Table 1:
Parameters chosen in the different
simulations and their results. These parameters are the dimensioning of the grid (
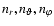 ),
the kind of spacing (lc = logarithmically centered around the planet),
the thermodynamics (iso = locally isothermal, rad = ideal gas plus radiation transport, rad+ = ideal gas,
radiation transport and conservation of total energy for gas accreted onto planet), the gravitational smoothing radius (
),
the kind of spacing (lc = logarithmically centered around the planet),
the thermodynamics (iso = locally isothermal, rad = ideal gas plus radiation transport, rad+ = ideal gas,
radiation transport and conservation of total energy for gas accreted onto planet), the gravitational smoothing radius (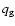 = fraction of the Hill radius over that smoothing is applied), the accretion radius (
= fraction of the Hill radius over that smoothing is applied), the accretion radius (
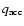 = fraction of the Roche lobe (respectively Hill radius) that mass is taken out of), the type of the initial model (G: starting with an
existing gap), and the total number of orbits calculated (
= fraction of the Roche lobe (respectively Hill radius) that mass is taken out of), the type of the initial model (G: starting with an
existing gap), and the total number of orbits calculated (
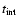 ). The results we give are the accretion rate onto the Planet (
). The results we give are the accretion rate onto the Planet (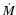 )
in units of Jupiter masses per orbit, the mass contained in the Roche lobe (
)
in units of Jupiter masses per orbit, the mass contained in the Roche lobe (
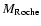 ), the maximum density and temperature in the Roche lobe (
), the maximum density and temperature in the Roche lobe (
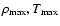 )
and the migration time-scale that we determined (
)
and the migration time-scale that we determined (
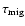 ).
).
| Name |
Grid |
EOS |
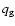 ; ;
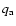 |
ini |
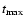 |
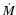 |
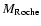 |
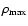 |
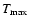 |
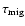 |
| CI |
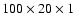 |
iso |
0.5 ; 0.5 |
|
300 |
- |
- |
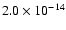 |
130 |
- |
|
CDI |
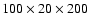 |
iso |
0.5 ; 0.5 |
G |
184 |
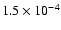 |
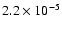 |
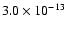 |
130 |
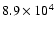 |
| CD4I |
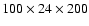 lc
lc |
iso |
0.2 ; 0.2 |
G |
81 |
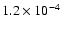 |
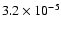 |
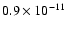 |
130 |
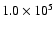 |
| CD |
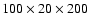 |
rad |
0.5 ; 0.5 |
G |
142 |
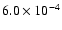 |
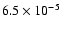 |
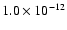 |
150 |
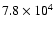 |
| CDS |
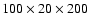 |
rad |
0.2 ; 0.2 |
G |
141 |
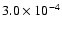 |
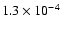 |
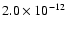 |
200 |
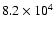 |
| CD4 |
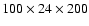 lc
lc |
rad |
0.2 ; 0.2 |
G |
75 |
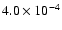 |
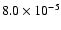 |
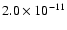 |
480 |
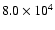 |
| CDNI |
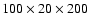 |
iso |
0.5 ; 0 |
G |
98 |
- |
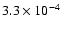 |
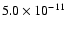 |
130 |
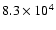 |
| CDN |
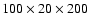 |
rad |
0.5 ; 0 |
G |
44 |
- |
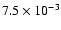 |
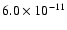 |
310 |
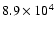 |
| CDN4 |
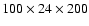 lc
lc |
rad |
0.2 ; 0 |
G |
122 |
- |
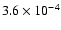 |
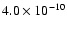 |
520 |
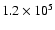 |
| DN |
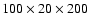 |
rad |
0.5 ; 0 |
|
121 |
- |
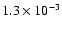 |
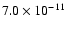 |
600 |
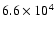 |
| DN4 |
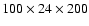 lc
lc |
rad |
0.2 ; 0 |
|
55 |
- |
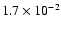 |
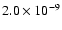 |
1150 |
|
| DR |
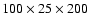 |
rad+ |
0.2 ; 0.2 |
|
121 |
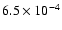 |
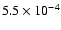 |
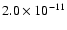 |
800 |
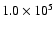 |
| DR4 |
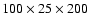 lc
lc |
rad+ |
0.1 ; 0.1 |
|
141 |
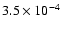 |
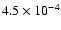 |
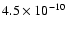 |
1500 |
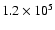 |
Source LaTeX |
All tables |
In the text