All Tables
- Table 1:
Radial scaling factors used in AUTOSTRUCTURE to minimize the total
energy of the nl orbital wave functions.
- Table 2:
Lowest 66 energy levels in Ry for the n=4 calculation compared to
experimental measurements listed on NIST (http://physics.nist.gov).
- Table 3:
Comparison of various calculated gf-values for the present
calculations with Cornille et al. (1992), Sampson et al. (1991), and
Fawcett (1984).
- Table 4:
List of the most prominent n=3 to n=2 transitions. The columns indicate:
(1) the observed wavelength; (2) transition; (3) the line ratio of
observation using the high-energy grating on Chandra (Desai et al. 2005); (4, 5)
the n=4 R-matrix results for
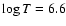 and 6.8 respectively; (6) ratio
of poulation of upper level due to radiative cascade to the population due to
direct excitation for the n=4 R-matrix calculation; (7-9) the same as Cols. (4-6) but for the n=3 R-matrix calculation; (10, 11) APEC (version 1.10)
intensities for
and 6.8 respectively; (6) ratio
of poulation of upper level due to radiative cascade to the population due to
direct excitation for the n=4 R-matrix calculation; (7-9) the same as Cols. (4-6) but for the n=3 R-matrix calculation; (10, 11) APEC (version 1.10)
intensities for
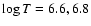 ;
(12) Desai et al. (2005) using an emission
measure distribution peaked at
;
(12) Desai et al. (2005) using an emission
measure distribution peaked at
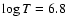 ;
(13) intensity ratios calculated
using the distorted wave collision strengths of Sampson et al. (1991). Note: the
16.076 Å feature was measured by both a high-energy grating (HEG) and a
medium-energy grating (MEG) which gave different results; the value in
parentheses is from the MEG.
;
(13) intensity ratios calculated
using the distorted wave collision strengths of Sampson et al. (1991). Note: the
16.076 Å feature was measured by both a high-energy grating (HEG) and a
medium-energy grating (MEG) which gave different results; the value in
parentheses is from the MEG.