- ...
estimator
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- In Perlmutter et al. (1999), it is checked that B-Vrest-frame colors of nearby and distant type agree on average, and the
color measurement is not used event per event.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
ESSENCE
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- http://www.ctio.noao.edu/wsne
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
SNLS
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- http://cfht.hawaii.edu/SNLS
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
features
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Most of the SN Ia photometric reductions transform
instrumental magnitudes into standard magnitudes using color
equations, derived from standard stars observations. This assumes
that color rather than spectral features dominates cross-filter
corrections.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
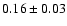
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- Note that this number takes into
account the number of parameters in the fit. The measured rms value is
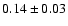 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... fit
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The uncertainties on the distance estimate formally depend
on
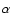 and
and 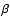 ,
and increase with them. As a consequence, the
,
and increase with them. As a consequence, the 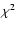 minimum is
biased toward large values of these parameters. We therefore
computed the uncertainties with the initial values, and use the result of the fit
at the final iteration.
minimum is
biased toward large values of these parameters. We therefore
computed the uncertainties with the initial values, and use the result of the fit
at the final iteration.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
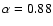
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- b=0.52 translates to
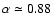 when using stretch and the first order
relation
when using stretch and the first order
relation
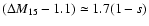 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...Phillips et al. (1999)
![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif)
- The proposed
relation is
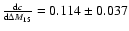 .
With the approximate
relation
.
With the approximate
relation
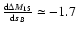 (at sB = 1),
we expect
(at sB = 1),
we expect
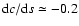 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.