of
is the radius of the object driving the shock in units
of 1016 cm. The X-ray luminosity of a bow shock is the minimum
of these two values. The multiplicative factor to take into account
line emission is 2.5 and 3.0 at 0.1 MK and 1 MK, respectively
(Raga et al. 2002). The HST/ACS observation of 154-040a HH 210
shows a radius of
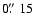 (Fig. 2), or about
1015 cm at a distance of 450 pc. Using this dimension for the
X-ray source, a shock speed of 170 km s-1, and a preshock
density of about 12 000 cm-3, we find
(Fig. 2), or about
1015 cm at a distance of 450 pc. Using this dimension for the
X-ray source, a shock speed of 170 km s-1, and a preshock
density of about 12 000 cm-3, we find
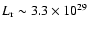 erg s-1. Thus taking into account line
emission, a bow shock flow can readily explain the X-ray
luminosities observed from COUP 703 and COUP 704.
Allen & Burton (1993) found a similar density of
erg s-1. Thus taking into account line
emission, a bow shock flow can readily explain the X-ray
luminosities observed from COUP 703 and COUP 704.
Allen & Burton (1993) found a similar density of 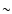 104 cm-3for the electronic density inferred from the [Fe II] spectra of
the emission knots.
The location of HH 210 inside OMC-1 but close to the limit of the
H II region may explain this density and why the medium is not
yet fully ionized by the radiation field of the Trapezium cluster.
104 cm-3for the electronic density inferred from the [Fe II] spectra of
the emission knots.
The location of HH 210 inside OMC-1 but close to the limit of the
H II region may explain this density and why the medium is not
yet fully ionized by the radiation field of the Trapezium cluster.
We conclude that COUP 703 is the counterpart of the emission knot
154-040a of HH 210, and its X-ray emission can be explained by a
radiative bow shock. The X-ray emission of COUP 704 can
also be explained by a fast-moving, radiative shock towards the tail of
HH 210. Optical/infrared observations are still needed at other
epochs to reveal in the complicated HH 210 region the proper motion
of the counterpart to this X-ray source.
Acknowledgements
We thanks an anonymous referee for useful comments which improved the
paper. COUP is supported by the Chandra Guest Observer grant SAO
GO3-4009A (E. Feigelson, PI). Further support was provided by the
Chandra ACIS Team contract SV4-74018.
- Allen, D. A.,
& Burton, M. G. 1993, Nature, 363, 54 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Anders, E., &
Grevesse, N. 1989, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 53, 197 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Axon, D. J., &
Taylor, K. 1984, MNRAS, 207, 241 [NASA ADS]
- Bally, J., Feigelson,
E., & Reipurth, B. 2003, ApJ, 584, 843 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef]
- Bally, J., Licht, D.,
Smith, N., & Walawender, J. 2005, AJ, 129, 355 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Bertin, E., &
Arnouts, S. 1996, A&AS, 117, 393 [EDP Sciences] [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Bonito, R.,
Orlando, S., Peres, G., Favata, F., & Rosner, R. 2004, A&A,
424, L1 [EDP Sciences] [NASA ADS] [CrossRef]
- Doi, T., O'Dell,
C. R., & Hartigan, P. 2002, AJ, 124, 445 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Favata, F.,
Fridlund, C. V. M., Micela, G., Sciortino, S., &
Kaas, A. A. 2002, A&A, 386, 204 [EDP Sciences] [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Güdel, M.,
Skinner, S. L., Briggs, K. R., et al. 2005, ApJ,
626, L53 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Garmire,
G. P., Bautz, M. W., Ford, P. G., Nousek,
J. A., & Ricker, G. R. 2003, in X-Ray and Gamma-Ray
Telescopes and Instruments for Astronomy, ed. J. E. Truemper,
& H. D. Tananbaum, Proc. SPIE, 4851, 28
(In the text)
- Getman,
K. V., Feigelson, E. D., Grosso, N., et al. 2005a,
ApJS, 160, 353 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef]
- Getman,
K. V., Flaccomio, E., Broos, P. S., et al. 2005b,
ApJS, 160, 319 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Haro, G. 1952, ApJ,
115, 572 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef]
- Herbig, G. H.
1950, ApJ, 111, 11 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X. 1996, AJ, 112,
2712 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef]
- Kastner,
J. H., Franz, G., Grosso, N., et al. 2005, ApJS, 160,
511 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Lupton, R.,
Blanton, M. R., Fekete, G., et al. 2004, PASP, 116,
133 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
-
McCaughrean, M. J., Rayner, J., Zinnecker, H., & Stauffer,
J. 1996, Lecture Notes in Physics: Disks and Outflows Around Young
Stars, 465, 33 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Morrison, R.,
& McCammon, D. 1983, ApJ, 270, 119 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- O'dell, C. R.,
Hartigan, P., Lane, W. M., et al. 1997, AJ, 114, 730 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef]
- Ostriker,
J. P., & McKee, C. F. 1988, Rev. Mod. Phys., 60,
1 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Pravdo, S. H.,
Feigelson, E. D., Garmire, G., et al. 2001, Nature, 413,
708 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Pravdo, S. H.,
Tsuboi, Y., & Maeda, Y. 2004, ApJ, 605, 259 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Raga, A. C.,
Noriega-Crespo, A., & Velázquez, P. F. 2002, ApJ,
576, L149 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Reipurth, B.,
& Bally, J. 2001, ARA&A, 39, 403 [NASA ADS] (In the text)
- Taylor, K., Dyson,
J. E., Axon, D. J., & Hughes, S. 1986, MNRAS, 221,
155 [NASA ADS]
- Vuong, M. H.,
Montmerle, T., Grosso, N., et al. 2003, A&A, 408, 581 [EDP Sciences] [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
- Weisskopf,
M. C., Brinkman, B., Canizares, C., et al. 2002, PASP,
114, 1 [NASA ADS] [CrossRef] (In the text)
Copyright ESO 2006
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.4cm,clip]{Hk231_f1.eps} \end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/11/aahk231/Timg17.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=7.8cm,clip]{Hk231_f2.eps} \end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/11/aahk231/Timg20.gif)
![\begin{figure}
\par\includegraphics[width=10.7cm,clip]{Hk231_f3a.eps}\hspace*{3mm} \includegraphics[width=4.8cm,clip]{Hk231_f3b.eps}\end{figure}](/articles/aa/full/2006/11/aahk231/Timg23.gif)